What is Brunnstrom’s approach to stroke recovery?
The Brunnstrom approach is a widely used movement therapy approach used by clinicians. This approach highly focuses synergic pattern of spastic muscles on the recovery of strokepatients through various stages. There is no specialized training available in …
What is the first stage of the Brunnstrom Approach?
Movement Therapy/ Brunnstrom Approach Uses primitive synergistic patterns in order to improve motor control through central facilitation. Based on concept that damaged CNS …
What is involved in the treatment of Brunnstrom's disease?
7. Describe practically different exercises based on treatment principles of Brunnstrom. Brunnstrom, a physical therapist, was particularly concerned with the problems of patients with …
What are the benefits of Brunnstrom physiotherapy?
Apr 22, 2020 · The brunnstrom stages is one of the most well-known stroke recovery stages which is also known as the Brunnstrom approach. The Brunnstrom stages was developed by …

When is Brunnstrom approach used?
The Brunnstrom approach is a type of physiotherapy treatment used with patients with movement problems following damage to the brain and spinal cord, (central nervous system/ CNS).
What is the difference between Bobath and Brunnstrom?
Brunnstrom supports the view that treatment should imitate ''evolution in reverse'', by superimposing de- veloped motor behaviour on primitive behaviour, whereas Bobath urges therapists to bypass this inter- mediate stage by suppressing the pathological spastic patterns and training normal patterns immediately after ...
What is synergistic movement?
Synergistic movement happens when you try to make one movement on your affected side, and you end up making multiple movements. For example, trying to move your affected arm might result in hand and shoulder movements too. While movement is a great sign during stroke recovery, synergistic movement is less than ideal.Sep 10, 2018
What are synergies in occupational therapy?
Muscle synergies result from muscles coordinating movements to perform different tasks. These synergies allow common patterns of movement that involve either cooperative or reciprocal activation of muscle. Because the muscles are linked, one activated muscle may lead to partial or complete responses in other muscles.Jun 9, 2018
What is bobath principle?
Principles of Bobath Focusing on quality of movement. Normalisation of tone to facilitate active movement. Positioning and posture in lying, sitting and standing. Discouragement of compensatory movements. Discouragement of muscle strength training.
What is the difference between Bobath and NDT?
In the United States the Bobath concept is usually referred to as 'neuro-developmental treatment' (NDT). It is based on the brain's ability to reorganise (neuroplasticity) It is a multidisciplinary approach, involving physiotherapists, occupational therapists and speech and language therapists.
How is extensor synergy treated?
Treating Flexion Synergy Patterns After StrokePassive Exercises and Stretching. Passive range-of-motion exercises can help you maintain range of motion and may assist in regaining control of your muscles. ... Sensory Exercises. Sensory stimulus plays a crucial role in synergistic movements. ... Active Range-of-Motion Exercises.Mar 23, 2020
What are the stages of stroke recovery?
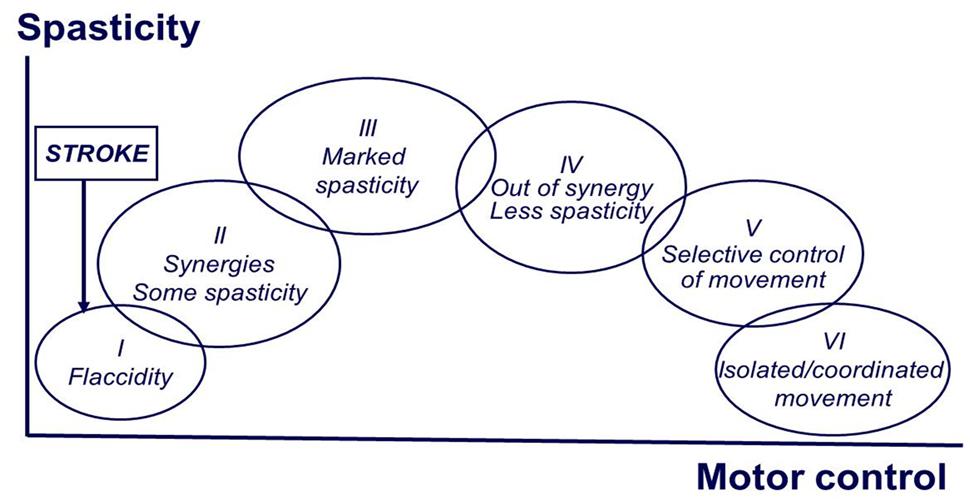
This pattern is detailed in Brunnstrom's seven stages of stroke recovery. The stages include flaccidity, spasticity appears, spasticity increases, spasticity decreases, complex movement combinations, spasticity disappears, and normal function returns.Feb 11, 2022
Does stretching help with spasticity?
