
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the collapse. Causes Of Atelectasis: Atelectasis may be the result of a blocked airway (obstructive) or of pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive). Obstructive atelectasis
Atelectasis
A condition where lungs collapse partially or completely.
What does atelectasis mean in medical terms?
Symptoms and Causes What causes atelectasis? Atelectasis has many causes. Any condition that makes it hard to take deep breaths or cough can lead to a collapse in the lung. People may call atelectasis or other conditions a “collapsed lung.” Another condition that commonly causes a collapsed lung is pneumothorax. Pneumothorax is the presence of air between the lung and the …
What does atelectasis sound like on exam?
If you have atelectasis, you'll feel like you can’t get enough air. Other symptoms can include: Coughing Chest pain A fast heart rate Bluish skin or lips If you’re having trouble breathing, get...
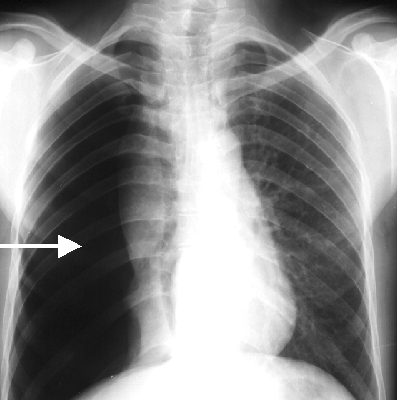
What does atelectasis mean on chest xray?
Which medications are used in the treatment of atelectasis?
What is the best treatment for atelectasis?
TreatmentPerforming deep-breathing exercises (incentive spirometry) and using a device to assist with deep coughing may help remove secretions and increase lung volume.Positioning your body so that your head is lower than your chest (postural drainage). ... Tapping on your chest over the collapsed area to loosen mucus.Sep 5, 2018
What causes atelectasis?
Atelectasis, the collapse of part or all of a lung, is caused by a blockage of the air passages (bronchus or bronchioles) or by pressure on the lung. Risk factors for atelectasis include anesthesia, prolonged bed rest with few changes in position, shallow breathing and underlying lung disease.
Is atelectasis serious?
Large areas of atelectasis may be life threatening, often in a baby or small child, or in someone who has another lung disease or illness. The collapsed lung usually reinflates slowly if the airway blockage has been removed. Scarring or damage may remain. The outlook depends on the underlying disease.
What are the three types of atelectasis?
There are three major types of atelectasis: adhesive, compressive, and obstructive.
What is atelectasis on chest xray?
Definition of Atelectasis: On x-rays and CT scans, reduced volume is seen, accompanied by increased opacity (chest radiograph) or attenuation (CT scan) in the affected part of the lung. Atelectasis is often associated with abnormal displacement of fissures, bronchi, vessels, diaphragm, heart, or mediastinum.
Which type of atelectasis is the most common?
Obstructive atelectasis is the most common type and results from reabsorption of gas from the alveoli when communication between the alveoli and the trachea is obstructed. The obstruction can occur at the level of the larger or smaller bronchus.Oct 22, 2020
Can atelectasis cause chest pain?
Difficulty breathing and chest pain are symptoms of both atelectasis and pneumothorax. Those symptoms may also indicate another serious condition, so always seek emergency medical attention if you experience: Sudden, sharp pain in the chest or radiating to the shoulder or back.
Can atelectasis be permanent?
After treatment, a collapsed lung usually begins working the way it should again. But atelectasis can cause permanent damage in some cases.Jun 21, 2020
Is atelectasis reversible?
Atelectasis is reversible collapse of lung tissue with loss of volume; common causes include intrinsic or extrinsic airway compression, hypoventilation, and a malpositioned endotracheal tube.
What are the complications of atelectasis?
What are the possible complications of atelectasis?Acute pneumonia.Bronchiectasis.Hypoxemia and respiratory failure.Postobstructive drowning of the lung.Sepsis.Pleural effusion and empyema.
How is atelectasis diagnosis?
To diagnose atelectasis, doctors usually start with X-rays (a test that provides pictures of the inside of your chest). Another test called a computed tomography (CT) scan can provide more detailed pictures. In more severe cases, a doctor may use a procedure called a bronchoscopy to see inside your airway.Jan 15, 2018
Is Bibasilar atelectasis serious?
The complications of bibasilar atelectasis can become serious if not treated by your doctor or a medical professional. The following are some possible complications of bibasilar atelectasis: Hypoxemia. This is when there are low oxygen levels in your blood.
What causes atelectasis?
Causes. Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive). General anesthesia is a common cause of atelectasis. It changes your regular pattern of breathing and affects the exchange of lung gases, which can cause the air sacs (alveoli) to deflate. Nearly everyone who has major surgery develops ...
What are the complications of atelectasis?
The following complications may result from atelectasis: Low blood oxygen (hypoxemia). Atelectasis makes it more difficult for your lungs to get oxygen to the air sacs (alveoli). Pneumonia. Your risk for pneumonia continues until the atelectasis goes away. Mucus in a collapsed lung may lead to infection.
