Healthline.com
1. Rest and relaxation...
2. Exercise...
3. Tai chi...
4. Creams, gels, and lotions...
5. Fish oil supplements...
6. Plant oils...
7. Heat and cold...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Exercise...
2. Hot and Cold Compresses...
3. Fish Oil...
4. Turmeric...
5. Apple Cider Vinegar...
6. Garlic...
7. Epsom Salt...
8. Ginger...
Learn More...Webmd.com
1. Acupuncture...
2. Heat and Cold...
3. Magnets...
4. Aromatherapy...
5. Biofeedback...
6. Deep Breathing...
7. Exercise...
8. Massage...
Learn More...What is the latest RA treatment?
The newest RA drugs to gain Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval are called Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. They work by blocking a very specific pathway to stop a person’s immune system from...
What are the natural treatments for RA?
Top 10 Alternative RA Remedies: The Natural Ways I Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
- Essential oils. Essential oils and aromatherapy have been used since ancient times — ever hear of frankincense and myrrh?
- Floating. Floatation therapy, also known as sensory deprivation therapy, is a new trend in natural health treatments.
- Cryotherapy. ...
- Herbal tea. ...
- Acupuncture. ...
- Chiropractic. ...
- Physical therapy. ...
- Massage. ...
What is the first line treatment for RA?
The people with RA in the study received one of four treatments:
- initial treatment with MTX, plus etanercept
- initial treatment with oral triple therapy: MTX, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine
- a step up from initial MTX monotherapy to one of the above combination therapies
- placebos
What are treatment options for RA?
What are the treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis?
- Traditional (nonbiologic) DMARDs. DMARDs are drugs that treat inflammatory diseases. ...
- Biologic DMARDs. ...
- Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. ...
- Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists. ...
- Other biologic DMARDs (abatacept and rituximab) Abatacept inhibits activation of immune cells called T cells. ...
- Janus kinase inhibitors. ...
- NSAIDs and steroids. ...

How does RA treatment work?
The main treatment goals with rheumatoid arthritis are to control inflammation, ease pain, and reduce disability linked to RA. Treatment usually includes medications, occupational or physical therapy, and exercise. Some people need surgery to correct joint damage. Early treatment is key to good results.
What is the number one treatment for RA?
Methotrexate is usually the first medicine given for rheumatoid arthritis, often with another DMARD and a short course of steroids (corticosteroids) to relieve any pain. These may be combined with biological treatments. Common side effects of methotrexate include: feeling sick.
Is RA a life threatening?
RA itself is not fatal, but complications of the disease may shorten survival by years in some individuals. In general, RA is progressive and cannot be cured, but in some patients, the disease gradually becomes less aggressive, and symptoms may even improve.
What causes RA?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition, which means it's caused by the immune system attacking healthy body tissue. However, it's not yet known what triggers this. Your immune system normally makes antibodies that attack bacteria and viruses, helping to fight infection.
What triggers an RA flare?
Flare Types and Triggers Overexertion, poor sleep, stress or an infection like the flu can all set off RA symptoms. With a predictable flare you'll temporarily feel worse, but your symptoms will resolve in time. Unpredictable flares have more uncertainty associated with them.
What are the five signs of rheumatoid arthritis?
Five signs of rheumatoid arthritisStiffness. Waking up refreshed in the morning is the best way to start the day. ... Chronic fatigue. If you've noticed joint stiffness with a decrease in energy, it may be time to give us a call. ... Joint swelling. ... Numbness and tingling. ... Fever.
Is RA a death sentence?
Overview. Share on Pinterest A person cannot die from RA, but the associated inflammation can lead to life-threatening complications. RA is a chronic medical condition that involves increased levels of inflammation in tissues throughout the body. A person cannot die from RA.
Can RA go away?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong disease. When it's treated, it may go away for a little while, but it usually comes back. It's important to see your doctor as soon as symptoms begin. The earlier you start treatment, the better your outcome.
What are the 4 stages of rheumatoid arthritis?
