Medication
Treatment - Addison's disease
- Medicine for Addison's disease. Treatment usually involves corticosteroid (steroid) replacement therapy for life. ...
- Living with Addison's disease. ...
- Adjusting your medicine. ...
- Emergency treatment. ...
- Treating adrenal crisis. ...
- Free prescriptions. ...
- Support. ...
Therapy
People who have Addison's disease may experience the following symptoms: weakness in the muscles. fatigue and tiredness. darkening in skin color. weight loss or decreased appetite. a decrease in heart rate or blood pressure. low blood sugar levels.
Nutrition
Typically, recovery will take somewhere between 6 and 18 months, but there is a very wide variation between patients. Some may take less than 6 months, but others may take two years before they can really claim to have returned to normal. It depends on the severity of the Adrenal Fatigue…
How to treat Addison disease?
If left untreated, an Addisonian crisis can lead to complications such as:
- Cardiac arrhythmias from multiple electrolyte abnormalities
- Cardiac arrest
- Hypotension can lead to orthostatic hypotension and syncope, with progression to a shock state with hypoperfusion to the organs causing sequelae such as elevated transaminitis (shock liver), bradycardia, and myocardial ...
- Hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic coma
What is it like living with Addison's disease?
Does adrenal insufficiency go away?
What happens during an Addisonian crisis?
See more

What is the most common cause of Addison disease?
Tuberculosis (TB) is the most common cause of Addison's disease worldwide, but it's rare in the UK. TB is a bacterial infection that mostly affects the lungs but can also spread to other parts of your body. It can cause Addison's disease if it damages your adrenal glands.
What were your first symptoms of Addison's disease?
Initial symptoms of Addison's disease can include:fatigue (lack of energy or motivation)lethargy (abnormal drowsiness or tiredness)muscle weakness.low mood (mild depression) or irritability.loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss.the need to urinate frequently.increased thirst.craving for salty foods.
Can Addison disease be cured?
Addison's disease cannot be cured, but replacement hormones can treat the adrenal failure symptoms. Addison's disease (primary adrenal insufficiency) is a condition that occurs when the body's adrenal glands do not work normally.
How serious is Addison disease?
People with Addison's disease must be constantly aware of the risk of a sudden worsening of symptoms, called an adrenal crisis. This can happen when the levels of cortisol in your body fall significantly. An adrenal crisis is a medical emergency. If left untreated, it can be fatal.
What is the life expectancy of a person with Addison's disease?
A study held in 2009 states that the average life expectancy of women with Addison disease is 75.7 years and men with Addison disease is 64.8 years, which is 3.2 and 11.2 years less than the respective life expectancy in otherwise normal women and men.
What foods to avoid if you have Addison's disease?
Foods to avoid if you have Addison's diseaseCoffee.Green tea.Black tea.Too much alcohol.Too many bananas.Too many oranges.Salt substitutes.
What organs are affected by Addison's disease?
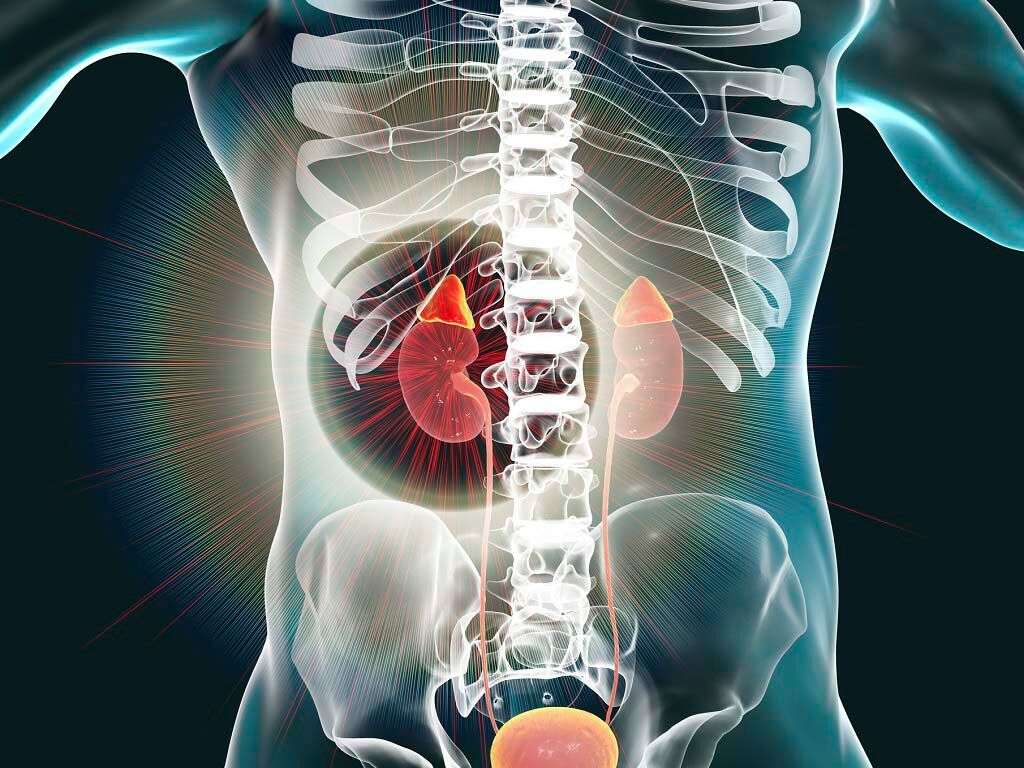
Description. Autoimmune Addison disease affects the function of the adrenal glands, which are small hormone-producing glands located on top of each kidney. It is classified as an autoimmune disorder because it results from a malfunctioning immune system that attacks the adrenal glands.
