2.1 Biological treatment method
| Name of enzyme | Producing microbes | Name of dye degraded | pH | Temperature (°C) |
| Laccase | Geobacillus stearothermophilus (thermoph ... | Indigo carmine, Congo red, Brilliant Gre ... | Stable in diverse pH | Temperature stable |
| Azoreductase | Shewanella sp. Strain IFN4 (bacteria) | Acid Yellow 19, Acid Red 88, Reactive Bl ... | 8 | 45 |
| Claccase (SmLac) | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia AAP56 (bact ... | Reactive Black 5 dye | Optimal pH neutral or basic | – |
| Soybean peroxidase | Immobilized Desmodesmus sp. (algae sourc ... | Methylene Blue | – | – |
Full Answer
How can we treat waste water with biological methods?
4 rows · Biological wastewater treatment is not a completely understood process at the intersection of ...
What is the biological treatment for waste water?
Apr 01, 2019 · What is a biological wastewater treatment system? In a simplified, top-level answer to this question, a biological wastewater treatment system is a technology that primarily uses bacteria, some protozoa, and possibly other specialty microbes to clean water. When these microorganisms break down organic pollutants for food, they stick together, which creates a …
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
What is Biological Wastewater Treatment 1. Process that uses natural processes to treat wastewater which involves the microbial activity of decomposing organic and other substances.
What is wastewater, and how is it treated?
Oct 15, 2019 · What is a biological wastewater treatment system? The primary goal of any wastewater treatment system is to reduce the concentration of undesirable components—or contaminants—present in a liquid waste stream. Biological treatment systems achieve this objective by harnessing microbes to break down and remove contaminants from wastewater.

What do you mean by biological treatment of wastewater?
Biological wastewater treatment is designed to degrade pollutants dissolved in effluents by the action of microorganisms. The microorganisms utilize these substances to live and reproduce. Pollutants are used as nutrients.
What is the biological treatment?
Biological or biologic therapy is a type of treatment used to stimulate or restore the ability of the body's immune system. Other names for this type of therapy include biotherapy or immunotherapy. It is used to treat cancer and other conditions, as it helps the body fight infection and disease.
What is the biological treatment of water?
The principle of biological water treatment methods is on the degradation of organic compounds present in the effluent by microorganisms (aerobic and/or anaerobic). On one hand, to develop them, they will consume the dissolved organic pollution.
What are the types of biological treatment?
There are two types of biological treatment process; aerobic and anaerobic. Biological wastewater treatment is an extremely cost effective and energy efficient system for the removal of BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand), since only micro-organisms are used.
What are biologics used for?
Biologics can treat a variety of conditions, such as cancer, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease. These medicines are given as a shot or through an infusion into a vein.Jun 23, 2021
Is biological wastewater treatment a complex process?
Biological wastewater treatment is a process that seems simple on the surface since it uses natural processes to help with the decomposition of organic substances, but in fact, it’s a complex, not completely understood process at the intersection of biology and biochemistry.
Why is biological treatment used?
Biological treatment is used worldwide because it’s effective and more economical than many mechanical or chemical processes. Biological treatment usually is divided into aerobic and anaerobic processes. “Aerobic” refers to a process in which oxygen is present, while “anaerobic” describes a biological process in which oxygen is absent.
What is biological wastewater?
Wastewater typically contains a buffet of organic matter, such as garbage, wastes, and partially digested foods. It also may contain pathogenic organisms, heavy metals, and toxins. The goal of biological wastewater treatment is to create a system in which the results of decomposition are easily collected for proper disposal.
What is a sandblaster used for?
It is well suited for treating waste streams high in organic or biodegradable content and is often used to treat municipal sewage ; wastewater generated by pulp and paper mills or food-related industries such as meat processing; and industrial waste streams containing carbon molecules.
What is MABR treatment?
MABR Treatment. In recent years, technological advances have been transforming biological processes. One example is the membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR), which refines this process to use 90% less energy for aeration, typically the most energy-intensive stage of traditional biological treatment. In Fluence’s MABR treatment, air ...
What is nitrification denitrification?
Nitrification-denitrification is achieved by a biofilm that forms on the membrane. The result is an effluent suitable for irrigation or release into the environment. Most legacy plants around the world use activated sludge treatment or other older aerobic treatment processes.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion drives one of the most robust areas of resource recovery: energy recovery. In this form of energy recovery, also known as waste-to-energy, anaerobic digestion is used to produce biogas, which is composed primarily of methane.
What are the different types of wastewater treatment?
Typically broken out into three main categories, biological wastewater treatment can be: 1 aerobic, when microorganisms require oxygen to break down organic matter to carbon dioxide and microbial biomass 2 anaerobic, when microorganisms do not require oxygen to break down organic matter, often forming methane, carbon dioxide, and excess biomass 3 anoxic, when microorganisms use other molecules than oxygen for growth, such as for the removal of sulfate, nitrate, nitrite, selenate, and selenite
What is an MBR system?
