
Biological Treatment of Waste Water
- Biological Aerobic Treatment: Aerobic wastewater treatment is a biological process that takes place in the presence...
- Biological Anaerobic Treatment: This treatment process is effectively utilized to treat high strength waste water and...
How can we treat waste water with biological methods?
Biological wastewater treatment method, also known as the conventional method, is a common and widely used method of treatment. It takes into account biodegradation bleaching by taking aid of several micro-organisms, fungi, bacteria, yeasts, and algae. This is a cheap and easy process that goes through a combination of aerobic and anaerobic processes.
What is the biological treatment for waste water?
Biological wastewater treatment leverages the effects of bacteria and other microorganisms to purify water. Biological wastewater treatment is a seemingly simple process because it uses natural processes to aid in the decomposition of organic matter, but in reality it is a complex and complete interface between biology and biochemistry.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Apr 01, 2019 · In a simplified, top-level answer to this question, a biological wastewater treatment system is a technology that primarily uses bacteria, some protozoa, and possibly other specialty microbes to clean water. When these microorganisms break down organic pollutants for food, they stick together, which creates a flocculation effect allowing the organic matter to settle out …
What are the side effects of biological therapy?
Biological treatment would seldom be selected as the primary means of treating a CMP wastewater, but it is useful to consider the fate and potential impacts of alumina, ceria, and silica particles in a biological wastewater treatment process. Biological wastewater treatment entails the use of an active microbial biomass to degrade soluble organic carbon, nitrogen, and …

What is the biological treatment?
A type of treatment that uses substances made from living organisms to treat disease. These substances may occur naturally in the body or may be made in the laboratory. In cancer, some biological therapies stimulate or suppress the immune system to help the body fight cancer.
What is a biological wastewater treatment system?
Biological wastewater treatment is designed to degrade pollutants dissolved in effluents by the action of microorganisms. The microorganisms utilize these substances to live and reproduce. Pollutants are used as nutrients.
What are the types of biological treatment?
There are two types of biological treatment process; aerobic and anaerobic. Biological wastewater treatment is an extremely cost effective and energy efficient system for the removal of BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand), since only micro-organisms are used.
What is biological treatment What are the advantages of biological treatment?
Compared to other treatment methods, biological methods have certain advantages such as (1) treatment technology is traditional and well understood; (2) enhanced efficiency in terms of organic content removal; (3) cost-effective; and (4) environment friendly and safe.
What are the objectives of biological treatment?
Main objectives of biological treatment to remove or reduce the concentration of organic, inorganic compounds nutrients specially nitrogen and phosphorus. Also denitrification of common terminology used for biological treatment process. presence of oxygen. Activated Sludge Process.
Why is biological treatment used?
Biological treatment is used worldwide because it’s effective and more economical than many mechanical or chemical processes. Biological treatment usually is divided into aerobic and anaerobic processes. “Aerobic” refers to a process in which oxygen is present, while “anaerobic” describes a biological process in which oxygen is absent.
What is biological wastewater?
Wastewater typically contains a buffet of organic matter, such as garbage, wastes, and partially digested foods. It also may contain pathogenic organisms, heavy metals, and toxins. The goal of biological wastewater treatment is to create a system in which the results of decomposition are easily collected for proper disposal.
What is aerobic wastewater treatment?
Aerobic wastewater treatment processes include simple septic or aerobic tanks, and oxidation ditches; surface and spray aeration; activated sludge; oxidation ditches, trickling filters; pond and lagoon-based treatments; and aerobic digestion. Constructed wetlands and various types of filtration are also considered biological treatment processes. Diffused aeration systems may be used to maximize oxygen transfer and minimize odors as the wastewater is treated. Aeration provides oxygen to the helpful bacteria and other organisms as they decompose organic substances in the wastewater.
What is MABR treatment?
MABR Treatment. In recent years, technological advances have been transforming biological processes. One example is the membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR), which refines this process to use 90% less energy for aeration, typically the most energy-intensive stage of traditional biological treatment. In Fluence’s MABR treatment, air ...
What is nitrification denitrification?
Nitrification-denitrification is achieved by a biofilm that forms on the membrane. The result is an effluent suitable for irrigation or release into the environment. Most legacy plants around the world use activated sludge treatment or other older aerobic treatment processes.
Is biological wastewater treatment a complex process?
Biological wastewater treatment is a process that seems simple on the surface since it uses natural processes to help with the decomposition of organic substances, but in fact, it’s a complex, not completely understood process at the intersection of biology and biochemistry.
What are the different types of wastewater treatment?
