
Explore
Vulvar cancer pictures and Remedies - Vulvar cancer is a cancer that attacks the outer surface of the pubic area of the woman. The Vulva is the part of the sexual organs the external female which is the area that surrounds the pee hole (urethra opening) and vagina. The sexual organs the external female includes the labia minora and majora (the“lips” in and out of the covering of the vagina ...
Is there a cure for vaginal cancer?
Vaginal cancer stages range from stage I (1) through IV (4). As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more. Although each person’s cancer experience is unique, cancers with similar stages tend to have a similar outlook and are often treated in much the same way.
What is the prognosis for Stage 4 vaginal cancer?
When found in early stages, vaginal cancer can often be cured. Treatment options depend on the following: The stage and size of the cancer. Whether the cancer is close to other organs that may be damaged by treatment. Whether the tumor is made up of squamous cells or is an adenocarcinoma. Whether the patient has a uterus or has had a hysterectomy.
Can vaginal cancer be cured?
This is called a second cancer. No matter what type of cancer you have had, it's still possible to get another (new) cancer, even after surviving the first. People who have had endometrial cancer can still get the same types of cancers that other people get.
Can I get another cancer after having vaginal cancer?
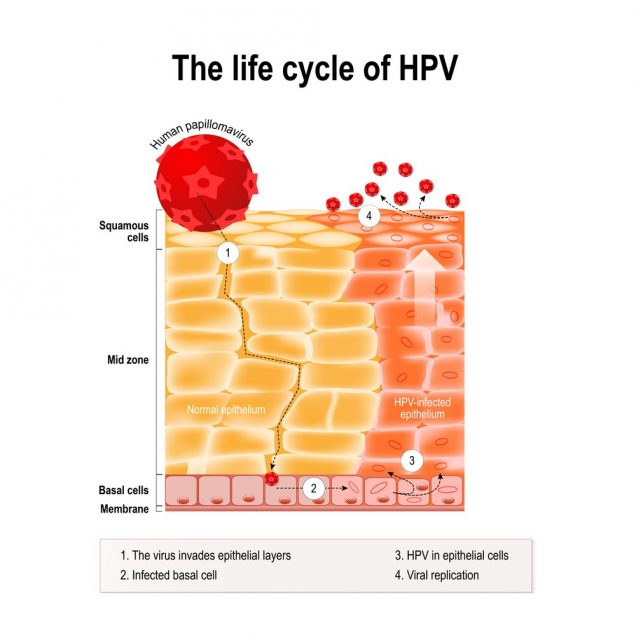
Is there any treatment for vaginal cancer?
Vaginal cancer is often treated with 1 treatment or a combination of treatments: surgery, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
What is the standard treatment for patients with vulvar cancer?
Surgery is the most common treatment for vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) and vulvar cancer. One of the following types of surgery may be done to treat VIN: Separate excision of a lesion: A surgical procedure to remove a lesion of concern.
Can cancer of the vulvar be cured?
When vulvar cancer is found and treated early, the cure rate is more than 90%. The key to a cure is to tell your doctor about any warning signs early and to have a biopsy right away. After treatment, be sure to go to all follow-up appointments that your doctor recommends.
How long can you live with vulvar cancer?
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time (usually 5 years) after they were diagnosed....5-year relative survival rates for vulvar cancer.SEER Stage5-Year Relative Survival RateDistant19%All SEER stages combined71%2 more rows•Feb 4, 2019
How long does it take to treat vulvar cancer?
Most often, your doctor will recommend that you start treatment within a few weeks of your diagnosis. If surgery is all that is required, treatment and recovery should be completed within six to eight weeks. If radiation or chemotherapy is required, this process may take longer.
What does the start of vulvar cancer look like?
An area on the vulva that looks different from normal – it could be lighter or darker than the normal skin around it, or look red or pink. A bump or lump, which could be red, pink, or white and could have a wart-like or raw surface or feel rough or thick. Thickening of the skin of the vulva. Itching.
What were your first symptoms of vulvar cancer?
Signs and symptoms of vulvar cancer may include:Itching that doesn't go away.Pain and tenderness.Bleeding that isn't from menstruation.Skin changes, such as color changes or thickening.A lump, wartlike bumps or an open sore (ulcer)
What is the last stage of vulvar cancer?