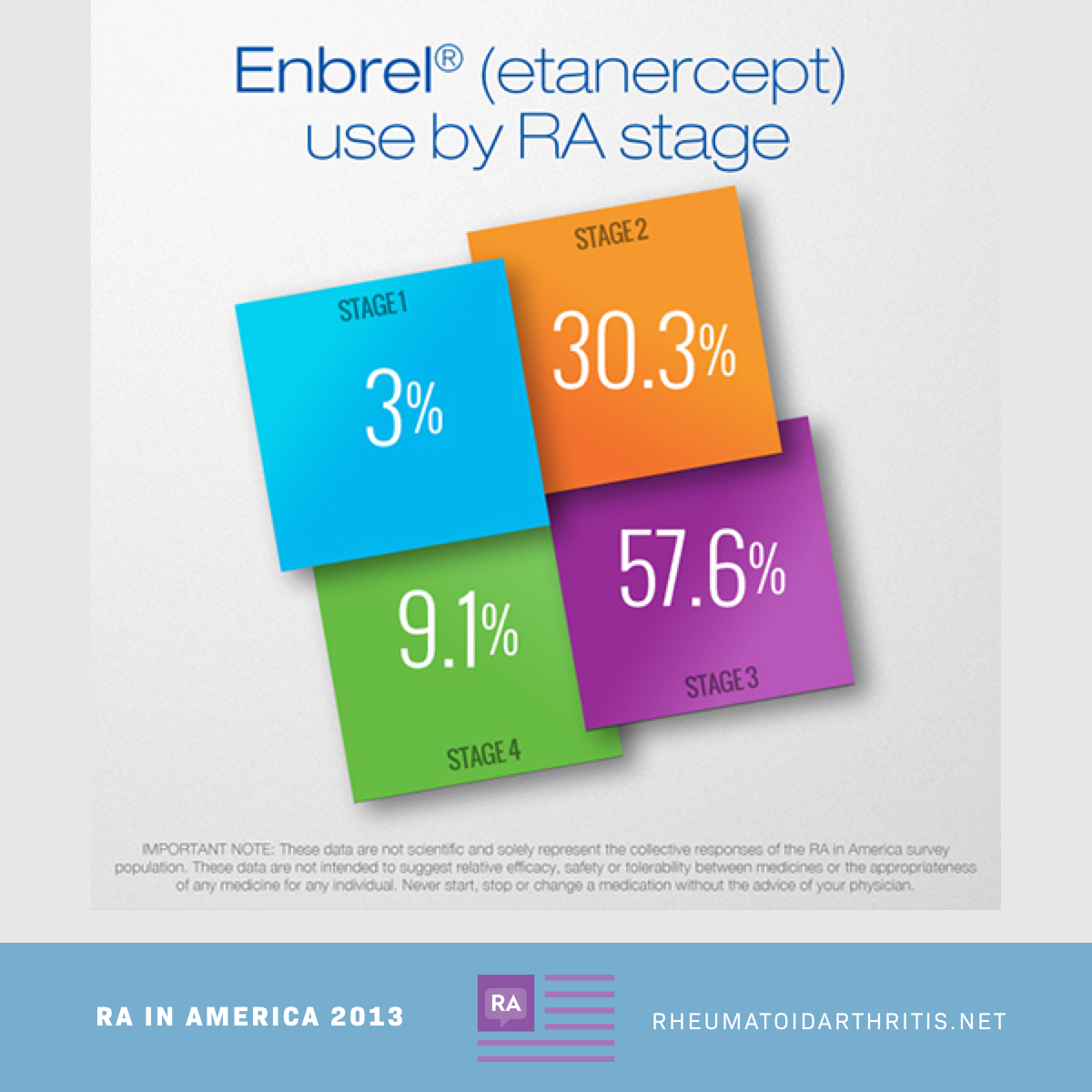
The four stages of rheumatoid arthritis are known as synovitis, pannus, fibrous ankylosis, and bony ankylosis.Stage I: Synovitis. During stage I, you may start having mild symptoms, including joint pain and joint stiffness. ... Stage II: Pannus. ... Stage III: Fibrous Ankylosis. ... Stage IV: Bony Ankylosis.
What does RA pain feel like?
A person with RA may feel intense pain in their joints during flares. This may feel like sustained pressure, a burning sensation, or a sharp pain. However, people with RA may also experience periods of remission when they feel few to no symptoms. In addition to causing pain in the joints, RA can affect the whole body.
Is RA caused by stress?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory joint condition and an autoimmune disease that can be caused by stress, according to research. Stress triggers rheumatoid arthritis by setting off the immune system's inflammatory response in which cytokines are released.
How does RA usually start?
