Which treatments are used as adjuvant therapies?
- Chemotherapy. . Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
- Hormone therapy. . For cancers sensitive to hormones, certain treatments can stop hormone production in your body or...
- Radiation therapy. . Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill cancer cells.
What is adjuvant therapy for colon cancer?
Gastric cancer confers a poor prognosis even when diagnosed as localized disease. Multimodality therapy improves the cure rate of patients with localized cancer. However, adjunctive therapeutic approaches differ in different regions of the world. This review focuses on the current standards and unre …
What is adjuvant chemotherapy and when is it recommended?
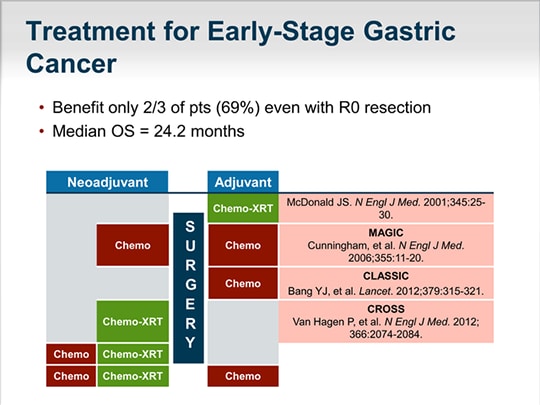
5 fluororuraci, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, docetaxel. MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL MAGIC TRIAL. ECF, epirubicin 50mg/m2, cisplatin 60mg/m2and continuous 5-fluorouracil 200mg/m2/d. Eligibility criteria. Stage ≥ II gastric, gastroesophageal junction, or lower oesophageal adenocarcinoma (after 1999) No metastases ECOG 0-1.
Is adjuvant therapy right for You?
Dec 03, 2019 · Purpose:The benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) for localized gastric cancer (GC) after D2-gastrectomy has been clearly demonstrated. However, adjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) remains controversial. This study aimed to assess the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of treatment for GC after D2-gastrectomy.
Does adjuvant chemotherapy improve outcomes after a D2 gastrectomy?
Sep 12, 2021 · Adjuvant Therapy Treatments Adjuvant Chemotherapy. The most often used adjuvant therapy is chemotherapy delivered before or after surgery to shrink... Immunotherapy. Immunotherapies are drugs that specifically prime the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. The... Hormone Therapy. Hormone ...

What is adjuvant treatment in cancer?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-joo-vunt THAYR-uh-pee) Additional cancer treatment given after the primary treatment to lower the risk that the cancer will come back. Adjuvant therapy may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, or biological therapy.
What is the difference between chemotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy?
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is delivered before surgery with the goal of shrinking a tumor or stopping the spread of cancer to make surgery less invasive and more effective. Adjuvant chemotherapy is administered after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells with the goal of reducing the chances of recurrence.
What drugs are used for adjuvant therapy?
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine: Used in adjuvant treatment of patient with HER2-positive early breast cancer who have residual invasive disease after neoadjuvant taxane- and trastuzumab-based treatment. Trastuzumab: Used in the adjuvant treatment in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.Jul 16, 2020
What is adjuvant surgery?
What is adjuvant therapy? Adjuvant therapy is often used after primary treatments, such as surgery, to lessen the chance of your cancer coming back. Even if your surgery was successful at removing all visible cancer, microscopic bits of cancer sometimes remain and are undetectable with current methods.
What does adjuvant mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of adjuvant (Entry 1 of 2) 1 : serving to aid or contribute. 2 : assisting in the prevention, amelioration, or cure of disease adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery.
Is adjuvant therapy effective?
H&O How effective is adjuvant therapy at preventing recurrence? AS Adjuvant therapy decreases the risk for recurrence by approximately one-third. So, if the 3-year recurrence rate in patients with stage III disease is 40% without adjuvant treatment, chemotherapy will reduce that to approximately 25% to 30%.Nov 17, 2019
Is adjuvant therapy chemotherapy?
Adjuvant chemotherapy is chemo that you get after your primary treatment, such as surgery or radiation.Mar 10, 2021
What is the difference between adjuvant and metastatic?
“Given the higher stakes of adjuvant therapy, this difference is logical: as opposed to the largely noncurative intent for most metastatic cancer treatments, adjuvant treatment is aimed at increasing the fraction of patients cured of their disease,” the authors wrote.Apr 25, 2020
How long is adjuvant chemotherapy?
Adjuvant chemotherapy (therapy after surgery has removed all visible cancer) may last 4-6 months. Adjuvant chemotherapy is common in cancers of the breast and colon. In cancers of the testis, Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and leukemias, length of chemotherapy treatment may be up to a year.
How do adjuvants work?
Adjuvants may act by a combination of various mechanisms including formation of depot, induction of cytokines and chemokines, recruitment of immune cells, enhancement of antigen uptake and presentation, and promoting antigen transport to draining lymph nodes.
What is neoadjuvant therapy?
Neoadjuvant therapy is used to select a subset of patients from the latter group for whom surgical resection is most appropriate. Many of the aforementioned advantages of neoadjuvant therapy in general are applicable to the treatment of GC.
Is gastric cancer curative?