Typically broken out into three main categories, biological wastewater treatment can be: 1 aerobic, when microorganisms require oxygen to break down organic matter to carbon dioxide and microbial biomass 2 anaerobic, when microorganisms do not require oxygen to break down organic matter, often forming methane, carbon dioxide, and excess biomass 3 anoxic, when microorganisms use other molecules than oxygen for growth, such as for the removal of sulfate, nitrate, nitrite, selenate, and selenite
What is a fixed bed wastewater system?
A well-engineered fixed-bed will allow wastewater to flow through the system without channeling or plugging. Chambers can be aerobic and still have anoxic zones to achieve aerobic carbonaceous removal and full anoxic denitrification at the same time.
How are suspended flocs removed from wastewater?
The suspended flocs enter a settling tank and are removed from the wastewater by sedimentation. Recycling of settled solids to the aeration tank controls levels of suspended solids, while excess solids are wasted as sludge.
How does a biological trickling filter work?
They work by passing air or water through a media designed to collect a biofilm on its surfaces. The biofilm may be composed of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria which breakdown organic contaminants in water or air.
What is aerobic microbiology?
aerobic, when microorganisms require oxygen to break down organic matter to carbon dioxide and microbial biomass. anaerobic, when microorganisms do not require oxygen to break down organic matter, often forming methane, carbon dioxide, and excess biomass. anoxic, when microorganisms use other molecules than oxygen for growth, ...
When was the moving bed bioreactor invented?
Moving bed bioreactors, or MBBRs, invented in the late 1980s in Norway, already has been applied in over 800 applications in more than 50 countries, with approximately half treating domestic wastewater and half treating industrial wastewater.
When was activated sludge first used?
Activated sludge was first developed in the early 1900s in England and has become the conventional biological treatment process widely used in municipal applications but can also be used in other industrial applications.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment entails the use of an active microbial biomass to degrade soluble organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus compounds in a manner that sustains the growth of the biomass.
What chapter does nutrient dosing in wastewater treatment?
Chapter 3, Reactivating Bacterial Community and Biochemical Events, demonstrated the nutrient exhaustion inside a bioreactor-based treatment process, and in Chapter 4 , Dosing With Product From the Waste: Use of Fractionsm we discussed in detail nutrient dosing. The reactivation of a nutrient exhausted bioreactor by nutrient dosing would be not only an eventual requirement, but also would arguably be the best possible method to improve the bioreactor’s performance.
How is oxygen supplied to wastewater?
In conventional aerobic biological wastewater treatment processes, oxygen is usually supplied as atmospheric air, either via immersed air-bubble diffusers or surface aeration. Diffused air bubbles (via fine bubble aeration) are delivered to the bulk liquid (as in an ASP, a biological/submerged aerated filter (BAF/SAF), fluidized bioreactors, etc.), or oxygen transfer occurs from the surrounding air to the bulk liquid via a liquid/air interface (as for a TF or a rotating biological contactor (RBC)).
What do thriving microbial assemblages feed on?
The thriving microbial assemblages feed on the root exudates for their metabolism and favor microbial oxidation of the azo dye’s reduced products that fasten their mineralization. The plants uptake some of the reduced and simplified products of dye, produced in the anaerobic region, for their growth.
When was the anaerobic filter invented?
Introduced by Coulter et al. in 1957 and developed by Young and McCarty in 1967, the anaerobic filter is a fixed-film biological wastewater treatment process in which a fixed matrix (support medium) provides an attachment surface that supports the anaerobic microorganisms in the form of a biofilm.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment is an effective way of breaking down and eliminating organic waste, typical of the waste products produced in the food and drink, chemical, oil and gas industries. Biological treatment is complex and has many different aspects to it.
What is a biological filter?
Biological trickling filters. Biological trickling filters can be used to remove organic contamination from either wastewater or air. The air or water is passed through some type of medium which will allow biofilm to collect on its surface. This biofilm, composed of both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria, will break down organic contamination.
How are flocs removed from wastewater?
Flocs can then be removed from the wastewater through the sedimentation process. The disadvantage of activated sludge processes is that they require a lot of space, and can produce large amounts of sludge. On the plus side, they are cheap to build and maintain when compared with other options.
What is an MBR tank?
A typical MBR will have both aerobic and anaerobic treatment tanks, a system for aeration, a tank with a membrane, and an ultrafiltration membrane. Although effective, the downside of a MBR system is that it is expensive to build initially, and also involves higher operating and maintenance costs.
What is the purpose of membrane modules in an aeration tank?
Membrane modules are submerged into the aeration tank, and air is used to scour the submerged membrane to keep them clear. This is an advanced treatment method which combines conventional activated sludge and membrane filtering to remove solids rather than depending on sedimentation.
What is the biological oxygen demand?