The typical case of rheumatoid arthritis begins insidiously, with the slow development of signs and symptoms over weeks to months. Often the patient first notices stiffness in one or more joints, usually accompanied by pain on movement and by tenderness in the joint.
How to fix rheumatoid arthritis?
Surgery may help restore your ability to use your joint. It can also reduce pain and improve function. Rheumatoid arthritis surgery may involve one or more of the following procedures: Synovectomy. Surgery to remove the inflamed lining of the joint (synovium) can help reduce pain and improve the joint's flexibility. Tendon repair.
What are the drugs that slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis?
Conventional DMARDs. These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage. Common DMARDs include methotrexate (Trexall, Otrexup, others), leflunomide (Arava), hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) and sulfasalazine (Azulfidine). Side effects vary but may include liver damage ...
How does rheumatoid arthritis affect your life?
The pain and disability associated with rheumatoid arthritis can affect a person's work and family life. Depression and anxiety are common, as are feelings of helplessness and low self-esteem. The degree to which rheumatoid arthritis affects your daily activities depends in part on how well you cope with the disease.
Why is rheumatoid arthritis so difficult to diagnose?
Rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose in its early stages because the early signs and symptoms mimic those of many other diseases. There is no one blood test or physical finding to confirm the diagnosis. During the physical exam, your doctor will check your joints for swelling, redness and warmth.
What tests can be done to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis?
Imaging tests. Your doctor may recommend X-rays to help track the progression of rheumatoid arthritis in your joints over time. MRI and ultrasound tests can help your doctor judge the severity of the disease in your body.
How to avoid painful joints?
Assistive devices can make it easier to avoid stressing your painful joints. For instance, a kitchen knife equipped with a hand grip helps protect your finger and wrist joints. Certain tools, such as buttonhooks, can make it easier to get dressed. Catalogs and medical supply stores are good places to look for ideas.
Does black currant oil help with arthritis?
The seeds of evening primrose, borage and black currant contain a type of fatty acid that may help with rheumatoid arthritis pain and morning stiffness. Side effects may include headache, diarrhea and gas. Some plant oils can cause liver damage or interfere with medications, so check with your doctor first. Tai chi.
What is the goal of rheumatoid arthritis treatment?
The goal of rheumatoid arthritis treatment now aims toward achieving the lowest possible level of arthritis disease activity and remission if possible, minimizing joint damage, and enhancing physical function and quality of life.
What are the different types of rheumatoid arthritis drugs?
There are three general classes of drugs commonly used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). NSAIDs and corticosteroids have a short onset of action while DMARDs can take several weeks or months to demonstrate a clinical effect. DMARDs include methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide (Arava®), etanercept (Enbrel®), infliximab (Remicade®), adalimumab (Humira®), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®), golimumab (Simponi®), abatacept (Orencia®), rituximab (Rituxan®), tocilizumab (Actemra®), anakinra (Kineret®), antimalarials (e.g. Plaquenil®). Other immunomodulators are occasionally used including azathioprine (Imuran) and cyclosporine. Because cartilage damage and bony erosions frequently occur within the first two years of disease, rheumatologists now move aggressively to a DMARD agent early in the course of disease, usually as soon as a diagnosis is confirmed. Analgesic drugs are also sometimes helpful in decreasing pain until DMARDs take effect. A summary table of how to monitor drug treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is included.
What are the benefits of DMARD?
Although both NSAIDs and DMARD agents improve symptoms of active rheumatoid arthritis, only DMARD agents have been shown to alter the disease course and improve radiographic outcomes. DMARDs have an effect upon rheumatoid arthritis that is different and may be slower. In most cases, when the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed, DMARD agents should be started. The presence of erosions or joint space narrowing on x-rays of the involved joints is a clear indication for DMARD therapy, however one should not wait for x-ray changes to occur. The currently available drugs include: 1 Methotrexate (Rheumatrex®, Trexall®) 2 Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil ®) 3 Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine®) 4 Leflunomide (Arava®) 5 Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors — etanercept (Enbrel®, adalimumab (Humira ®), and infliximab (Remicade®), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®), golimumab (Simponi®) 6 T-cell Costimulatory Blocking Agents —abatacept (Orencia®) 7 B cell Depleting Agents —rituximab (Rituxan®) 8 Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors– tocilizumab (Actemra®) 9 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Receptor Antagonist Therapy —anakinra (Kineret®) 10 Intramuscular Gold 11 Other Immunomodulatory and Cytotoxic agents — azathioprine (Imuran®) and cyclosporine A (Neoral®, Sandimmune®)
Why is rest important for musculoskeletal health?
