What are the pros and cons of ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure that deliberately applies electric current to the brain, through the scalp, to cause a short seizure. It is used to treat people with severe mental illnesses, like depression, that did not respond to other treatments.
What is the success rate of ECT therapy?
Feb 28, 2022 · Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT, is a medical treatment that involves electrically stimulating the brain with electrodes to prompt a general seizure. This impacts the neurochemicals of the brain. It has been found to be a safe and effective treatment for treatment-resistant depression and bipolar disorder, as well as other mental health disorders not …
What is the maximum number of ECT treatments?
Aug 31, 2017 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a time tested treatment modality for the management of various psychiatric disorders. There have been a lot of modifications in the techniques of delivering ECT over decades. Despite lots of criticisms encountered, ECT has still been used commonly in clinical practice due to its safety and efficacy.
What disorders is ECT used to treat?
Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure). The aim of the treatment is to relieve the …

What mental illness does ECT treat?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
Is electric shock therapy painful?
Freeman and R. E. Kendell of the University of Edinburgh found that 68 percent reported that the experience was no more upsetting than a visit to the dentist. For the others, ECT was more unpleasant than dentistry, but it was not painful. Still, the treatment is not hazard-free.
How long do the effects of ECT last?
There is considerable variability in the trajectories, but most commonly there is progressive symptomatic improvement within the first week and complete remission within 3 to 4 weeks.May 11, 2010
Why would someone get an ECT?
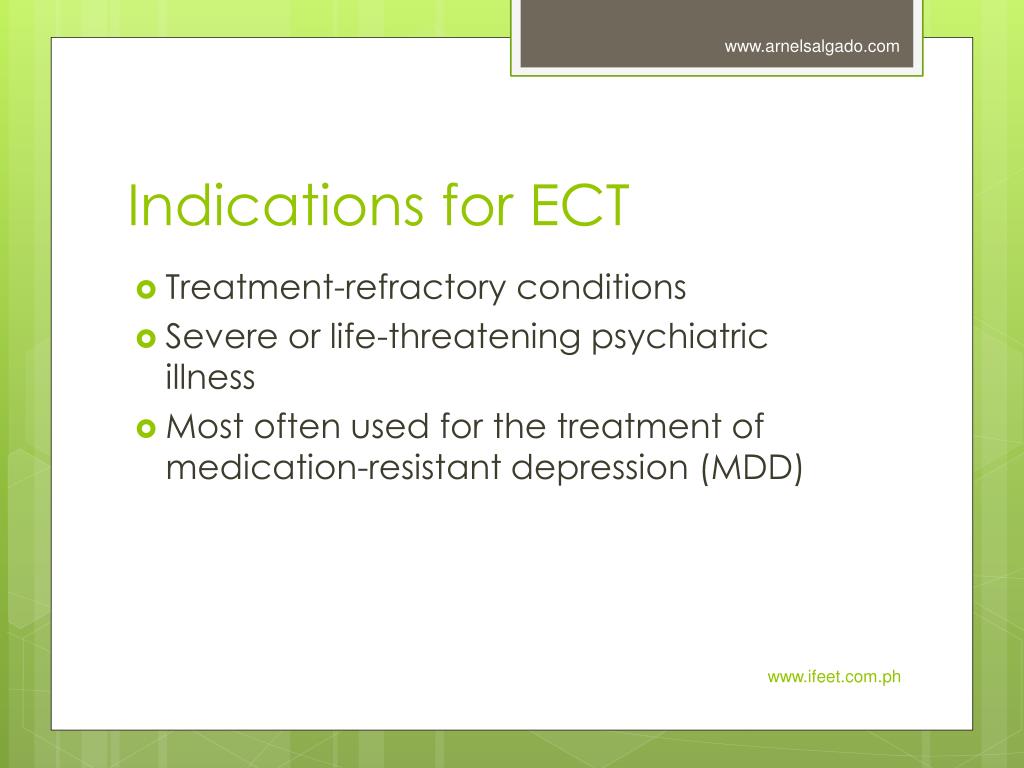
Why it's done ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments.Oct 12, 2018
Does ECT damage the brain?
