
What is meant by SBR?
styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a general-purpose synthetic rubber, produced from a copolymer of styrene and butadiene.
What is SBR tank?
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are industrial processing tanks for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat waste water such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches.
What are the advantages of SBR?
An SBR reduces both the mechanical and manual resources used. Since it uses one tank which does all three tasks, equalize, aerate and clarify the water, it does not require separate tanks for each of these. Therefore, reduces the resources required. It is mostly automated and hence, does not require supervision.Jun 10, 2019
How is a mixing done in SBR?
How is mixing done in SBR? Explanation: The inlet valve opens and the tank is being filled in, while mixing is provided by mechanical means (no air). This stage is also called the anoxic stage.
What type of reactor is used for SBR?
The SBR process utilizes a fill-and-draw reactor in which cBOD oxidation, nitrification, denitrification, and settling are accomplished in a single reactor (Figure 12). The reactor is operated in six or more stages, which accomplish in time what an MLE process does in space.
Is SBR an activated sludge process?
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are a type of activated sludge process for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat wastewater such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches.
In which stage of the SBR is aeration performed?
This stage is also called the anoxic stage. 6. In which stage of the SBR is aeration performed? Clarification: The fixed or floating mechanical pumps are used or air is transferred into fine bubble diffusers fixed to the floor of the tank during the second stage aeration of the mixed liquor.
What are reactors in wastewater treatment?
Units are the vessels or basin that holds wastewater for the treatment by chemical or biological processes. They can be of any shape.
What is MBR STP?
Membrane Bioreactor or MBR Sewage Treatment Plant is an innovative wastewater treatment method. As the name suggests, it combines two technologies, membrane filtration and the biological treatment.May 10, 2018
What is necessary prior to trickling filter?
Explanation: Primary clarification is necessary prior to trickling filters. Screening of the materials prior to letting it into the trickling filter is necessary. This is done to prevent clogging.
How many types of trickling filters are used in sewage treatment?
Such industrial wastewater trickling filters consist of two types: Large tanks or concrete enclosures filled with plastic packing or other media. Vertical towers filled with plastic packing or other media.
How are Colour and order removed Mcq?
How are colour and odour removed? Explanation: Odour and colour present in water and waste water are removed by aeration and adsorption process. The odour and colour causing elements are adsorbed and aerated that the water is free from impurities for use and wastewater for reuse and recycling. 9.
How long does sludge settle in a tank?
The sludge is allowed to settle until clear water is on the top 20 to 30 percent of the tank contents.
What is sequential batch reactor?
Sequencing batch reactors ( SBR) or sequential batch reactors are a type of activated sludge process for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat wastewater such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the mixture of wastewater and activated sludge to reduce the organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD)). The treated effluent may be suitable for discharge to surface waters or possibly for use on land.
What is extended aeration?
Extended aeration plants are more flexible in flow rate, eliminating restrictions presented by pumps located throughout the SBR systems. Clarifiers can be retrofitted in the equalization tanks of the SBR.
Available models
No two projects are the same. That is why we offer a range of Rewatec SBR systems, each designed according to your unique wastewater treatment needs and preferences.
Additional options
When regulations call for tighter controls, take advantage of our additional treatment options to maximize the performance of your Rewatec SBR system.
Get in touch
We are here to help. For more information about our products and services, including their availability around the world and in your home country, please contact our team of experts today.
How is SBR water transferred?
Once extracted from the SBR chamber, the biologically treated clear water is transferred via the air lift system to the disinfection chamber where chlorine disinfection treatment occurs. This is an effective and economical method to eliminate pathogenic organisms on contact.
What is the rest phase of a SBR?
A rest phase now follows, during which the live sludge sinks to the bottom of the system. This allows a clarified water zone to form at the top of the SBR chamber.
Where does biological cleaning take place?
The actual biological cleaning by microorganisms now takes place in the wastewater treatment tank. Short aeration and rest phases alternate in a controlled cleaning process. The so-called activated sludge can now develop with millions of microorganisms and clean the water thoroughly.
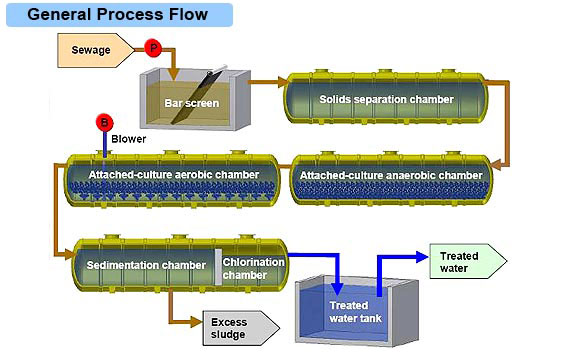
Summary
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are a type of activated sludge process for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat wastewater such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the mixture of wastewater and activated sludge to reduce the organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand(COD)). The treated effluent …
Overview
While there are several configurations of SBRs, the basic process is similar. The installation consists of one or more tanks that can be operated as plug flowor completely mixed reactors. The tanks have a “flow through” system, with raw wastewater (influent) coming in at one end and treated water (effluent) flowing out the other. In systems with multiple tanks, while one tank is in settle/decan…
Treatment stages
There are five stages in the treatment process:
1. Fill
2. React
3. Settle
4. Decant
Removal of constituents
Aeration times vary according to the plant size and the composition/quantity of the incoming liquor, but are typically 60 to 90 minutes. The addition of oxygen to the liquor encourages the multiplication of aerobic bacteria and they consume the nutrients. This process encourages the conversion of nitrogen from its reduced ammonia form to oxidized nitrite and nitrate forms, a process known as nitrification.
Conversion
In some situations in which a traditional treatment plant cannot fulfill required treatment (due to higher loading rates, stringent treatment requirements, etc.), the owner might opt to convert their traditional system into a multi-SBR plant. Conversion to SBR will create a longer sludge age, minimizing sludge handling requirements downstream of the SBR.
The reverse can also be done, in which SBR Systems would be converted into extended aeration …
See also
• Aerobic granulation
• Diffuser (sewage)
• List of waste-water treatment technologies
• Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket digestion