
Explore
Hyperplasia of the Breast Diagnosis of hyperplasia. Hyperplasia doesn’t usually cause a lump that can be felt, but it can sometimes cause changes... Treatment of hyperplasia. Usual ductal hyperplasia is considered a normal finding in the breast and does not need to be... Reducing breast cancer risk ...
What is the treatment for simple hyperplasia without atypia?
Atypical hyperplasia (or atypia) means that there are abnormal cells in breast tissue taken during a biopsy. (A biopsy means that tissue was removed from the body for examination in a …
What is usual ductal hyperplasia?
Mar 15, 2022 · The NCCN strongly recommends women with atypical hyperplasia (but not usual hyperplasia) take a risk-lowering drug (such as tamoxifen) to lower their risk of developing …
What are the treatments for atypical ductal hyperplasia?
Nov 29, 2017 · Supplements 1. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that lowers free radical damage, which can trigger hyperplasia. 2. Vitamin D helps regulate hormones and immune functioning. …
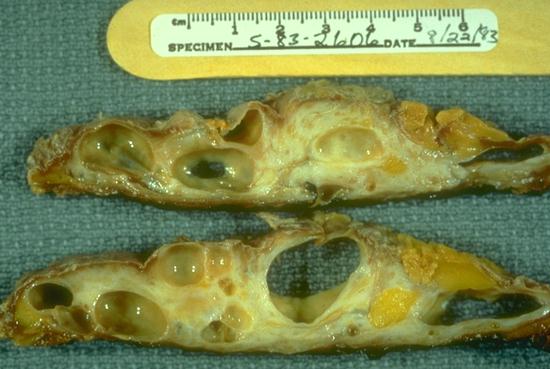
Can breast hyperplasia go away?
Usual ductal hyperplasia is considered a normal finding in the breast and does not need to be treated. If either ADH or ALH is found in a needle biopsy sample, surgery may be recommended to remove more breast tissue around it.Jan 25, 2022
How long does it take for breast hyperplasia to turn into cancer?
Does breast hyperplasia always mean cancer?
Is breast hyperplasia common?
What causes hyperplasia?
Is hyperplasia reversible?
What are the symptoms of hyperplasia?
- Menstrual bleeding that is heavier or longer lasting than usual.
- Menstrual cycles (amount of time between periods) that are shorter than 21 days.
- Menstrual bleeding between menstrual periods.
- Not having a period (pre-menopause).
- Post-menopause uterine bleeding.
What are the early signs of breast cancer?
- New lump in the breast or underarm (armpit).
- Thickening or swelling of part of the breast.
- Irritation or dimpling of breast skin.
- Redness or flaky skin in the nipple area or the breast.
- Pulling in of the nipple or pain in the nipple area.
What are the types of hyperplasia?
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.
- Cushing's Disease.
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia.
- Hemihyperplasia.
- Intimal Hyperplasia.
- Compensatory Liver Hyperplasia.
- Endometrial Hyperplasia.
Is hyperplasia a tumor?
What is breast hypoplasia?
Does mastitis require surgery?
How to treat breast cancer?
Take preventive medications. Treatment with a selective estrogen receptor modulator, such as tamoxifen or raloxifene (Evista), for five years may reduce the risk of breast cancer. These drugs work by blocking estrogen from binding to estrogen receptors in breast tissue.
What is atypical hyperplasia?
Atypical hyperplasia is usually discovered after a biopsy to evaluate a suspicious area found during a clinical breast exam or on an imaging test, such as a mammogram or ultrasound.
How is atypical hyperplasia treated?
Atypical hyperplasia is generally treated with surgery to remove the abnormal cells and to make sure no in situ or invasive cancer also is present in the area. Doctors often recommend more-intensive screening for breast cancer and medications to reduce your breast cancer risk.
What is the procedure to remove atypical hyperplasia?
A diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia may lead to a surgical biopsy (wide local excision or lumpectomy) to remove all of the affected tissue. The pathologist looks at the larger specimen for evidence of in situ or invasive cancer.
Why do we do self-exams for breast awareness?
Self-exams for breast awareness in order to develop breast familiarity and to detect any unusual breast changes
What to do if you have a family history of breast cancer?
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer, you might benefit from meeting with a genetic counselor to evaluate your risk of carrying a genetic mutation and the role of genetic testing in your situation. Make healthy lifestyle choices.
How to reduce the risk of breast cancer?
Make healthy lifestyle choices. Make healthy choices in your daily life in order to reduce your risk of breast cancer. For instance, exercise most days of the week, maintain a healthy weight, don't smoke and limit the amount of alcohol you drink, if you choose to drink alcohol.
When is breast hyperplasia surgically removed?