Is Addison's disease painful?
During an addisonian crisis, affected individuals may develop a sudden loss of strength; severe pain in the lower back, abdomen or legs; vomiting and diarrhea potentially causing dehydration; and low blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
Who is at risk for Addison's disease?
Women are more likely than men to develop Addison's disease. This condition occurs most often in people between the ages of 30 and 50, 2 although it can occur at any age, even in children. Secondary adrenal insufficiency occurs in people with certain conditions that affect the pituitary.
Does Addison's disease affect the brain?
Regardless of the specific terminology used, it is clear that some patients with Addison's disease have a disturbance in brain function and may develop a range of neuropsychiatric symptoms as a result.
What are the long term effects of Addison's disease?
Long-lasting fatigue is a common symptom of adrenal insufficiency. People with Addison's disease may also have darkening of their skin. This darkening is most visible on scars; skin folds; pressure points such as the elbows, knees, knuckles, and toes; lips; and mucous membranes such as the lining of the cheek.
How do you get diagnosed with Addison's disease?
Blood tests A low sodium, high potassium or low cortisol level may indicate Addison's disease. You may need to see a hospital hormone specialist (endocrinologist) for your blood to be tested for the following: a low level of the hormone aldosterone. a high level of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
What tests are done to test for Addison's disease?
Dark patches on your skin might be a clue for your doctor to consider testing for Addison’s disease. Blood tests: These will be done to measure the levels of sodium, potassium, cortisol and ACTH in your blood. ACTH stimulation test: This tests the adrenal glands’ response after you are given a shot of artificial ACTH.
How many people have Addison's disease?
In the United States, Addison’s disease affects 1 in 100,000 people. It occurs in both men and women equally and in all age groups, but is most common in the 30-50 year-old age range.
What is the name of the disorder in which the adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys?
What is Addison's disease ? Addison’s disease is a disorder in which the adrenal glands – which sit on top of the kidneys – do not produce enough of the hormones cortisol and aldosterone. (Hormones are chemicals that control the function of tissues or organs.) Cortisol helps the body respond to stress, including the stress of illness, injury, ...
What is the term for an acute adrenal insufficiency?
In some cases – such as an injury, illness, or time of intense stress – symptoms can come on quickly and cause a serious event called an Addisonian crisis, or acute adrenal insufficiency. An Addisonian crisis is a medical emergency. If it is not treated, it can lead to shock and death. Symptoms of an Addisonian crisis include:
What is the name of the disorder that affects the amount of fluid the kidneys remove as urine?
This in turn controls the amount of fluid the kidneys remove as urine, which affects blood volume and blood pressure. Addison’s disease is also called “primary adrenal insufficiency.”. A related disorder, “secondary adrenal insufficiency,” occurs when the pituitary, a small gland at the base of the brain, does not secrete enough adrenocorticotropic ...
How does cortisol help the body?
Cortisol helps the body respond to stress, including the stress of illness, injury, or surgery. It also helps maintain blood pressure, heart function, the immune system and blood glucose (sugar) levels.
Can you live a normal life with Addison's disease?
People who have Addison’s disease will need to take medicine for the rest of their lives and can live normal healthy lives.
