What is a type II hypersensitivity reaction?
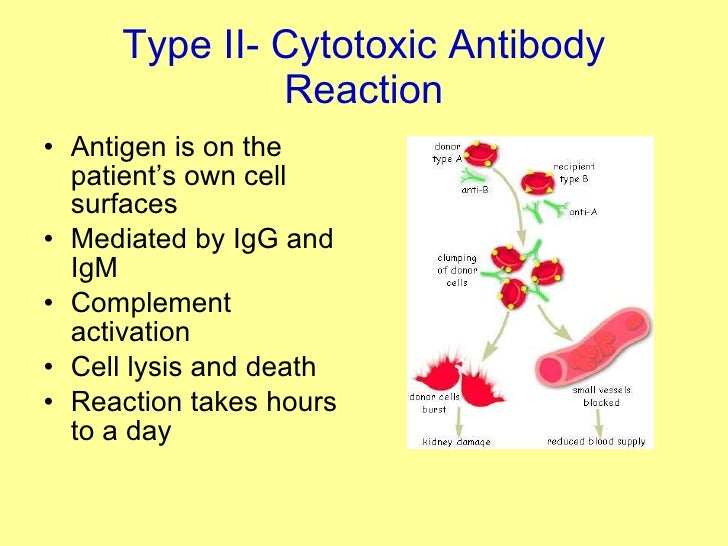
Type II hypersensitivity reaction refers to an antibody-mediated immune reaction in which antibodies (IgG or IgM) are directed against cellular or extracellular matrix antigens with the resultant cellular destruction, functional loss, or damage to tissues. Damage can be accomplished via three different mechanisms:
What are the treatment options for hypersensitivity reactions?
Treatment for anaphylactic symptoms is injection with epinephrine, a potent neurotransmitter and hormone that effectively halts the immune response. IgG blockers are also used to treat type I hypersensitivity. Type II hypersensitivity is also known as cytotoxic hypersensitivity or antibody-mediated hypersensitivity reactions.
How are antihistamines used to treat type 1 hypersensitivity?
Antihistamines are used for the treatment of type I hypersensitivity. These medications block histamine receptors on cell membrane surfaces. Treatment for anaphylactic symptoms is injection with epinephrine, a potent neurotransmitter and hormone that effectively halts the immune response.
What is a nonallergic drug hypersensitivity reaction?
Although hypersensitivity reactions are allergic reactions, some people may experience a non-immune anaphylactic reaction to certain drugs or foods. Some people may call this a nonallergic drug hypersensitivity reaction or refer to it as a pseudoallergic, idiosyncratic, or anaphylactoid reaction.

How is hypersensitivity type 2 treated?
Treatment for type 2 hypersensitivity typically involves immunosuppressants to prevent the action of unusual antibodies. Treatment options may include: systemic glucocorticoids. cyclophosphamide and cyclosporin agents.
What is the treatment for hypersensitivity reaction?
The treatment of immediate hypersensitivity reactions includes the management of anaphylaxis with intramuscular adrenaline (epinephrine), oxygen, intravenous (IV) antihistamine, support blood pressure with IV fluids, avoid latex gloves and equipment in patients who are allergic, and surgical procedures such as ...
What drugs are used to treat immediate hypersensitivity?
Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions MedicationVasopressors.Bronchodilators.Corticosteroids.Histamine 1 receptor antagonists (antihistamines)Histamine 2 receptor antagonists (H2 antagonists)Leukotriene inhibitors.Immunomodulators.Monoclonal Antibodies.More items...•
What happens in type II hypersensitivity?
Type II hypersensitivity reaction is a form of immune-mediated reaction in which antibodies are directed against cellular or extracellular matrix antigens. This antibody-mediated response leads to cellular destruction, functional loss, or damage to tissues.
What is the best medicine for an allergic reaction?
Antihistamines. Antihistamines are the main medicines for allergies. They can be used: as and when you notice the symptoms of an allergic reaction.
How long does it take for an allergic reaction to medicine to go away?
Most people with drug allergy recover very quickly once the medication is stopped, although the rash can take 10-14 days to fade. People with severe reactions may take a long time to get better, especially if they are elderly or have other medical conditions.
Is Benadryl an antihistamine?
Benadryl. The first-generation antihistamine diphenhydramine is the main active ingredient in Benadryl. Benadryl helps relieve runny nose, sneezing, itchy or watery eyes, and nose or throat itching. These symptoms may be due to hay fever, other upper respiratory allergies, or the common cold.
How do you treat an allergic reaction to ibuprofen?
If your allergic reaction to a drug is not life-threatening, your allergist may give you:An antihistamine to counteract the allergic reaction.A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, or a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation.
Which drugs can induce all four types of hypersensitive reactions?
Antibiotics (particularly beta-lactams) and anticonvulsants are the most common triggering drugs, accounting for three-quarters of all cases of hypersensitivity (e7).
How is type 2 hypersensitivity diagnosed?