Biological Oxygen Demand, or BOD, is the name of the measurement used to quantify the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by the anaerobic bacteria in the system to break down organic matter. A high level of BOD means that there is a high level of biodegradable material in the water.
What is a fixed bed bioreactor?
Fixed-bed bioreactors or FBBRs are a technology that was developed in the 1970s and 80s. FBBRs comprise a series of tanks with multiple chambers, packed with a porous material such as ceramic, foam or plastic. The wastewater flows through the various chambers, with contaminants being eaten by microbes along the way.
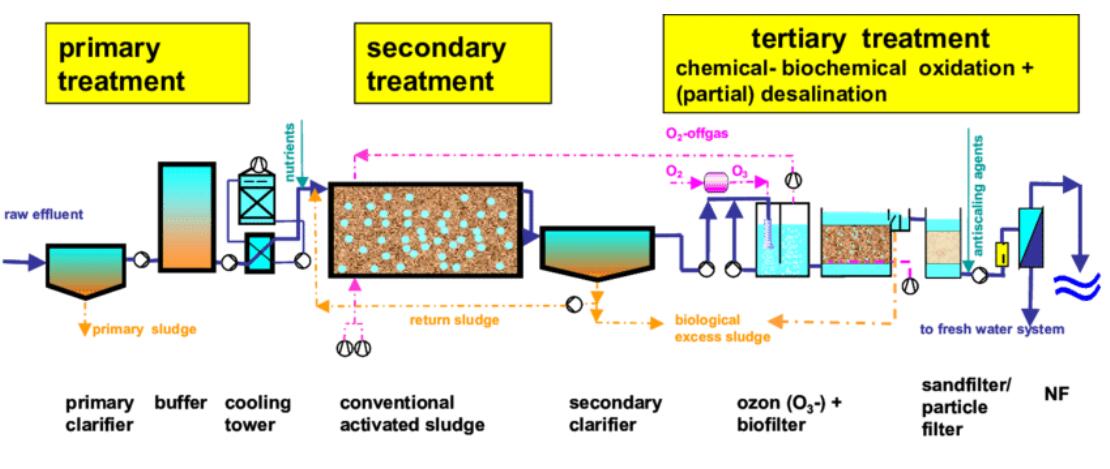
Introduction
Goals
- The goal of biological wastewater treatment is to create a system in which the results of decomposition are easily collected for proper disposal. Scientists have been able to control and refine both aerobic and anaerobic biological processes to achieve the optimal removal of organic substances from wastewater.
Scope
- The biological processes used to treat wastewater include subsurface applications, such as septic or aerobic tank disposal systems; many types of aeration, including surface and spray aeration; activated sludge processes; ponds and lagoons; trickling filters; and anaerobic digestion. Constructed wetlands and various types of filtration are also considered biological treatment pr…
Subdivisions
- These processes are usually divided into anaerobic and aerobic processes. Aerobic refers to a process in which oxygen is present, while anaerobic describes a biological process in which oxygen is absent.
Applications
- Aerobic wastewater treatment processes include treatments such as activated sludge process, oxidation ditches, trickling filters, lagoon-based treatments, and aerobic digestion. Diffused aeration systems may be used to maximize oxygen transfer and minimize odors as the wastewater is treated. Aeration provides oxygen to the helpful bacteria and other organisms as t…
Technology
- An exciting new technology, the membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR), refines this process to use 90% less energy for aeration. Air is gently blown into a spirally wound membrane in a tank, with air on one side of the membrane and mixed liquor on the other. Nitrification-denitrification is achieved by a biofilm that forms on the membrane. The result is an effluent suitable for irrigatio…
Examples
- By contrast, anaerobic treatment uses bacteria to help organic material deteriorate in an oxygen-free environment. Lagoons and septic tanks may use anaerobic processes. The best-known anaerobic treatment is anaerobic digestion, which is used for treating food and beverage manufacturing effluents, as well as municipal wastewater, chemical effluent, and agricultural wa…
Treatment
- The type of biological treatment selected for wastewater treatment, whether aerobic or anaerobic, depends on a wide range of factors, including compliance with environmental regulations on discharge quality. Biological treatments are often supplemented with treatments including chlorination and carbon filtration, as well as technologies like reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration.
Research
- Researchers continue to look for ways to optimize conventional biological wastewater treatment. In one example, Finnish researchers added iron sulfate to wastewater before biological treatment to reduce phosphorous in tough-to-treat pulp mill wastewater. Other researchers have used ultraviolet light to remove challenging substances such as chemical residues and pharmaceutic…
Evolution
- So, while biological treatment has a long history, its continuing to evolve in ways that make it more effective, efficient, and available.