Despite many scientific and governmental authorities having concluded that ECT does not cause brain damage, there is significant evidence that ECT has indeed caused brain damage in some patients, both historically and recently, and evidence that it always causes some form or degree of brain damage.
Do they shave your head for ECT?
During surgery prep, you'll have your head shaved. You may be kept unconscious throughout brain surgery with general anesthesia or stay awake with a local anesthetic used on your scalp. A sturdy frame will hold your head to prevent movement during surgery.Feb 21, 2021
Does ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
Can ECT make you worse?
ECT may have a role in people who have comorbid depression and anxiety. The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.Mar 22, 2020
Does ECT cause weight gain?
During ECT, all patients increased their caloric intake (280 +/- 180 to 1,510 +/- 60 kcal/day, mean +/- SEM) to exceed their basal energy expenditure; major improvements in their depressive symptoms and weight gain were seen in five of the six patients.
Who qualifies for ECT?
Who can get ECT in California? Any adult age 18 or older with an appropriate clinical diagnosis and who is capable of giving voluntary informed consent can receive ECT.
Does ECT wear off?
The duration of improvement (how long recovery lasts). The benefits of ECT may last for years or they may disappear in a matter of weeks. After a series of ECT treatments, your doctor may prescribe medication to help prevent symptomsfrom returning.
What is the success rate of ECT?
What is the Success Rate of Electroconvulsive Therapy? ECT is an effective medical treatment option, helping as many as 80-85 percent of patients who receive it. Most patients remain well for many months afterwards.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
What is consent process?
In situations where a person is too ill to make decisions for him or herself, the consent process is governed by state law (for example, a court-appointed guardian). Patients and their families should discuss all options for treatment with the psychiatrist before making a specific treatment decision.
How long does a seizure last after ECT?
This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery. Most insurance plans offering coverage for psychiatric disorders at least partially reimburse the cost of ECT.
How often is TMS given?
TMS is usually administered four or five times a week for four-to-six weeks. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) was developed as a treatment for seizure disorders but can also be used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies.
Is ECT a cure for mental illness?
Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, it is not a cure. To prevent a return of the illness, most people treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is TMS in medical terms?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat people who have severe or prolonged mania; NICE recommends it only in life-threatening situations or when other treatments have failed and as a second-line treatment for bipolar mania.
Who performs ECT?
In the US, the medical team performing the procedure typically consists of a psychiatrist, an anesthetist, an ECT treatment nurse or qualified assistant, and one or more recovery nurses. Medical trainees may assist, but only under the direct supervision of credentialed attending physicians and staff.
How many ECT machines are there in China?
As of 2012, there are approximately 400 ECT machines in China, and 150,000 ECT treatments are performed each year. Chinese national practice guidelines recommend ECT for the treatment of schizophrenia, depressive disorders, and bipolar disorder and in the Chinese literature, ECT is an effective treatment for schizophrenia and mood disorders. Although the Chinese government stopped classifying homosexuality as an illness in 2001, electroconvulsive therapy is still used by some establishments as a form of " conversion therapy ".
When did ECT become popular?
