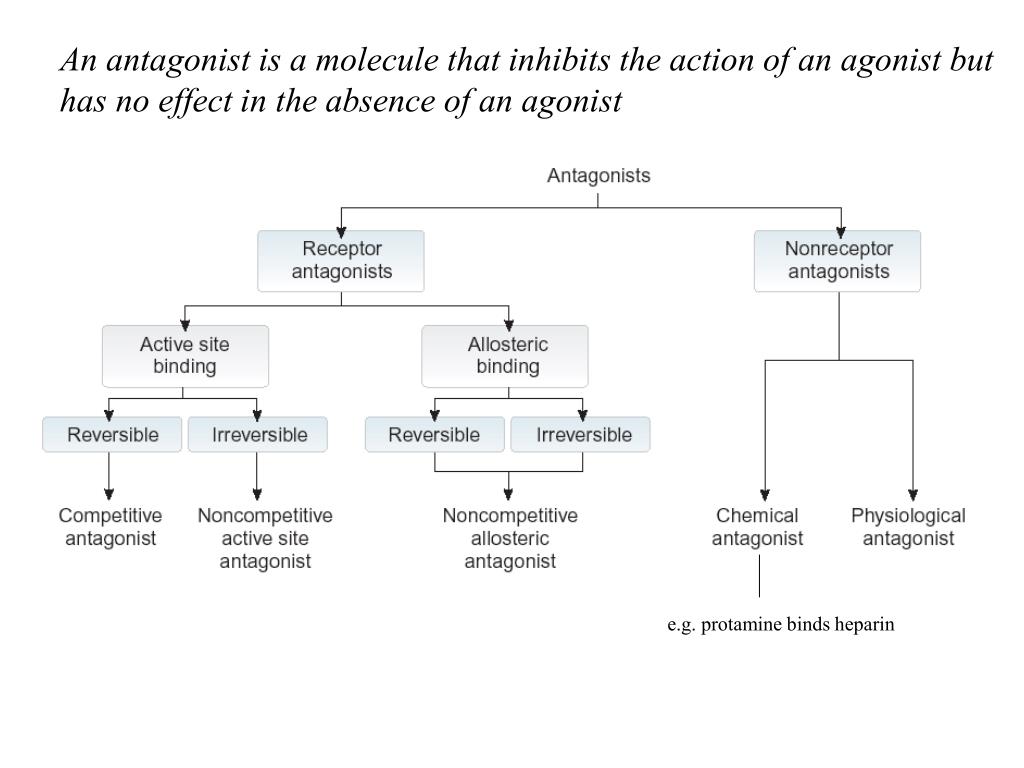
What are antagonist treatments?
Antagonist drugs are used to block addictive drugs from activating the brain's receptors. Antagonist therapy has several benefits. Patients receiving antagonist drugs, such as Naltrexone, which is used in the treatment of opioid addiction, do not develop a tolerance to the medication.
What is the purpose of antagonist drug?
In medicine, a substance that stops the action or effect of another substance. For example, a drug that blocks the stimulating effect of estrogen on a tumor cell is called an estrogen receptor antagonist.
What is the purpose of an opioid antagonist?
Naloxone is a medication approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designed to rapidly reverse opioid overdose. It is an opioid antagonist—meaning that it binds to opioid receptors and can reverse and block the effects of other opioids, such as heroin, morphine, and oxycodone.
What is an agonist antagonist drug?
In pharmacology the term agonist-antagonist or mixed agonist/antagonist is used to refer to a drug which under some conditions behaves as an agonist (a substance that fully activates the receptor that it binds to) while under other conditions, behaves as an antagonist (a substance that binds to a receptor but does not ...
What are some examples of antagonist?
Examples of antagonists include Iago from William Shakespeare's Othello, Darth Vader from the original Star Wars trilogy, the ancient evil Sauron from Tolkien's The Lord of the Rings, and President Snow in The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins.Sep 29, 2021
What are examples of opioid antagonist?
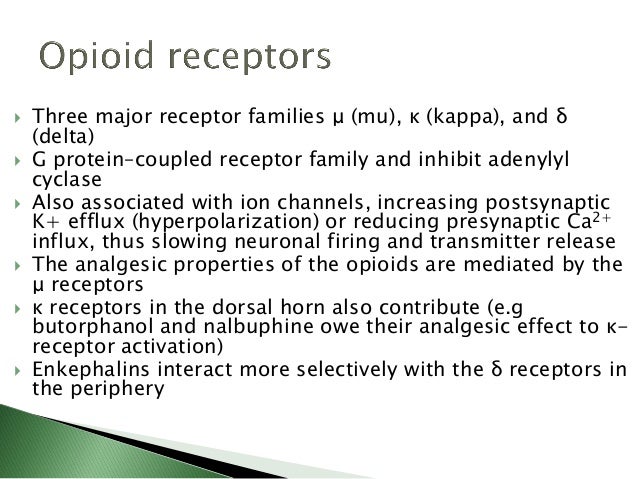
The opioid receptor antagonists include methylnaltrexone, nalbuphine, nalmefene, nalorphine, naloxone, naltrexone, and nalorphine.