Prolonged passive muscle stretching is a common treatment for people with spasticity CP. Sustained passive muscle stretching for a long duration improves the range of movements, and reduces the spasticity of muscles11, 12).Jan 30, 2016
What is Roods approach?
Rood approach is a neurophysiological approach developed by Margaret Rood in 1940. (1-2) Rood approach. deals with the activation or de-activation of sensory receptors, which is concerned with the interaction of somatic, autonomic and psychic factors and their role in the regulation of motor behavior.Sep 9, 2018
What are flexion synergies?
Originally described clinically [3, 4], the flexion synergy has subsequently been quantified in individuals with chronic hemiparetic stroke [1, 5, 6] and is defined as the involuntary neural coupling of shoulder abductor activity with activation of elbow flexors in the paretic upper limb.
What is synergy in neurology?
The signals that the central nervous system (CNS) produces and sends to the muscles to effect movement are not entirely understood. Muscle synergy theory suggests that the central nervous system produces a small number of signals that pass through a network that distributes combinations of these signals to the muscles.Aug 30, 2014
What is Brunnstrom approach?
What is the Brunnstrom approach? The Brunnstrom approach is a type of physiotherapy treatment used with patients with movement problems following damage to the brain and spinal cord, (central nervous system/ CNS).
What are the principles of Brunnstrom?
The Brunnstrom treatment approach is based around two principles: 1st Principle - Normal movement (how a healthy individual moves) requires muscles working together (synergistically) following damage to the CNS the muscles will not work as well together. During recovery muscles will start working together ...
What is the first stage of Brunnstrom approach?
Stage 1: Flaccidity. The first stage of the Brunnstrom approach is the period immediately after a stroke when the connection between the muscles and brain are so damaged that flaccid paralysis (flaccidity) sets in. This means that the stroke survivor cannot initiate any muscle movements on their affected side.
What is the Brunnstrom stage of stroke recovery?
It’s called the Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery, and it’s one of the best ways to measure how far you are on your stroke recovery journey. The Brunnstrom stages (also called the Brunnstrom Approach) are used by many physical ...
How many stages of recovery did Brunnstrom have?
With the seven stages of recovery, Brunnstrom effectively changed the way stroke recovery is approached by occupational and physical therapists. She theorized that spastic and primitive muscle movements were a natural part of the recovery process after a stroke.
What is the Brunnstrom approach?
The Brunnstrom Approach was developed in the 1960’s by Signe Brunnstrom, an occupational and physical therapist from Sweden. With seven stages, the Brunnstrom Approach breaks down how motor control can be restored throughout the body after suffering a stroke. Normally, muscle movements are the result of different muscle groups working together.
What happens during stage 4 of stroke recovery?
During stage four of stroke recovery, spastic muscle movement begins to decline. Patients will regain control mostly in the extremities, and they will have a limited ability to move normally. The movements may still be out of sync with muscle synergies, but this will improve quickly over the length of this stage.
How many stages of stroke recovery are there?
There are seven recognized stages of stroke recovery through which most patients progress. Also known as the Brunnstrom Approach, the seven stages framework views spastic and involuntary muscle movement as part of the process and uses them to aid in rehabilitation.
What is synergy in muscles?
Muscle synergies result from muscles coordinating movements to perform different tasks. These synergies allow common patterns of movement that involve either cooperative or reciprocal activation of muscle. Because the muscles are linked, one activated muscle may lead to partial or complete responses in other muscles.
Why do muscles become weak after a stroke?
After the stroke has occurred, your muscles become weak due to the lack of coordination between the brain and body. This causes the muscle synergies to move in abnormal patterns.