ECT became popular in the US in the 1940s. At the time, psychiatric hospitals were overrun with patients whom doctors were desperate to treat and cure. Whereas lobotomies would reduce a patient to a more manageable submissive state, ECT helped to improve mood in those with severe depression. A survey of psychiatric practice in the late 1980s found that an estimated 100,000 people received ECT annually, with wide variation between metropolitan statistical areas. Accurate statistics about the frequency, context and circumstances of ECT in the US are difficult to obtain because only a few states have reporting laws that require the treating facility to supply state authorities with this information. In 13 of the 50 states, the practice of ECT is regulated by law. In the mid-1990s in Texas, ECT was used in about one third of psychiatric facilities and given to about 1,650 people annually. Usage of ECT has since declined slightly; in 2000–01 ECT was given to about 1500 people aged from 16 to 97 (in Texas it is illegal to give ECT to anyone under sixteen). ECT is more commonly used in private psychiatric hospitals than in public hospitals, and minority patients are underrepresented in the ECT statistics. In the United States, ECT is usually given three times a week; in the United Kingdom, it is usually given twice a week. Occasionally it is given on a daily basis. A course usually consists of 6–12 treatments, but may be more or fewer. Following a course of ECT some patients may be given continuation or maintenance ECT with further treatments at weekly, fortnightly or monthly intervals. A few psychiatrists in the US use multiple-monitored ECT (MMECT), where patients receive more than one treatment per anesthetic. Electroconvulsive therapy is not a required subject in US medical schools and not a required skill in psychiatric residency training. Privileging for ECT practice at institutions is a local option: no national certification standards are established, and no ECT-specific continuing training experiences are required of ECT practitioners.
Is electroconvulsive therapy fiction?
Electroconvulsive therapy has been depicted in fiction, including fictional works partly based on true experiences. These include Sylvia Plath 's autobiographical novel, The Bell Jar, Ken Loach's film Family Life, and Ken Kesey 's novel One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest; Kesey's novel is a direct product of his time working the graveyard shift as an orderly at a mental health facility in Menlo Park, California.
How long does it take for a person to relapse from ECT?
There is little agreement on the most appropriate follow-up to ECT for people with major depressive disorder. When ECT is followed by treatment with antidepressants, about 50% of people relapsed by 12 months following successful initial treatment with ECT, with about 37% relapsing within the first 6 months.
When was the ECT procedure first used?
The ECT procedure was first conducted in 1938 by Italian psychiatrist Ugo Cerletti and rapidly replaced less safe and effective forms of biological treatments in use at the time. ECT is often used with informed consent as a safe and effective intervention for major depressive disorder, mania, and catatonia.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure that deliberately applies electric current to the brain, through the scalp, to cause a short seizure. It is used to treat people with severe mental illnesses, like depression, that did not respond to other treatments. Appointments 866.588.2264. Appointments & Locations.
When to use ECT?
ECT is generally used as a later treatment option when severe depression is unresponsive to other forms of therapy, or when the patient is so ill that his or her life is in danger. It also is used when these patients pose a severe threat to themselves or others, and it is dangerous to wait until medications take effect.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) used? ECT is one of the fastest ways to relieve symptoms in severely depressed or suicidal patients, in patients who suffer from mania, and in other mental illnesses.
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure in which a brief application of electric current to the brain, through the scalp, induces a seizure. It is typically used to treat a patient who is suffering from severe depression. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Is ECT a quick fix?
There also is a misconception that ECT is used as a "quick fix" instead of long-term therapy or hospitalization. Unfavorable news reports and media coverage have added to the controversy of this treatment. In fact, ECT is safe and among the most effective treatments available for depression.
What is the effect of ECT on the brain?
ECT causes the patient to have a seizure. Electrodes are placed on the patient’s scalp and a finely controlled electric current is applied, which causes a brief seizure in the brain. Because the muscles are relaxed, the seizure will usually be limited to slight movement of the hands and feet. Patients are carefully monitored during the treatment.
How long does it take for short term memory loss to go away?
Short-term memory loss is the major side effect, although this usually goes away 1 to 2 weeks after treatment. You should be educated and informed about ECT and any treatment prior to receiving it. Ask for educational literature, videos, and an honest discussion with your doctor about the potential benefits and side effects.
What is ECT therapy?
What is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy, or ECT for short, is a treatment that involves sending an electric current through your brain, causing a brief surge of electrical activity within your brain (also known as a seizure).
Why is ECT used?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment.
What are the benefits of ECT?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends that ECT is only used to achieve quick, short-term improvements if you have: 1 severe or life-threatening depression and your life is at risk so you need urgent treatment 2 moderate to severe depression and other treatments such as medication and talking therapies haven't helped you 3 catatonia (staying frozen in one position, or making very repetitive or restless movements) 4 a severe or long-lasting episode of mania.