Although surgical resection remains the only potentially curative treatment for gastric cancer (GC), poor long-term outcomes with resection alone compel a multimodality approach to this disease. Multimodality strategies vary widely; while adjuvant approaches are typically favored in Asia and the United States (USA), ...
What is adjuvant therapy?
Adjuvant therapy is often used after primary treatments, such as surgery, to lessen the chance of your cancer coming back. Even if your surgery was successful at removing all visible cancer, microscopic bits of cancer sometimes remain and are undetectable with current methods. Adjuvant therapy given before the main treatment is called neoadjuvant ...
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Chemotherapy . Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Hormone therapy. For cancers sensitive to hormones, certain treatments can stop hormone production in your body or block the effect of hormones. Radiation therapy.
How does immunotherapy work?
Immunotherapy works with your body's immune system to fight off any remaining cancer cells by stimulating your body's own defenses or supplementing them. Targeted therapy. Targeted therapy is designed to alter specific abnormalities present within cancer cells.
Is hormonal therapy effective for cancer?
Hormone therapy won't be effective if your tumor is not hormonally sensitive. Other cancer-specific changes. Certain cancers may have specific changes within their cells that indicate the likelihood that your cancer will return, making adjuvant therapy more likely to be beneficial. If tests show your cancer is unlikely to recur, ...
What is targeted therapy for breast cancer?
For example, a targeted therapy is available to block the action of a protein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in women with breast cancer.
Can cancer spread after surgery?
If the cancer is at a very early stage — before it has had time to spread — then the chance of cancer recurring after surgery may be very small . Adjuvant therapy may offer little benefit in this case. But if a cancer is at a later stage or it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, adjuvant therapy may be more beneficial.
What is the treatment for stage IV gastric cancer?
Standard treatment options for stage IV, inoperable, and recurrent gastric cancer, including medically or surgically unresectable patients, include a combination of cytotoxic therapies, targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and palliative locoregional therapies.
What is the prognosis of gastric cancer?
The prognosis of patients with gastric cancer is related to tumor extent and includes both nodal involvement and direct tumor extension beyond the gastric wall. [ 8, 9] Tumor grade may also provide some prognostic information. [ 10 ]
What is diffuse adenocarcinoma?
Diffuse adenocarcinomas are undifferentiated or poorly differentiated, and they lack a gland formation. Clinically, diffuse adenocarcinomas can give rise to infiltration of the gastric wall (i.e., linitis plastica). Some tumors can have mixed features of intestinal and diffuse types.
Is PDQ cancer information updated?
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
What is a T4 tumor?
If there is perforation of the visceral peritoneum covering the gastric ligaments or the omentum, the tumor should be classified T4. c The adjacent structures of the stomach include the spleen, transverse colon, liver, diaphragm, pancreas, abdominal wall, adrenal gland, kidney, small intestine, and retroperitoneum.
Is PDQ a registered trademark?
PDQ is a registered trademark. Although the content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text, it cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless it is presented in its entirety and is regularly updated. However, an author would be permitted to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks succinctly: [include excerpt from the summary].”
What is stage 0 in cancer?
Stage 0 is gastric cancer confined to mucosa. Experience in Japan, where stage 0 is diagnosed frequently, indicates that more than 90% of patients treated by gastrectomy with lymphadenectomy will survive beyond 5 years. An American series has confirmed these results. [ 1]
What is adjuvant treatment?
In addition to chemotherapy, adjuvant treatments can include: Hormone therapy is often used for hormone receptor positive cancers. Immunotherapy may be used to help your immune system recognize and fight cancer cells. Radiation therapy can help target a particular tumor or organ.
What is neoadjuvant chemotherapy?
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy means that chemo takes place before the main treatment. The goal is to improve the likelihood that the main treatment, usually surgery or radiation therapy, will be successful. As with adjuvant chemotherapy, there are many factors involved in choosing the timing of neoadjuvant chemo.
Can chemo kill cancer cells?
It’s also important to know that chemo drugs can destroy healthy cells too because traditional chemotherapy does not specifically only target cancer cells.
Is chemo a neoadjuvant?
As with adjuvant chemotherapy, there are many factors involved in choosing the timing of neoadjuvant chemo. Your doctor might recommend neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the following situations: The primary tumor is large or pressing on vital organs, which can make surgery complicated and risky. Chemo may be able to shrink the tumor first so it’s less ...
Can cancer cells be left behind after surgery?
Sometimes cancer cells can be left behind after surgery. It’s also possible that cancer cells may be circulating in your bloodstream or lymphatic system. The traveling cancer cells don’t show up on imaging tests. Without treatment, they can find their way to distant organs to form new tumors.
Can you get chemo for stage 2 colon cancer?
But not all people with stage 2 colon cancer get the same benefit. In stage 2 colon cancer, the use of adjuvant chemo may depend on certain biomarkers. All these factors must be considered when deciding if adjuvant chemo is likely to be beneficial.
Can chemo shrink a tumor?
Chemo may be able to shrink the tumor first so it’s less risky to remove. There’s a chance that cancer cells have broken away from the primary tumor. Any complications from surgery can delay the start of adjuvant chemo. Starting with chemo can prevent tumors from developing in distant organs.