What is the treatment for Addison's disease?
Medically reviewed by Xixi Luo, M.D. — Written by Tim Newman on August 15, 2017. Treatment of Addison’s disease generally involves corticosteroid replacement therapy. The medications are taken for life. The corticosteroid medication, which is usually taken orally (by mouth), replaces the cortisol and aldosterone the body is not producing.
What is the name of the medication that replaces cortisol?
Hydrocortisone – these tablets replace the missing cortisol. Prednisolone or dexamethasone are prescribed less commonly.
What are the side effects of hydrocortisone?
Side effects of hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone: include sleep problems, acne, slow wound healing, dizziness, nausea, and increased sweating. Side effects of DHEA in women: similar to above but may also include changes in menstrual cycle, developing a deeper voice, and facial hair growth.
Does Addison's disease cause cortisol?
Addison’s disease patients do not produce enough cortisol, so when they have an accident or serious injury, medical staff need to know what medication the individual immediately requires (cortisol) to prevent any complications.
Does Addison's disease affect adrenal glands?
Share on Pinterest. Addison’s disease affects the adrenal glands. The drugs required to effectively treat Addison’s depends on the hormones that are no longer being effectively produced in the adrenal glands.
How to reduce stress from Addison's disease?
Talk to your doctor about alternative ways to relieve stress, such as yoga and meditation .
What is an Addisonian crisis?
An Addisonian crisis is a life-threatening medical emergency. Call 911 immediately if you or someone you know begins to experience: mental status changes, such as confusion, fear, or restlessness. loss of consciousness. high fever. sudden pain in the lower back, belly, or legs.
What is the name of the disease where the adrenal glands are damaged?
This type of Addison’s disease is most often caused when your immune system attacks your adrenal glands. This is called an autoimmune disease.
What are the two major classifications of Addison's disease?
There are two major classifications for Addison’s disease: primary adrenal insufficiency and secondary adrenal insufficiency. In order to treat the disease, your doctor will need to find out which type is responsible for your condition.
How do you know if you have Addison's disease?
People who have Addison’s disease may experience the following symptoms: muscle weakness. fatigue and tiredness. darkening in skin color. weight loss or decreased appetite. a decrease in heart rate or blood pressure. low blood sugar levels. fainting spells. sores in the mouth.
Can you develop adrenal insufficiency if you don't take corticosteroid?
It’s also possible to develop adrenal insufficiency if you do not take the corticosteroid medications your doctor prescribes. Corticosteroids help control chronic health conditions like asthma.
Can Addison's disease be untreated?
Untreated Addison’s disease can lead to an Addisonian crisis. If your condition has gone untreated for too long, and has progressed to a life-threatening condition called Addisonian crisis , your physician may prescribe medication to treat that first.
What is the cause of Addison's disease?
Addison's disease is caused by damage to your adrenal glands , resulting in not enough of the hormone cortisol and, often, not enough aldosterone as well. Your adrenal glands are part of your endocrine system. They produce hormones that give instructions to virtually every organ and tissue in your body.
How to avoid an Addison's disease crisis?
Addison's disease can't be prevented, but there are steps you can take to avoid an addisonian crisis: Talk to your doctor if you always feel tired, weak, or are losing weight. Ask about having an adrenal shortage. If you have been diagnosed with Addison's disease, ask your doctor about what to do when you're sick.
What is the function of the adrenal glands?
Perched atop each of your kidneys, your adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure and other essential functions. Addison's disease is caused by damage to your adrenal glands, resulting in not enough of the hormone cortisol and, often, not enough aldosterone as well.
What is it called when your body doesn't produce enough cortisol?
Addison's disease, also called adrenal insufficiency, is an uncommon disorder that occurs when your body doesn't produce enough of certain hormones. In Addison's disease, your adrenal glands, located just above your kidneys, produce too little cortisol and, often, too little aldosterone.
What is the Addisonian crisis?
An addisonian crisis is a life-threatening situation that results in low blood pressure, low blood levels of sugar and high blood levels of potassium. You will need immediate medical care. People with Addison's disease commonly have associated autoimmune diseases.
Why is adrenal cortex damaged?
When the cortex is damaged and doesn't produce enough adrenocortical hormones, the condition is called primary adrenal insufficiency. This is most commonly the result of the body attacking itself (autoimmune disease). For unknown reasons, your immune system views the adrenal cortex as foreign, something to attack and destroy. People with Addison's disease are more likely than others to have another autoimmune disease as well.