Stage IVB. This is the most advanced stage of vulvar cancer. The cancer has spread to organs, such as the lungs or bone, or to lymph nodes further away in the body. It may or may not have spread to nearby lymph nodes and organs.
What are the risk factors for vaginal cancer?
Risk factors for vaginal cancer include the following: Being 60 years or older. Having a human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the vagina is linked to HPV infection and has many of the same risk factors as SCC of the cervix. Being exposed to DES while in the mother's womb .
What is the procedure to remove cells from the vagina?
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues from the vagina and cervix so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. If a Pap test shows abnormal cells in the vagina, a biopsy may be done during a colposcopy.
What is HPV test?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) test: A laboratory test used to check DNA or RNA for certain types of HPV infection. Cells are collected from the cervix and DNA or RNA from the cells is checked to find out if an infection is caused by a type of HPV that is linked to cervical cancer.
What is the procedure called when the cervix is cut?
If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a large incision (cut) in the abdomen, the operation is called a total abdominal hysterectomy.
What is the disease of the vagina?
Vaginal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the vagina. Older age and having an HPV infection are risk factors for vaginal cancer. Signs and symptoms of vaginal cancer include pain or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
What is the procedure called to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina?
The cells are viewed under a microscope to find out if they are abnormal. This procedure is also called a Pap smear.
Why was DES given to pregnant women?
In the 1950s, the drug DES was given to some pregnant women to prevent miscarriage (premature birth of a fetus that cannot survive). This is linked to a rare form of vaginal cancer called clear cell adenocarcinoma. The rates of this disease were highest in the mid-1970s, and it is extremely rare now.
What is the treatment for a tumor in the lower third of the vagina?
If the tumor is in the lower third of the vagina, external radiation may be used to treat lymph nodes in the groin or pelvis. Chemotherapy (chemo) with radiation may also be used to treat stage II disease. Giving chemo to shrink the cancer before radical surgery may be helpful.
What type of radiation therapy is used for cancer in the vagina?
For cancers lower down in the vagina, external beam radiation therapy may be used, along with either interstitial or intracavitary radiation therapy. The lymph nodes in the groin and/or pelvis are often treated with external beam radiation therapy.
What is the treatment for stage 2 vaginal squamous cell cancer?
Stage II. The usual treatment is radiation, using both brachytherapy and external beam radiation. Radical surgery (radical vaginectomy or pelvic exenteration) is an option for some women with stage II vaginal squamous cell cancer if it’s small and in the upper vagina. Radiation might be given after surgery. Surgery is also used to treat women who ...
What is the treatment for stage 3 ovarian cancer?
Stage III or IVA. The usual treatment is radiation therapy, often with both brachytherapy and external beam radiation. Chemo might be combined with radiation to help it work better. Surgery is rarely used.
What is the treatment for adenocarcinoma?
Adenocarcinomas: For cancers in the upper part of the vagina, the treatment is surgery -- a radical hysterectomy, partial or radical vaginectomy, and removal of pelvic lymph nodes. This can be followed by reconstructive surgery if needed or desired. Both internal and external radiation therapy may be given as well.
What is it called when cancer comes back?
If a cancer comes back after treatment it's called recurrent cancer. If it comes back in the same place it was the first time, it's called a local recurrence. If it comes back in another part of the body, like the liver or lungs, it's called a distant recurrence.
Is vaginal cancer hard to treat?
Because vaginal cancer is rare, it's has been hard to study it well. There are no "standard" treatments that experts agree on. Most experts agree that treatment in a clinical trial should be considered for any type or stage of vaginal cancer. This way women can get the best treatments available now and may also get the treatments ...
How to treat invasive vaginal cancer?
Treatments for invasive vaginal cancer. Invasive vaginal cancer is treated mainly with radiation therapy and surgery. Chemotherapy given along with radiation might be used to treat advanced disease. Radiation Therapy for Vaginal Cancer. Surgery for Vaginal Cancer.
What are the factors that determine the best treatment for cancer?
Your treatment will depend on the type and stage of your cancer, but other factors might also play a part in choosing the best treatment plan. These could include your age, your overall health, whether you plan to have children, and your personal preferences.