What is the term for a complete collapse of the lung?
Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid.
What to do if you have trouble breathing?
Always seek medical attention right away if you have trouble breathing. Other conditions besides atelectasis can cause breathing difficulties and require an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment. If your breathing becomes increasingly difficult, seek emergency medical help.
What causes nonobstructive atelectasis?
Possible causes of nonobstructive atelectasis include: Injury. Chest trauma — from a fall or car accident, for example — can cause you to avoid taking deep breaths (due to the pain), which can result in compression of your lungs. Pleural effusion.
What causes a lung to collapse?
Air leaks into the space between your lungs and chest wall, indirectly causing some or all of a lung to collapse. Scarring of lung tissue. Scarring could be caused by injury, lung disease or surgery. Tumor. A large tumor can press against and deflate the lung, as opposed to blocking the air passages.
Can you get atelectasis after surgery?
If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk. Some research suggests that certain breathing exercises and muscle training may lower the risk of atelectasis after certain surgeries. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
How to treat atelectasis?
Atelectasis treatments include: Bronchoscopy to clear blockages like mucus. Medicine that you breathe in through an inhaler. Physiotherapy such as tapping on your chest to break up mucus, lying on one side or with your head lower than your chest to drain mucus, and exercises to help you breathe better.
What causes atelectasis in the lungs?
Cicatricial. This type of atelectasis is when the tissue that makes up your lungs has scars that keep them from being able to hold as much air as they should.
What happens when you breathe in and out?
When you breathe in and out, your lungs inflate and deflate like balloons. But if your airways get blocked or something puts pressure on your lungs, they might not inflate the way they should. Doctors call that condition atelectasis. It can be life-threatening in small children or people who have another lung problem.
What is lung disease?
A long-term lung disease like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD) Conditions that damage your nerves and muscles, such as a spinal cord injury or muscular dystrophy. An illness or injury that makes it harder to breathe or swallow. Medications that affect your breathing.
Can you get atelectasis after surgery?
It’s common to get atelectasis after you have surgery. The medication that puts you to sleep (called anesthesia) can affect how your lungs work. The surgery itself could also make it hurt to breathe deeply. You may get atelectasis when your airways are physically blocked by something like: Mucus.
What tests are needed to diagnose atelectasis?
A doctor's examination and plain chest X-ray may be all that is needed to diagnose atelectasis. However, other tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis or determine the type or severity of atelectasis. They include:
How to help with lung surgery?
These techniques are best learned before surgery. They include: Performing deep-breathing exercises (incentive spirometry) and using a device to assist with deep cough ing may help remove secretions and increase lung volume. Positioning your body so that your head is lower than your chest (postural drainage).
What is the procedure to remove a tumor from the throat?
Bronchoscopy. A flexible, lighted tube inserted down your throat allows your doctor to see what may be causing a blockage, such as a mucus plug, tumor or foreign body. This procedure may also be used to remove the blockages.
What is the treatment for atelectasis?
If a tumor is causing the atelectasis, treatment may involve removal or shrinkage of the tumor with surgery, with or without other cancer therapies (chemotherapy or radiation).
What doctor do you see when you need emergency care?
Unless you require emergency care, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. However, in some cases when you call to set up an appointment, you may be referred immediately to a lung specialist (pulmonologist).

Overview
- Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid. Atelectasis is one of the most common breathing (respiratory) complications after surgery. It's also a possible complication of other respiratory problems, inclu…
Symptoms
- There may be no obvious signs or symptoms of atelectasis. If you do have signs and symptoms, they may include: 1. Difficulty breathing 2. Rapid, shallow breathing 3. Wheezing 4. Cough
Causes
- Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive). General anesthesia is a common cause of atelectasis. It changes your regular pattern of breathing and affects the exchange of lung gases, which can cause the air sacs (alveoli) to deflate. Nearly everyone who has major surgery develops some amount of atelectasi…
Risk Factors
- Factors that make you more likely to develop atelectasis include: 1. Older age 2. Any condition that makes it difficult to swallow 3. Confinement to bed with infrequent changes of position 4. Lung disease, such as asthma, COPD, bronchiectasis or cystic fibrosis 5. Recent abdominal or chest surgery 6. Recent general anesthesia 7. Weak breathing (respiratory) muscles due to mus…
Complications
- A small area of atelectasis, especially in an adult, usually is treatable. The following complications may result from atelectasis: 1. Low blood oxygen (hypoxemia).Atelectasis makes it more difficult for your lungs to get oxygen to the air sacs (alveoli). 2. Pneumonia.Your risk for pneumonia continues until the atelectasis goes away. Mucus in a collapsed lung may lead to infection. 3. Re…
Prevention
- Atelectasis in children is often caused by a blockage in the airway. To decrease atelectasis risk, keep small objects out of reach of children. In adults, atelectasis most commonly occurs after major surgery. If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk. Some research suggests that certain breathing exercises and muscle training may low…