How long does it take for Addison's disease to develop?
Addison's disease symptoms usually develop slowly, often over several months. Often, the disease progresses so slowly that symptoms are ignored until a stress, such as illness or injury, occurs and makes symptoms worse. Signs and symptoms may include:
What is the best treatment for Addisonian crisis?
In people who may be having an Addisonian crisis, doctor-prescribed injections of salt, fluids, and glucocorticoid hormones may be given immediately -- even before a diagnosis of Addison's disease is confirmed.
What are the symptoms of Addison's disease?
The doctor will also check for hyperpigmentation, or darkening, of the skinor gums -- a sign of long-term Addison's disease.
How to diagnose Addison's disease?
The most definitive way to diagnose Addison’s is to measure hormone levels in the blood before and after giving ACTH. ACTH is a hormone in the brainthat normally increases cortisol release from the adrenal glands. With Addison's disease, the adrenal glands cannot respond to ACTH stimulation, and cortisol levels remain low. Measuring cortisol and ACTH levels can help determine whether adrenal insufficiency is there, and if so, whether the problem is with the adrenal glands or brain.
Why is Addison's disease considered a medical emergency?
Because symptoms of Addison's disease progress slowly, they may go unrecognized until a physically stressful event, such as another illness, surgery, or an accident, worsens symptoms quickly. When this happens, it's called an Addisonian crisis. For one in four people with Addison's disease, this is the first time they realize they are ill. An Addisonian crisis is considered a medical emergency because it can be fatal.
Is Addison's disease a successful treatment?
Treatment is almost always completely successful. When treated, people with Addison's disease can lead a full, normal life. It is important to carry a medic alert bracelet and emergency ID card at all times. You should also keep a small supply of medicine at work or school. Missing even one dose can be dangerous.
Is Addison's disease a hormonal disorder?
Addison’s disease is a hormonal disorder that is very treatable but may not be diagnosed for years. Find out the symptoms and treatments.
Is Addison's disease a primary adrenal disease?
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, has symptoms that are vague and non-specific. Addison's diseasecan be difficult to diagnose, and it often takes years for a diagnosis to be made. Symptoms of Addison's disease include:
What is Addison's disease?
Addison's disease is a disorder of the adrenal glands where they do not make enough hormones.
How to diagnose Addison's disease?
First, your doctor will review your medical history and go over your symptoms. The next step is blood tests. Your doctor may order such tests as: ACTH stimulation test, which monitors your body’s response to ACTH and is the most common test for diagnosing Addison’s disease.
What is the best cortisol replacement?
Hydrocortisone is the most common corticosteroid for replacing cortisol. If your adrenal glands don’t make enough aldosterone, you may be prescribed fludrocortisone. Your doctor will prescribe a dosage according to your specific needs.
What tests can show up in Addison's disease?
These tests might include: Antibody tests, which tests for antibodies that show up in your system as a result of autoimmune Addison’s disease. Computed tomography (CT) scan, which can show changes to your adrenal glands. Tuberculosis tests.
What happens if you have Addisonian crisis?
One complication that can occur as a result of Addison’s disease is an Addisonian crisis. It happens when the condition goes untreated for too long, generally as a result of physical stress. The crisis can lead to low blood pressure, low blood sugar, and too much potassium in your blood. Without immediate treatment, it could be life-threatening. Treating a crisis involves immediate intravenous corticosteroids as well as a salt and sugar solution.
What are the most common causes of Addison's disease?
Those most at risk for Addison’s disease are those who have autoimmune conditions such as Graves disease, have cancer, experience chronic infections, or underwent procedures that removed parts of the adrenal glands.
What test can be done to determine if you have Addison's disease?
Insulin tolerance test, which can test your pituitary gland’s response to low blood pressure. If your doctor diagnoses you with Addison’s disease, they will run some tests to determine the type of adrenal insufficiency and prescribe you the most effective treatment. These tests might include:
What to do if your adrenal glands aren't making aldosterone?
NIH external link. . If your adrenal glands aren’t making aldosterone, you will take a medicine called fludrocortisone. NIH external link. , which helps balance the amount of sodium and fluids in your body. People with secondary adrenal insufficiency usually make enough aldosterone, so they don’t need to take this medicine.
What is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases?
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
What is the best treatment for anesthesia?
If you’re having surgery that uses general anesthesia, you’ll need treatment with IV corticosteroids and saline.