Why are clinical trials important?
Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they're not right for everyone.
What do people with cancer need?
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
What is a radiation oncologist?
A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer. A medical oncologist: a doctor who uses chemotherapy and other medicines to treat cancer. You might have many other specialists on your treatment team as well, including physician assistants (PAs), nurse practitioners (NPs), nurses, psychologists, nutritionists, social workers, ...
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
A gynecologic oncologist: a doctor who specializes in the treatment of cancers of the female reproductive system (including surgery and chemotherapy) A radiation oncologist: a doctor who uses radiation to treat cancer. ...
What are the services offered by the American Cancer Society?
These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help. The American Cancer Society also has programs and services – including rides to treatment, lodging, and more – to help you get through treatment.
How to treat vaginal cancer?
In general, early non-advanced types of cancer and precancerous cells may be treated with laser surgery and topical treatments . Vaginal cancer is staged in three ways, based on how far the tumor has progressed in the vagina, whether it has spread to the lymph nodes, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
What is the most common type of vaginal cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma: The most common type of vaginal cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 70% of all cases. This cancer begins in the cells that line the vagina and occurs near to the cervix. Adenocarcinoma: This type of cancer begins in gland cells in the vagina.
What is the procedure to check for cancer in the vagina?
This can also be done in your doctor’s office. In this procedure, your doctor will use an instrument called a colposcope to examine the cervix and vagina and look for abnormal cells. He or she will also likely take a tissue sample, called a biopsy, to examine your cells for cancer in the laboratory.
What is the most common type of cancer in women over 60?
Vaginal cancer is a type of cancer that affects women. This type of cancer is more common in women over the age of 60. Women who have the human papillomavirus (HPV) are at higher risk of developing vaginal cancer.
What is the rarest form of vaginal cancer?
Clear cell adenocarcinoma is the exception, often affecting younger women who were exposed to DES in their mother’s womb. Melanoma: A more rare form of vaginal cancer, making up about 9% of all cases. Melanoma usually occurs in the outer portion of the vagina.
What are the symptoms of invasive vaginal cancer?
A noticeable mass in the vagina. Painful urination. Constipation. Pelvic pain. Although 8 out of 10 women with invasive vaginal cancer have one or more of these symptoms, most of the time these symptoms are likely to be much less serious than vaginal cancer.
How long do you live with vaginal cancer?
Early stage vaginal cancers can often be successfully treated, and you can go on to a full life. The National Institutes of Health reports an overall 5-year survival rate of 80% to 90% for early stages. Later stage cancers are harder to treat and may require ongoing chemotherapy and other treatment options.
What is the most common type of cancer that starts in the vagina?
Overview. Vaginal cancer is a rare type of cancer that starts in the vagina. It accounts for about 1 percent of female genital cancers, estimates the National Cancer Institute. There are several main types of vaginal cancer , including: Squamous cell. This type of cancer starts in the vaginal lining and develops slowly.
How long does vaginal cancer last?
Overall, the American Cancer Society estimates vaginal cancer has a five-year survival rate of 47 percent. Survival rates differ greatly by stage. For stage 1 cancers, there’s a five-year survival rate of 75 percent. Stage 4 has a survival rate of 15 to 50 percent. Survival rates also depend on how far the cancer has spread ...
What do they do if you have a Pap smear?
They’ll then do a pelvic exam to look for possible causes of your symptoms. They’ll also do a Pap smear to check for any abnormal cells in your vaginal area. If the Pap smear shows any abnormal cells, your doctor will do a colposcopy.
What are the stages of vaginal cancer?
Vaginal cancer stages tell you how far the cancer has spread. There are four main stages, plus one precancerous stage of vaginal cancer: Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN). VAIN is a type of precancer. There are abnormal cells in the vaginal lining, but they’re not growing or spreading yet. VAIN isn’t cancer.
What percentage of vaginal cancer is caused by adenocarcinoma?
It accounts for approximately 75 percent of vaginal cancers, according to the University of Texas. Adenocarcinoma. This type of cancer starts in the vaginal gland cells. It’s most common in women over 50. It’s the second-most common type of vaginal cancer. Melanoma.
What do doctors do if you have cancer?