If the breast hyperplasia is atypical, or at a late stage, when there are a large number of tumors, surgical removal of tumors is used.
How to diagnose breast hyperplasia?
It is necessary to pay attention to the state of the breast before, during and after menstruation. At the slightest changes, pains, neoplasms it is necessary to address to mammologu, for carrying out of the further analyzes. The doctor will conduct a mammogram (chest x-ray), and in case he finds a tumor, he will take an analysis for cytology, that is, he will check the good quality.
What is mammary hyperplasia?
Dyshormonal hyperplasia of mammary glands. It occurs against the background of development of hormonal imbalance in the body of a woman, usually has the character of benign changes in the structure of breast tissue and is treated with hormones selected by a doctor, after a detailed study of the results of the study.
How old are women with hyperplastic mammary glands?
Hyperplastic processes in the mammary gland in women have recently been a fairly common disease, the age of people suffering from this pathology from 20 to 70 years, is found in 2/3 of women in different forms.
How does hyperplasia differ from normal hyperplasia?
It differs from ordinary hyperplasia in that, in addition to excessive tissue formation, structural changes occur in the cells themselves. This process is a more neglected form of pathology, in fact, even a precancerous condition. This form of the disease is amenable to drug treatment, but more often surgical intervention is used.
What are the two types of lobular hyperplasia?
They are very mobile. In the second form of lobular hyperplasia, atypical, in addition to the appearance of the tumors themselves, the cellular structure changes.
Why is it called protocolal hyperplasia?
Protocolal hyperplasia of mammary glands. Its name was given to this form because of the proliferation of epithelial tissues in the ducts of the breast. Symptoms and course of the disease are quite typical, in the early stages completely cured, at later stages it passes into a precancerous state.
How many women will develop breast cancer after atypical hyperplasia?
Specifically, five years after the diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia, 7% of women will develop breast cancer.
What is atypical hyperplasia?
Atypical hyperplasia (or atypia) means that there are abnormal cells in breast tissue taken during a biopsy. (A biopsy means that tissue was removed from the body for examination in a laboratory.) These abnormal cell collections are benign (not cancer), but are high-risk for cancer. Findings of atypical hyperplasia account for 10% ...
How long does atypical hyperplasia last?
These medications block estrogen and help decrease the risk of estrogen receptor-positive invasive breast cancer. The effects can remain for up to 15 years after taking them.
What is estrogen receptor positive breast cancer?
What is estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer? Most breast cancer cells respond to hormones, specifically estrogen or progesterone. These hormones circulate in the blood. A cancer is called estrogen receptor-positive if it responds to estrogen. This means that estrogen triggers the cancer to grow.
What hormone makes breast cancer grow?
One study showed that of the women who did develop breast cancer, 88% of the breast cancers were estrogen receptor-positive.
How often should I have breast cancer screening?
After surgery, increased screening is recommended. Clinical breast exams will be done every six months and you’ll have annual mammograms. As an adjunct, some patients may also have high risk screening annual MRIs, alternating with the mammogram; which means you will undergo breast imaging every six months. Your medical breast specialist will help determine if you qualify for an annual breast MRI based on your risk factors. An MRI is especially helpful if you are a woman with dense breast tissue.
What is the best medication for menopause?
Tamoxifen (Nolvadex®) is recommended for women who aren’t yet in menopause. Other drugs are recommended for women in menopause. Menopause is defined as the absence of your menstrual period for 12 months. The medications for menopausal women are: 1 Raloxifene (Evista®). 2 Exemestane (Aromasin®). 3 Anastrozole (Arimidex®).
What is the most common proliferative breast condition?
The most common proliferative breast condition is hyperplasia.
What is atypical hyperplasia?
Atypical hyperplasia. In atypical hyperplasia, the proliferating (dividing) cells look abnormal. Atypical hyperplasia is less common than usual hyperplasia. Women with atypical hyperplasia have about 3-5 times the breast cancer risk of women without a proliferative breast condition [ 183-186 ].
How often should I get a breast MRI?
Have a clinical breast exam every 6-12 months. Talk with a health care provider about screening with breast MRI every year, starting at age 25. This medical care helps ensure if breast cancer does develop, it’s caught early when the chances of survival are highest.
Can cysts cause breast cancer?
Non-proliferative breast conditions (such as cysts) are not linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
How to treat hyperplasia?
Anyone with this condition should also be aware of these five natural methods of hyperplasia treatment. 1. Naturally Balance Your Hormones.
What is hyperplasia in the body?
Hyperplasia is a condition characterized by an abnormal overgrowth of cells. When you hear this, you may think “cancer” right off the bat, and for good reason. Abnormal cell growth can occur in different parts of the body, including the prostate, breast tissue, and uterus. Unfortunately, inaccurate information about hyperplasia is common.