MBRs primarily target BOD and total suspended solids (TSS). MBR system design varies depending on the nature of the wastewater and the treatment goals, but a typical MBR might consist of aerobic (or anaerobic) treatment tanks, an aeration system, mixers, a membrane tank, a clean-in-place system, and either a hollow fiber or flat sheet ...
When was activated sludge first used?
Activated sludge was first developed in the early 1900s in England and has become the conventional biological treatment process widely used in municipal applications but can also be used in other industrial applications.
What is anaerobic digester?
Anaerobic digesters also useanaerobic bacteria to break down organic waste without oxygen and produce biogas, mostly for sewage treatment, and there are a variety of anaerobic digesters available. They each perform the same process in slightly different ways.
What does high BOD mean?
High levels of BOD indicate an elevated concentration of biodegradable material present in the wastewater and can be caused by the introduction of pollutants such as industrial discharges, domestic fecal wastes, or fertilizer runoff. When pollutant levels are elevated, BOD can deplete the oxygen needed by other aquatic organisms to live, ...
How does a biological trickling filter work?
They work by passing air or water through a media designed to collect a biofilm on its surfaces. The biofilm may be composed of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria which breakdown organic contaminants in water or air.
What are the different types of biological treatment systems?
Biological treatment systems are typically characterized by a subset of system types, which include: 1 Aerobic: Aerobic treatment systems utilize microorganisms that require oxygen to function. While they are effective for streams with low to moderate contaminant levels, aerobic systems require proper management to avoid problems stemming from BOD/COD overload, improper aeration, and excess sludge buildup. 2 Anaerobic: Anaerobic wastewater treatment systems utilize microorganisms that do not require oxygen. They are excellent for handling concentrated waste streams, but because they are sensitive to oxygen exposure, pH, temperature, and variations in the waste stream, anaerobic systems also require careful planning and management to avoid problems. 3 Anoxic: Anoxic treatment systems are specialized for removal of nitrogen and other materials from wastewater, leveraging microbes that can use oxidized inorganic compounds in place of oxygen during respiration.
What is biological wastewater?
Beverage biological wastewater treatment. Beverage producers generate wastewater through various aspects of operation, including cleaning and rinsing of bottles and equipment. Wastewater most typically includes sugars and other carbohydrates from beverage production, as well as residual cleaners and solvents.
Is biological wastewater treatment efficient?
The good news is that biological wastewater treatment can be quite efficient for helping food and beverage producers stay in compliance with discharge standards—and avoid costly fines. While some concerns, such as discharge compliance and space restrictions, are broadly shared, the food and beverage industry represents a diverse set of subsectors, ...
What is aerobic treatment?
Aerobic: Aerobic treatment systems utilize microorganisms that require oxygen to function. While they are effective for streams with low to moderate contaminant levels, aerobic systems require proper management to avoid problems stemming from BOD/COD overload, improper aeration, and excess sludge buildup.
What is dairy wastewater?
Dairy wastewater may result from packaging of milk and production of dairy products, including butter, cheese, and yogurt, among other examples. Dairy production is a water-intensive process that creates large volumes of wastewater, generally with significant organic content in the form of protein, fats, and carbohydrates.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is an effective way of breaking down and eliminating organic waste, typical of the waste products produced in the food and drink, chemical, oil and gas industries. Biological treatment is complex and has many different aspects to it.
Where does wastewater enter the system?
With up-flow anaerobic sludge blankets, or UASBs, the theory is that wastewater enters at the base of the system and up through a blanket of sludge before into a upper gas separator, where biogas is sucked away.