If the cells are cancerous, your doctor will most likely do an MRI, CT scan, or PET scan to see if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
What is the survival rate of stage 4 cancer?
Stage 4 has a survival rate of 15 to 50 percent . Survival rates also depend on how far the cancer has spread and where it has spread to. Certain factors can affect survival rate, too. For example, women over 60 have lower survival rates.
What is the treatment for cancerous vagina?
Generally, there are three kinds of treatment available for patients with cancerous or precancerous conditions of the vagina: Radiation therapy: the use of X-rays, gamma rays and charged particles to fight cancer. Chemotherapy (topical): the use of anticancer drugs to treat cancerous cells.
What is the most common type of cancer in the vagina?
There are several types of cancer of the vagina. The two most common are: Squamous cell cancer (squamous carcinoma): Squamous carcinoma is most often found in women older than 60 and accounts for about 70 percent of all vaginal cancers. Adenocarcinoma:
What are the risk factors for vaginal cancer?
Risk factors that may increase a woman’s chances of developing vaginal cancer include age, prior diagnosis of HPV and exposure to diethylstilbestrol as a fetus. When found early, treatment for vaginal cancer is typically very successful.
What is a gynecologic oncologist?
Gynecologic oncologists are subspecialists with advanced training in the diagnosis, treatment and surveillance of female cancers, including vaginal cancer. [ [gynoncsurgery]]
What are the different types of cancers that can be found in the vagina?
Other Types of Vaginal Cancer. Other, less common types of cancer that can be found in the vagina include: Malignant melanoma. Leiomyosarcoma. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers that begin in other organs, such as the cervix and rectum, and spread to the vagina.
What is the most common cancer in women over 50?
Adenocarcinoma is more often found in women older than 50 and accounts for about 15 percent of all vaginal cancers. A rare form of cancer called clear-cell adenocarcinoma results from the use of the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) given to pregnant women between 1940 and 1971 to keep them from miscarrying.
How many women get vaginal cancer each year?
In the U.S., close to 3,000 women are diagnosed with vaginal cancer each year. There is no screening test for vaginal cancer. The HPV vaccine can prevent the strains of HPV responsible for most cervical, vaginal and vulvar cancers. Risk factors that may increase a woman’s chances of developing vaginal cancer include age, ...
What are the treatments for vulvar cancer?
Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
How to treat stage III vulvar cancer?
Treatment of stage III vulvar cancer may include the following: Surgery ( modified radical vulvectomy or radical vulvectomy with removal of lymph nodes in the groin and upper thigh) with or without radiation therapy. Radiation therapy or chemotherapy and radiation therapy followed by surgery.
What is vulvar cancer?
Vulvar cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the vulva. Having vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia or HPV infection can increase the risk of vulvar cancer. Signs of vulvar cancer include bleeding or itching in the vulvar area.
Where does vulvar cancer grow?
Vulvar cancer usually forms slowly over many years. Abnormal cells can grow on the surface of the vulvar skin for a long time.
How does chemo work?
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle , the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). Topical chemotherapy for vulvar cancer may be applied to the skin in a cream or lotion. The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
What is HPV test?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) test: A laboratory test used to check DNA or RNA for certain types of HPV infection. Cells are collected from the vulva and DNA or RNA from the cells is checked to find out if an infection is caused by a type of human papillomavirus that is linked to vulvar cancer.
What is it called when cancer spreads to another part of the body?
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis . Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.

Diagnosis
- Screening for vaginal cancer
Vaginal cancer is sometimes found during a routine pelvic exam before signs and symptoms become evident. During a pelvic exam, your doctor carefully inspects the outer genitals, and then inserts two fingers of one hand into your vagina and simultaneously presses the other hand on y…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- How you respond to your cancer diagnosis is unique. You might want to surround yourself with friends and family, or you may ask for time alone to sort through your feelings. The shock and confusion of your diagnosis may leave you feeling lost and unsure of yourself. To help you cope, try to: 1. Learn enough about your cancer to make decisions about your care.Write down the que…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by making an appointment with your family doctor or a gynecologist if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If it's determined that you have vaginal cancer, you'll likely be referred to a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system (gynecologic oncologist). Because appointments can be brief and there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to …