What is the peak of spasticity?
Spasticity in muscles increases during stage three of stroke recovery, reaching its peak. Spasticity is a feeling of unusually stiff, tight, or pulled muscles. It is caused by damage from a stroke to nerve pathways within the brain or spinal cord that control muscle movement. The lack of ability to restrict the brain’s motor neurons causes muscles to contract too often. Spasticity causes an abnormal increase in muscle stiffness and tone that can interfere with movement, speech, or cause discomfort and pain.
What are associated reactions?
Associated reactions are automatic responses of the involved limb resulting from action occurring in some other part of the body, either by voluntary or reflex stimulation (e.g., resistance or ATNR). They are commonly elicited when some degree of spasticity is present and are infrequently seen in a limb exhibiting minimal muscle tone. Generally speaking, although not true in every case, associated reactions elicit the same direction of movement (i.e., flexion evokes flexion) and the opposite direction (i.e., flexion evokes extension) in the lower extremity.
What is the result of flexion of the neck?
Flexion of the neck results in flexion of the arms and extension of the legs; extension of the neck results in extension of the arms and flexion of the legs.
Does flexion of the upper extremity elicit flexion of the lower extremity?
Thus, flexion of the involved upper extremity will elicit flexion of the involved lower extremity.
What are the stages of stroke recovery?
What are the Brunnstrom Stages of Stroke Recovery? 1 Stage 1: Flaccidity 2 Stage 2: Spasticity Appears 3 Stage 3: Increased Spasticity 4 Stage 4: Decreased Spasticity 5 Stage 5: Spasticity Continues to Decrease 6 Stage 6: Spasticity Disappears and Coordination Reappears 7 How long will it take to recover from stroke?
What is the Brunnstrom stage?
The Brunnstrom stages was developed by physical therapist Signe Brunnstrom in the 1960’s. When a stroke occurs, typically it affects one side of the body. The Brunnstrom approach describes the sequence of motor development and reorganization of the brain after stroke. So you can check the status of your stroke recovery through the Brunnstrom stages.
What is it called when muscles fire together?
Multiple muscles might fire together when we try to move our affected side. This is called a muscle synergy and we can use our synergies to complete an activity if we understand it.
What is the second stage of muscle contraction?
Stage 2: Spasticity Appears. In this stage, muscles may begin to tighten reflexively and have difficulty relaxing. This is called spasticity. This movement is usually involuntary and in response to an outside stimulus, such as a poke.
Why is repetition important in neurology?
Repetition is critical for neural-reorganization. We can’t repair the damage that was done to the brain after stroke, but we can teach a different area of the brain to do its job. We want to do movements outside of our muscle synergies to improve how our brain sends signals.
What happens to muscles during motor recovery?
During this stage of motor recovery, the involuntary muscle tightness (spasticity) starts to decrease. Your brain is more successful at sending signals to specific muscles to activate. You’re still likely to use muscle synergies, but you're able to move outside of them as well.
Why do we do passive exercises?
The main reason to complete these exercises is that it increases sensory input to the brain.
What is the Brunnstrom approach to stroke?
On the other hand, the Brunnstrom Approach encourages and teaches stroke patients to use the abnormal synergy patterns for their greater good.
What is the first stage of Brunnstrom's stroke recovery approach?
The first stage in Brunnstrom’s stroke recovery approach is the first shock period where flaccid paralysis sets in after stroke. Flaccid paralysis (flaccidity) is a medical term used to explain the total lack of voluntary movement.
What is it called when your muscles are tight?
In this stage, muscles may begin to tighten reflexively and have difficulty relaxing. This is called spasticity . This movement is usually involuntary and in response to an outside stimulus, such as a poke. The brain is still having a difficult time sending any signals to the muscles for voluntary movement.
What happens to muscles during motor recovery?
During this stage of motor recovery, the involuntary muscle tightness (spasticity) starts to decrease. Your brain is more successful at sending signals to specific muscles to activate. You’re still likely to use muscle synergies, but you're able to move outside of them as well.
How many stages of recovery are there after stroke?
There are six Brunnstrom stages that describe the process of movement recovery after stroke. Here's what each stage means for your arm and what you can do for home exercise to maximize function.