What does Narcan do to a sober person?
Narcan doesn't have an effect on a person who's sober from opioids. (“Sober” means they don't have any opioids in their system.) If you suspect, but aren't certain, that a person has overdosed on opioids, you should still give them a dose of Narcan.Mar 20, 2021
What are the different types of agonists?
The following is a list of commonly used agonist drugs: 1 Methadone is a full agonist used in the treatment of opioid addiction 2 Buprenorphine is a partial agonist used in the treatment of opioid addiction 3 Chantix is a partial agonist used in the treatment of nicotine addiction
Why are antagonists used in the brain?
Antagonist drugs are used to block addictive drugs from activating the brain’s receptors.
What is an agonist in drugs?
A drug that is an agonist attaches itself to receptors in the brain, and then produces a chemical reaction. For example, heroin is an opioid agonist. It binds to opioid receptors that control pleasure and pain, the result being a feeling of euphoria and well being. Other examples of opioid agonists, sometimes referred to as “full agonists,” are ...
Is buprenorphine an agonist?
For instance, buprenorphine is a commonly used agonist in the treatment of heroin addiction. Buprenorphine is a “partial agonist.”.
What is the difference between methadone and buprenorphine?
Methadone is a full agonist used in the treatment of opioid addiction. Buprenorphine is a partial agonist used in the treatment of opioid addiction. Chantix is a partial agonist used in the treatment of nicotine addiction.
Is Naltrexone an antagonist?
Antagonist therapy has several benefits. Patients receiving antagonist drugs, such as Naltrexone, which is used in the treatment of opioid addiction, do not develop a tolerance to the medication. Additionally, antagonist drugs are not addictive in and of themselves.
What is the purpose of naltrexone?
Naltrexone is used in the treatment of opioid addiction. Naloxone is often used to stabilize patients suffering from opiate overdose. There are no agonist or antagonist therapies for the treatment of alcohol addiction. However, there are other options. Aversion therapy uses medications, such as Antabuse, which discourage patients ...
How do receptor antagonists work?
How Receptor Antagonists Work. A receptor antagonist works by binding itself to dopamine receptors. In doing so, the drug dampens or blocks the ability of the receptors to receive dopamine. In other words, it effectively turns down dopamine activity.
What is a dopamine antagonist?
Dopamine antagonists are primarily used as antiemetics, atypical antipsychotics, and tricyclic antidepressants. * Antiemetics in the dopamine antagonist category include droperidol, metoclopramide, and domperidone. These medications are commonly used to treat nausea or vomiting.
What is the drug that blocks dopamine receptors?
Blocking dopamine receptors through the antagonism of the receptors is a drug known as a dopamine antagonist. This drug works in the opposite way of a dopamine agonist, which stimulates rather than blocks dopamine receptors. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, is present in a number of animals as well as humans.
How does dopamine work?
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, is present in a number of animals as well as humans. It works by activating dopamine receptors. There are five recognized kinds of dopamine receptors in the human body, located in the central nervous system, the brain, the kidney, and blood vessels. These five types are known as D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5.
Does cocaine increase dopamine levels?
Yet these effects are achieved through very different processes. Cocaine increases dopamine levels by preventing the reuptake of dopamine. It does this by attaching itself to the proteins that would usually carry dopamine. Furthermore, it hangs onto these proteins for a greater time period than dopamine.
What is the process of down regulation?
The receptors that remain can become less sensitive to dopamine, in a process known as desensitization .
How does cocaine affect dopamine?
Drugs such as cocaine and amphetamine can affect dopamine function either through the stimulation or the blocking of dopamine receptors. By changing the flow of dopamine, these drugs produce their pleasurable effects. Amphetamine and cocaine produce similar effects on drug-takers.
What is the FDA approved drug for?
These medications are Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for opioid use disorder and have shown effectiveness in reducing opioid use and harmful opioid related behaviors when used as part of a comprehensive treatment program. Methadone. Full opioid agonist. Relieves withdrawal and prevents cravings.
Is buprenorphine an antagonist?
Buprenorphine is an example of a partial agonist. An antagonist is a drug that blocks opioids by attaching to the opioid receptors without activating them. Antagonists cause no opioid effect and block full agonist opioids. Examples are naltrexone and naloxone. Current medication examples include:
What is OTP in medical?