Can ECT cause memory loss?
This has sometimes been shown in films and TV shows, which may not reflect how ECT is carried out today. It can sometimes cause memory loss. This is often short-term, but can be longer-lasting as well. See our page on the side effects of ECT for more information.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
ECT works much faster than medications. On average, ECT takes two tothree weeks to take effect. By contrast, medications usually take six to eightweeks for improvements to become apparent.
What is consent before ECT?
Before the first ECT treatment, a patient will have a thorough psychiatricevaluation as well as a complete physical exam. The patient must also signinformed consent documents authorizing the use of ECT. “Consent” meansthat you understand the procedure as well as its risks and benefits. (See pages33–35 to review the informed consent forms we use at Johns Hopkins.)
Who is Irving Reti?
Irving M. Reti, M.B.B.S., is the director of the Electroconvulsive Therapy Service at TheJohns Hopkins Hospital and an assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry andBehavioral Sciences at The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. He has receivednumerous honors in his distinguished career, including The Johns Hopkins UniversitySchool of Medicine Clinician Scientist Award, and his research work is funded by theNational Institutes of Health. His research papers have been published in such medicaljournals asNeuropsychopharmacology, the Journal of Neurochemistry, and theEuropean Journal of Neuroscience.
What is HRQOL in medical terms?
Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is a measure of a person’s perceivedphysical and mental health over time. People with major depression sufferfrom poorer HRQOL than people with hypertension, arthritis, angina, orother common medical conditions. Not surprisingly, HRQOL is especiallycompromised in severely depressed patients who are referred for ECT.
How long does it take for a patient to wake up after a syringe?
Patients awaken three to five minutes after the treatment is over. For any-where from five to 45 minutes, patients may experience a period of acute post-treatment delirium. They are typically very confused, and some experienceheadache, muscle stiffness, and disorientation.
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
How long does an ECT last?
A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
The immediate side effects of the procedure which may last for about an hour include: 1 Headaches 2 Nausea 3 Muscle aches and soreness 4 Disorientation and confusion
Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to e…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…
Overview
Medical use
Effects
- Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, it is not a cure. To prevent a return of the illness, most people treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
Procedure
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders. Typically, 70 to 120 volts are applied externally to the patient's head, resulting in approximately 800 milliamperes of direct current passing through the brain, for a duration of 100 millisecondsto 6 seconds, eith…
Mechanism of action
ECT is used, where possible, with informed consent in treatment-resistant major depressive disorder, treatment-resistant catatonia, prolonged or severe mania, and in conditions where "there is a need for rapid, definitive response because of the severity of a psychiatric or medical condition (e.g., when illness is characterized by stupor, marked psychomotor retardation, depressive delusions or hallucinations, or life-threatening physical exhaustion associated with m…
Use
Aside from effects in the brain, the general physical risks of ECT are similar to those of brief general anesthesia; the US Surgeon General's report says that there are "no absolute health contraindications" to its use. Immediately following treatment, the most common adverse effects are confusion and memory loss. Some patients experience muscle sorenessafter ECT. A meta-analysis from 2017 found that the death rate of ECT is around 2.1 per 100,000 procedures. Ther…
History
The placement of electrodes, as well as the dose and duration of the stimulation is determined on a per-patient basis.
In unilateral ECT, both electrodes are placed on the same side of the patient's head. Unilateral ECT may be used first to minimize side effects such as memory loss.
Society and culture
Despite decades of research, the exact mechanism of action of ECT remains elusive. Neuroimaging studies in people who have had ECT, investigating differences between responders and nonresponders, and people who relapse, find that responders have anticonvulsant effects mostly in the frontal lobes, which corresponds to immediate responses, and neurotrophic effects primarily in the medial temporal lobe. The anticonvulsant effects are decreased blood flow and d…