What are the symptoms of hyperplasia?
The condition causes symptoms like weight loss, nervousness, bugling eyes and irregular periods.
What causes endometrial hyperplasia?
Causes of Hyperplasia. A variety of factors can cause hyperplasia. Hormonal imbalances, like abnormal estrogen dominance, can contribute to endometrial hyperplasia. Obesity, a lack of exercise, and inflammation caused by factors like a poor diet are other factors. Another known factor is toxin exposure.
What is C cell hyperplasia?
C-cell hyperplasia is often a precursor to medullary thyroid cancer. Intimal hyperplasia is a rare type that affects one’s blood vessels after an injury or surgery. This is also called intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia.
Does hyperplasia cause cell reproduction?
Also called hypergenesis, this condition causes the overgrowth of cells. For example, hyperplasia increases the rate of cell reproduction associated with the initial stage of cancer development. Yes, we want our cells to replicate, but an overgrowth of cells that the body can’t accommodate may lead to problems.
Does compensatory liver hyperplasia affect the liver?
Compensatory liver hyperplasia affects the liver after injury or damage. Interestingly, this is also actually beneficial and is what allows liver transplants to work, but it differs from the physiologic hypergenesis.
What is the best treatment for atypical ductal hyperplasia?
Another treatment option for atypical hyperplasia of the breast is hormone replacement therapy. Two of these medications are tamoxifen and raloxifene, which are typically prescribed after menopause to balance hormones. Long-term use may prevent atypical ductal hyperplasia from progressing into breast cancer. There are possible side effects associated with these drugs, including blood clots, vaginal dryness or a stroke. Women should thoroughly discuss the disadvantages of side effects compared to the possibility of getting breast cancer with their physician.
What is atypical ductal hyperplasia?
Atypical ductal hyperplasia is a condition in the breast ducts that may lead to cancer.
What is the best way to monitor breast cancer?
When a physical exam and biopsy — the removal of sample cells — indicate the possibility of breast cancer forming, a physician may begin close monitoring of the cells. The physician usually checks during regularly scheduled appointments to determine if the cells are developing into a tumor. At-home monitoring by performing monthly self-breast exams is another method that doctors may recommend as part of close monitoring.
Can a woman have a mastectomy?
A woman may choose to have a mastectomy if it is determined that she has atypical ductal hyperplasia.
Can ductal hyperplasia be treated?
Since breast cancer is possible with atypical ductal hyperplasia, doctors may recommend procedures to monitor the potential development of breast cancer. Early detection of cancerous cells can improve treatment. Surgery, clinical trials, and medications are other forms of treatment for atypical ductal hyperplasia.
What You Need to Know
If tests confirm you have atypical ductal hyperplasia in one or both of your breasts, your doctor will want to follow your breast health very carefully.
What is atypical ductal hyperplasia?
To better understand the pathophysiology, imagine looking through a normal duct in the breast like a hollow tube. In a normal and healthy duct, you see uniform and orderly cells growing next to each other in a single layer lining the inside of the duct.
Symptoms of Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia
There are no symptoms specific to ADH. The condition might be discovered when you are being seen or tested for a problem with your breast such as pain, a lump or discharge.
How is atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed?
A breast biopsy, which is usually done to evaluate an abnormality seen on imaging or during a physical exam, can reveal atypical ductal hyperplasia.
What is the treatment for atypical ductal hyperplasia?
After the excisional biopsy, close breast surveillance is usually recommended. Finding a provider who specializes in breast health is important to ensure you are getting the appropriate follow-up care. In addition, there are risk-reducing strategies that your breast care specialist will discuss with you.
Will I get breast cancer if I have ADH?
If you’ve been diagnosed with ADH, you have an increased risk of developing breast cancer in the future. Specifically, at five years after the diagnosis of ADH, 7% of women will develop breast cancer, and at 10 years post-diagnosis, 13% of these women will develop breast cancer.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Atypical hyperplasia is generally treated with surgery to remove the abnormal cells and to make sure no in situ or invasive cancer also is present in the area. Doctors often recommend more-intensive screening for breast cancer and medications to reduce your breast cancer risk.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- An atypical hyperplasia diagnosis can be stressful, since it increases your risk of breast cancer. Not knowing what the future holds may make you fearful for your health. With time, you'll develop you own way of coping with atypical hyperplasia and your increased risk of breast cancer. Until you find your way of coping, consider trying to: 1. Understand your individual risk of breast canc…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If a mammogram reveals a suspicious area in your breast, your doctor may refer you to a breast health specialist or a specialized breast center.