Because obesity stresses the musculoskeletal system , ideal body weight should be achieved and maintained. Rest, in general, is an important feature of management. When the joints are actively inflamed, vigorous activity should be avoided because of the danger of intensifying joint inflammation or causing traumatic injury to structures weakened by inflammation. On the other hand, patients should be urged to maintain a modest level of activity to prevent joint laxity and muscular atrophy. Splinting of acutely inflamed joints, particularly at night and the use of walking aids (canes, walkers) are all effective means of reducing stress on specific joints. A consultation with a physical and an occupational therapist is recommended early in the course.
Is there a cure for rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disorder for which there is no known cure . Fortunately in the last few years, a shift in strategy toward the earlier institution of disease modifying drugs and the availability of new classes of medications have greatly improved the outcomes that can be expected by most patients.
Is Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center educational?
All information contained within the Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center website is intended for educational purposes only. Physicians and other health care professionals are encouraged to consult other sources and confirm the information contained within this site. Consumers should never disregard medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something they may have read on this website.
Do anti-inflammatory drugs affect rheumatoid arthritis?
It is important to note however that these drugs alone do not change the course of the disease of rheum atoid arthritis or prevent joint destruction.
How to help RA?
In addition, your doctor or physical therapist can help create an exercise program that supports your goals.
What is a biologic for RA?
Work by targeting a specific part of the immune system in order to reduce the inflammation seen in RA—one example of a biologic is a TNF inhibitor
Can you take pain medicine for RA?
But continued use of pain medicine may be a sign your RA symptoms are not being managed effectively.
Is rheumatoid arthritis a treatment plan?
An effective rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment plan is unique to everyone. People can react differently to different medications, so it can be normal to try a number of treatment options to see what works for you. Effective treatment plans, including the appropriate medication for you, can help limit the impact RA has on your life.
What is RA in medical terms?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory type of arthritis that can causes joint pain, swelling and damage. Learn what causes RA and how to treat it. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causes joint inflammation and pain. It happens when the immune system doesn’t work properly and attacks the lining of the joints (called the synovium).
When does RA start?
In women, RA most commonly begins between ages 30 and 60.
How long does RA pain last?
In the early stages, people with RA may not see redness or swelling in the joints, but they may experience tenderness and pain. Joint pain, tenderness, swelling or stiffness that lasts for six weeks or longer. Morning stiffness that lasts for 30 minutes or longer. More than one joint is affected.
What percentage of people with RA have high ESR?
A high ESR or CRP combined with other clues to RA helps make the diagnosis. Rheumatoid factor (RF) is an antibody found (eventually) in about 80 percent of people with RA. Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) are found in 60 to 70 percent of people with RA. However, they are also found in people without RA.
How to help RA flare ups?
Rest helps reduce inflammation and fatigue that can come with a flare. Taking breaks throughout the day protects joints and preserves energy.
What is the best doctor for arthritis?
A doctor with specialized training in treating arthritis (called a rheumatologist) is the best person to make a correct diagnosis, using medical history, a physical examination and lab tests. Medical history.
What is the name of the joint that is affected by RA?
It happens when the immune system doesn’t work properly and attacks the lining of the joints (called the synovium). The disease commonly affects the hands, knees or ankles, and usually the same joint on both sides of the body. But sometimes, RA causes problems in other parts of the body as well, such as the eyes, ...
How to treat RA?
RA can be effectively treated and managed with medication (s) and self-management strategies. Treatment for RA usually includes the use of medications that slow disease and prevent joint deformity, called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs); biological response modifiers (biologicals) are medications that are an effective second-line treatment. In addition to medications, people can manage their RA with self-management strategies proven to reduce pain and disability, allowing them to pursue the activities important to them. People with RA can relieve pain and improve joint function by learning to use five simple and effective arthritis management strategies.
What is RA in medical terms?
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)? Rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means that your immune system attacks healthy cells in your body by mistake, causing inflammation (painful swelling) in the affected parts of the body. RA mainly attacks the joints, usually many joints at once.
What are the consequences of RA?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has many physical and social consequences and can lower quality of life. It can cause pain, disability, and premature death.
Why is RA risk the highest?