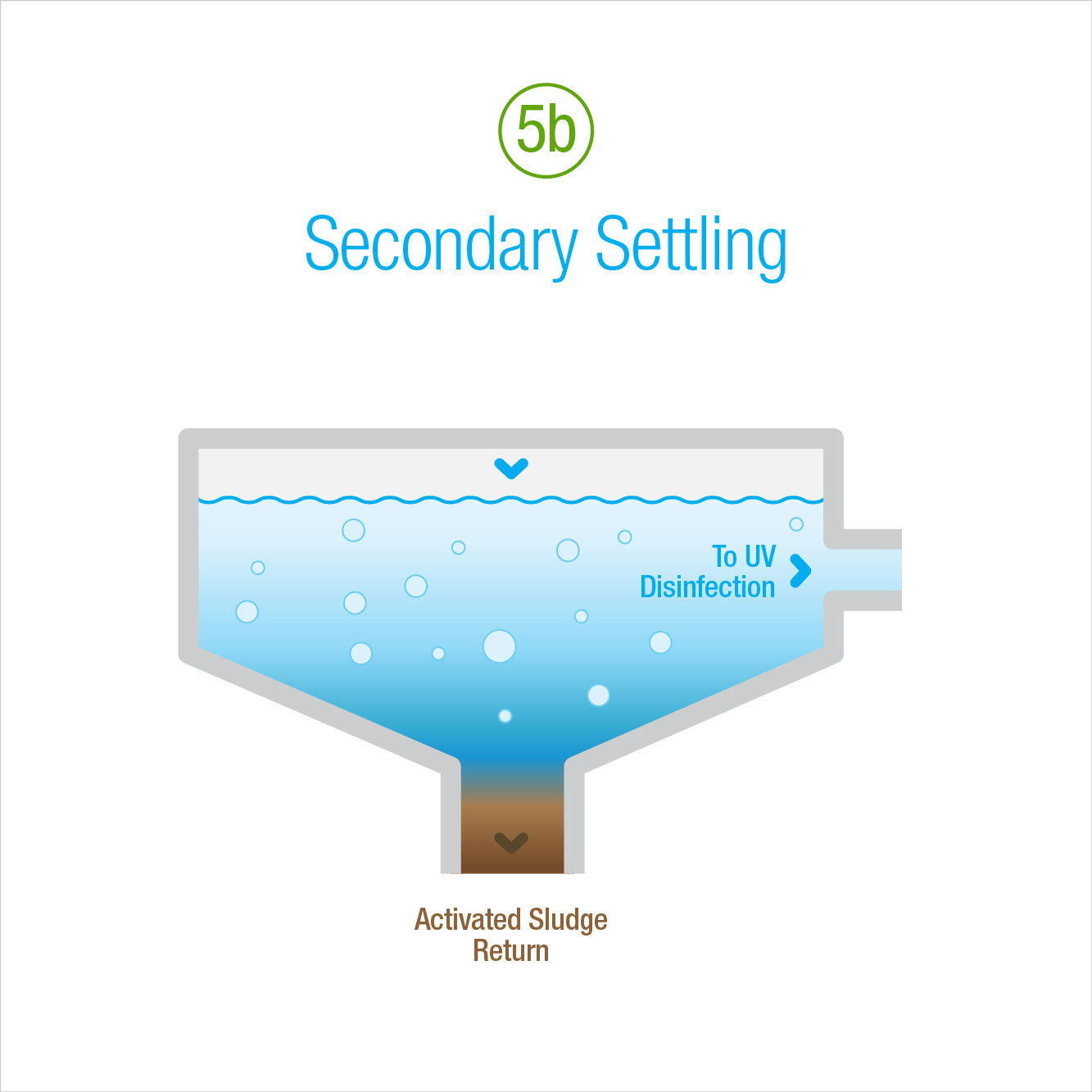
What is activated sludge?
Activated sludge is a system that has been around since the start of the 20 th century. It’s the most common biological treatment used in large utility type water treatment plants but also has a place in other industrial settings. Wastewater first flows into an aeration tank, where oxygen is pumped into the water to feed ...
What is a fixed bed bioreactor?
Fixed-bed bioreactors or FBBRs are a technology that was developed in the 1970s and 80s. FBBRs comprise a series of tanks with multiple chambers, packed with a porous material such as ceramic, foam or plastic. The wastewater flows through the various chambers, with contaminants being eaten by microbes along the way.
What is a biological filter?
Biological trickling filters. Biological trickling filters can be used to remove organic contamination from either wastewater or air. The air or water is passed through some type of medium which will allow biofilm to collect on its surface. This biofilm, composed of both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria, will break down organic contamination.
What is the biological oxygen demand?
Biological Oxygen Demand, or BOD, is the name of the measurement used to quantify the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by the anaerobic bacteria in the system to break down organic matter. A high level of BOD means that there is a high level of biodegradable material in the water.
What is an MBR tank?
A typical MBR will have both aerobic and anaerobic treatment tanks, a system for aeration, a tank with a membrane, and an ultrafiltration membrane. Although effective, the downside of a MBR system is that it is expensive to build initially, and also involves higher operating and maintenance costs.
What are the biological processes used in wetland systems?
The basic biological treatment processes used in the system include waste stabilization ponds and constructed wetland systems, trickling (or percolating) filter systems, and activated sludge systems. An aerobic stabilization pond is a large and shallow excavation in the ground, where the treatment of the waste occurs by natural processes involving the use of both bacteria and algae. In aerobic ponds, oxygen is supplied by natural surface re-aeration and by algal photosynthesis. Higher animals such as rotifers and protozoa are also present in the pond. Their main function is to predate on the bacteria, and to a lesser extent on algae, which helps in controlling the suspended solids (SS) concentration in the effluent. Ponds in which the stabilization of wastes is brought about by a combination of aerobic, anaerobic, and facultative bacteria are known as facultative stabilization ponds. The three zones in such ponds include a surface zone where aerobic bacteria and algae exist in a symbiotic relationship, an intermediate zone that is partly aerobic and partly anaerobic in which the decomposition of organic matter is carried out by facultative bacteria, and an anaerobic bottom zone in which accumulated solids are decomposed by anaerobic bacteria.