Prescribed and administered through licensed Opioid Treatment Programs (OTP) Regulated by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) and must meet both federal and state regulations. Unable to be prescribed in an office based clinic setting for opioid use disorder.
What is an agonist in a drug?
An agonist is a chemical that binds and activates the receptor to produce a specific biological response. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist and has an inverse agonist effect.
What is the most common opioid antagonist?
Opioid Antagonists. The two most common opioid antagonists are naloxone and naltrexone. Naloxone is FDA-approved for use in an opioid overdose and is sold in intravenous, intramuscular, and intranasal formulations. Naltrexone, on the other hand, is available in both oral and monthly injectable formulations ...
What is Waismann treatment?
Waismann Treatment™ for Opioid Use Disorder Exclusive Features: 1 Quadruple board-certified physician and a leader in the field of medical opioid detoxification and rapid detox. Our medical director, Michael H. Lowenstein M.D., has himself successfully medically detoxed thousands of patients. 2 Patients receive a private room at a full-service accredited JCAHO hospital. Just in an accredited hospital, vast medical specialists and resources immediately available for patients. 3 Admission on the day before anesthesia assisted rapid detox treatment for comprehensive medical evaluation and proper stabilization 4 Every rapid detox procedure is performed in a private ICU room. The medical team treats patients individually and privately. 5 Additional opioid detox protocol options available with and without anesthesia based on patient needs and preferences 6 Hospital discharge is based on the doctors’ evaluation and not by a pre-established time or facility limits. 7 Inclusive recovery retreat for a few days with multiple services to ensure comfort and well-being throughout the regulation and adaptation period 8 Nearly 100% opioid detox success rate
Why is methadone used in addiction?
It can help patients ween off opiates of abuse because it decreases drug cravings. Patients must go to licensed methadone clinics to receive their doses. Because it is a narcotic, methadone has its potential to cause dependence.
What is a partial agonist?
Buprenorphine, Suboxone, and Subutex are partial opiate agonist drugs. These partial antagonist drugs bind to the opioid receptors but do not have a “full agonist” effect like heroin. These drugs are typical for the treatment of heroin addiction. Again, they can help prevent withdrawal and cravings.
What is the color of heroin?
Its appearance can be powdery white, rose gray, brown, or black. The different colors come from additives, including sugar, caffeine, or other, sometimes lethal substances.
When was methadone first used?
German scientists first developed it in 1937 by searching for a surgical painkiller named “Dolophine.”. Later, exported to the US and renamed Methadone, the drug became the treatment of heroin addiction. Unfortunately, it proved to be even more addictive than heroin.
What is an antagonist?
Agonists and antagonists are chemicals that bind to the receptor sites of specific neurotransmitters. An antagonist binds to the receptor and then stops that neurotransmitter from binding and sending a signal. Remember that the process of neurotransmission is a bit like a lock-and-key: the right neurotransmitters can only bind with ...
What is the drug used for depression?
Ketamine: An antagonist used in the treatment of depression. Ketamine is an antagonist drug and is the new superstar in medication for depression. Ketamine is the newest drug in the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). But how does it work? In this post, we’ll look at how ketamine is an antagonist of the neurotransmitter glutamate ...
What neurotransmitter blocks glutamate?
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter, so when it binds to its receptor sites it sends a signal for the post-synaptic neuron to “fire.”. But ketamine is an antagonist of the receptor sites for glutamate. So when ketamine binds to the receptor sites, it blocks the glutamate and prevents that neuron from firing.
Is ketamine good for depression?
According to some experts, ketamine is the most significant breakthrough for the treatment of depression in over 50 years ( source ). Grady et al. (2017) reviewed 7 clinical drug trials that tested the safety and effectiveness of ketamine for treating depression. They found that ketamine had a significant effect on the reduction ...
Does serotonin cause depression?
For years serotonin has been the main focus of causes and cures for depression. As low levels of serotonin and serotonergic dysfunction are commonly linked with depression, logically the focus for treatment has been on boosting serotonin levels. This is why the SSRI drugs (that increase serotonin) have been the first choice drug for psychiatrists.
What is the process of neurotransmission?
Remember that the process of neurotransmission is a bit like a lock-and-key: the right neurotransmitters can only bind with the right receptor sites on the post-synaptic neuron (see image). Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors and send signals to the next neuron.
Does glutamate help with depression?
Blocking the glutamate could help to reduce depression symptoms by reducing the transmission of glutamate in key areas of the brain. Not surprisingly, multiple studies have found that people with depression have high levels of glutamate ( source ).