The risk of RA may be highest when people with these genes are exposed to environmental factors like smoking or when a person is obese. Smoking. Multiple studies show that cigarette smoking increases a person’s risk of developing RA and can make the disease worse. History of live births.
How to help arthritis?
Learn more about physical activity for arthritis. Go to effective physical activity programs. If you are worried about making arthritis worse or unsure how to safely exercise, participation in physical activity programs can help reduce pain and disability related to RA and improve mood and the ability to move.
How do you know if you have RA?
Signs and symptoms of RA include: Pain or aching in more than one joint. Stiffness in more than one joint. Tenderness and swelling in more than one joint. The same symptoms on both sides of the body (such as in both hands or both knees) Weight loss. Fever.
What are the effects of RA on the body?
RA can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes. Top of Page.
How to treat RA?
There are three primary strategies that doctors follow when treating RA patients with medications. These treatment strategies include: 1 Aggressively treating symptoms as early as possible 2 Targeting remission to eliminate signs of inflammation for as long as possible 3 Tightly controlling disease activity to keep it to a minimum and to prevent further joint damage
How to treat RA with medication?
These treatment strategies include: Aggressively treating symptoms as early as possible. Targeting remission to eliminate signs of inflammation for as long as possible.
What is the name of the drug that is used for RA?
This form of medication is only taken by injection, unlike the others which are typically oral medications. Some of the most common brand names of RA biologics include Humira, Amjevita, Rituxan, Orencia, and many more. Biologics are a newer form of RA medication and so the long-term side effects, if any, are unknown at the present.
What is biologics in RA?
Biologics. Biologics, or biological response modifiers, are a type of DMARD. Biologics alleviate RA symptoms by targeting the part of the immune system that attacks joint tissue and causes inflammation. Biologics are also found to work effectively on moderate to severe cases of RA.
Why have RA medications evolved over time?
RA medications have greatly evolved over time as a result of the ongoing need for treating these patients and their varying symptoms.
What is the best medicine for RA?
This is crucial for allowing patients to maintain their quality of life. The two most common types of NSAIDs are ibuprofen and naproxen, which are well-known and commonly available by the brand names of Advil and Aleve, ...
Is there a cure for RA?
Treating RA. RA has no cure; however, there are some highly effective treatment methods available. These treatment methods help to achieve several key goals for RA patients by attacking the inflammation in different ways. The main goals of RA treatments include: Prevent progressive damage to joints, bones, and cartilage.
What is the best treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Methotrexate. Methotrexate is a conventional disease-modifying anti-inflammatory drug (DMARD). It works to lower inflammation and slow an overactive immune system, which occurs in rheumatoid arthritis. The new guidelines strongly recommend methotrexate alone (monotherapy) as the first treatment for people with moderate to high disease activity who ...
When was the last time the ACR updated its guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis?
The ACR updates its guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) every few years. The last changes appeared in 2015. Since then, new drugs have hit the market, older drugs have been reassessed, and there’s more evidence for the role of nondrug treatments for RA.
What is the most important factor in all treatment considerations?
The most important factor in all treatment considerations is shared decision-making, where patients are informed of all their options, including nondrug ones, and have a full voice in their own care. “Patients were involved in every step of the process [of creating the update], and the recommendations truly reflect their perspectives,” Dr. Fraenkel says.
What is the treatment to target approach?
Although there’s not much evidence to support it, a treat-to-target approach is strongly recommended for patients who haven’t taken biologics or small molecule drugs. In treat-to-target, doctors and patients decide on a goal and adjust treatment until the goal is reached. Though everyone hopes for remission, many patients may not be able to achieve it. A more realistic aim is low disease activity, which keeps symptoms under control and helps maintain a good quality of life. Still, the guideline states the goal should be tailored to each patient and remission can be the target when possible.
Is methotrexate monotherapy or adalimumab?
The new guidelines strongly recommend metho trexate alone (monotherapy) as the first treatment for people with moderate to high disease activity who haven’t taken DMARDs before. Methotrexate mono therapy is strongly recommended over other conventional DMARDs, a biologic DMARD like adalimumab ( Humira) and small molecule drugs such as Janus kinase ...

Diagnosis
- Following a strict treatment regimen could bring RA into remission. Remission means that the level of disease activity has decreased in the body. It is never an indication that symptoms will not return, but following remission, many patients can go for long periods of time without experi…
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.