How is oxidation accomplished?
Oxidation is accomplished by adding chlorine to the pretreated wastes in an aeration basin. Oxygen from air and chlorine are the oxidizing agents. Spent activated carbon can then be recovered (partially) by the process of heating (incinerating). View chapter Purchase book.
What is aerobic stabilization pond?
An aerobic stabilization pond is a large and shallow excavation in the ground, where the treatment of the waste occurs by natural processes involving the use of both bacteria and algae. In aerobic ponds, oxygen is supplied by natural surface re-aeration and by algal photosynthesis. Higher animals such as rotifers and protozoa are also present in ...
What is biological treatment of industrial wastewater?
Biological treatment of industrial wastewater is a process whereby organic substances are used as food by bacteria and other microorganisms. Almost any organic substance can be used as food by one or more species of bacteria, fungi, ciliates, rotifers, or other microorganisms.
What is biological treatment?
Biological treatment Biological treatment processes are widely used in both developed and developing countries to control and accelerate the natural process of organic matter decomposition. The process is often used to treat biodegradable waste materials, such as plants, food residues, and paper products, before they are disposed. Anthropogenic compounds (those created by humans), such as aliphatic and aromatic compounds, may also be degraded or transformed through biological treatment. Further, biological treatment can be used to reduce volume in the waste materials, destruct human pathogens, and produce biogas for energy uses.
What is thermal treatment?
Thermal treatment Thermal treatment is the waste treatment technology that involves high temperatures in the processing of waste materials. Systems that are generally considered as thermal treatment include gasification, incineration, mechanical heat treatment, pyrolysis, and waste autoclaves.
What is the purpose of incinerating waste?
Incineration is a combustion process designed to recover energy and reduce the volume and pathogenicity of wastes going to disposal , and it is the most widely used method in thermal treatment. Depending on the physical and chemical characteristics of the wastes, different incinerator designs are applied.

Introduction
Goals
- The goal of biological wastewater treatment is to create a system in which the results of decomposition are easily collected for proper disposal. Scientists have been able to control and refine both aerobic and anaerobic biological processes to achieve the optimal removal of organic substances from wastewater.
Scope
- The biological processes used to treat wastewater include subsurface applications, such as septic or aerobic tank disposal systems; many types of aeration, including surface and spray aeration; activated sludge processes; ponds and lagoons; trickling filters; and anaerobic digestion. Constructed wetlands and various types of filtration are also considered biological treatment pr…
Subdivisions
- These processes are usually divided into anaerobic and aerobic processes. Aerobic refers to a process in which oxygen is present, while anaerobic describes a biological process in which oxygen is absent.
Applications
- Aerobic wastewater treatment processes include treatments such as activated sludge process, oxidation ditches, trickling filters, lagoon-based treatments, and aerobic digestion. Diffused aeration systems may be used to maximize oxygen transfer and minimize odors as the wastewater is treated. Aeration provides oxygen to the helpful bacteria and other organisms as t…
Technology
- An exciting new technology, the membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR), refines this process to use 90% less energy for aeration. Air is gently blown into a spirally wound membrane in a tank, with air on one side of the membrane and mixed liquor on the other. Nitrification-denitrification is achieved by a biofilm that forms on the membrane. The result is an effluent suitable for irrigatio…
Examples
- By contrast, anaerobic treatment uses bacteria to help organic material deteriorate in an oxygen-free environment. Lagoons and septic tanks may use anaerobic processes. The best-known anaerobic treatment is anaerobic digestion, which is used for treating food and beverage manufacturing effluents, as well as municipal wastewater, chemical effluent, and agricultural wa…
Treatment
- The type of biological treatment selected for wastewater treatment, whether aerobic or anaerobic, depends on a wide range of factors, including compliance with environmental regulations on discharge quality. Biological treatments are often supplemented with treatments including chlorination and carbon filtration, as well as technologies like reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration.
Research
- Researchers continue to look for ways to optimize conventional biological wastewater treatment. In one example, Finnish researchers added iron sulfate to wastewater before biological treatment to reduce phosphorous in tough-to-treat pulp mill wastewater. Other researchers have used ultraviolet light to remove challenging substances such as chemical residues and pharmaceutic…
Evolution
- So, while biological treatment has a long history, its continuing to evolve in ways that make it more effective, efficient, and available.