These reactions can only be diagnosed accurately using the drug provocation test (DPT), since skin tests are not reliable and no biological tests are currently available. However, DPT represents a high-risk method of diagnosis testing, as it can reproduce the type 2 hypersensitivity reaction.
Is type 2 hypersensitivity an autoimmune disease?
Type II hypersensitivity, which is the underlying mechanism of several autoimmune disorders, is usually limited to one type of tissues or organ.
Are autoimmune diseases hypersensitivity?
Hypersensitivity diseases include autoimmune diseases, in which immune responses are directed against self-antigens, and diseases that result from uncontrolled or excessive responses to foreign antigens.
What is type 2 hypersensitivity?
Type II hypersensitivity reaction involves antibody mediated destruction of cells. It is also known as cytotoxic reaction. In this hypersensitivity reaction, specific antibody (IgG or IgM) bound to cell surface antigen and destroy the cell. If the cell is microorganism, killing of cell is beneficial to host. However in Type II hypersensitivity, the ...
Is RBC a type 2 hypersensitivity reaction?
This drug induced hemolytic anemia is an example of Type II hypersensitivity reaction.
What is the treatment for anaphylactic hypersensitivity?
These medications block histamine receptors on cell membrane surfaces. Treatment for anaphylactic symptoms is injection with epinephrine, a potent neurotransmitter and hormone that effectively halts the immune response.
What type of reaction is hypersensitive?
Type I hypersensitive reactions can induce by a special type of antigen refer to as allergens which have all the hallmarks of the normal humoral response. Thus, an allergen induces a humoral antibody response, resulting in a generation of antibody secreting plasma cells and memory cells.
What is the term for a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
In 1890, Robert Koch observed this type of hypersensitivity in tuberculosis as a localized reaction. It is also known as the tuberculin reaction. Later, on the realization that the reaction can be induced in various pathologic conditions, it was renamed as delayed – type hypersensitivity.
What are some examples of atopic reactions?
An example of atopic reactions is bronchial asthma. Atopic hypersensitivity does not transfer through lymphoid cells but it can transfer by serum.
How to avoid DTH?
At present the best way to avoid a DTH response to avoid the causative antigen. After the development of hypersensitivity, topical or oral corticosteroids used to suppress the destructive immune response. 2. Tuberculin-type hypersensitivity reaction. Tuberculin reaction is a typical example of delayed hypersensitivity.
What is a type 1 reaction?
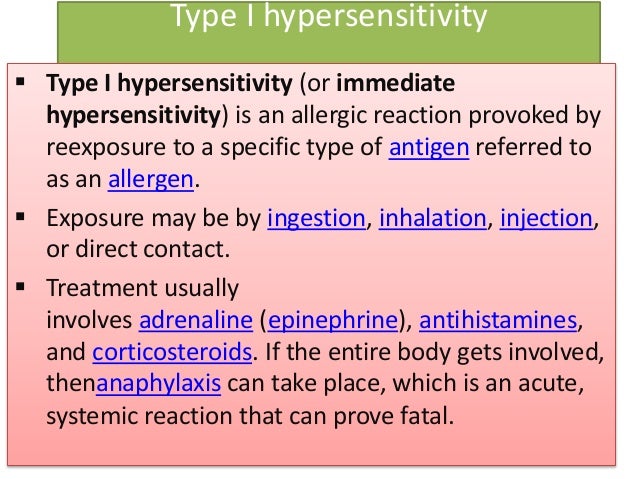
Type I hypersensitivity reaction is commonly called an allergic or immediate hypersensitivity reaction. This reaction is always rapid and can occur within minutes of exposure to an antigen. Type I hypersensitivity reactions are initiated by the interactions between an IgE antibody and a multivalent antigen.
How long does a delayed type reaction last?
you can also call it as delayed-type cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions. It starts hours or days after primary contact with the antigen and often lasts for days. There is a large influx in non-specific inflammatory cells, in particular, macrophages in this reaction. It differs from the other types of hypersensitivity because it mediates through cell-mediated immunity. This reaction occurs due to the activation of specifically sensitized T lymphocytes rather than the antibodies.
What is type 2 hypersensitivity?
Type II hypersensitivity, in the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, is an antibody mediated process in which IgG and IgM antibodies are directed against antigens on cells (such as circulating red blood cells) or extracellular material (such as basement membrane).
What is the purpose of a preformed antibody?
anti-A IgM in an individual with blood group B), bind to the donor red cell surface and lead to rapid complement mediated haemolysis and potentially life-threatening clinical consequences.
What is type II antibody?
Definition. In type II, the target is fixed in tissue or on the cell surface. This is mediated by IgG or IgM binding to the specific cell or tissue. The damage will be limited to the tissue or the cells where this reaction will take place. Antigen: It is present or is a part of the cell membrane.
What temperature do autoantibodies react with?
Warm-reactive autoantibody, these autoantibodies react with antigen at 37 °C. Cold reactive autoantibodies react with antigen below 37 °C and mostly at 4 °C. These antibodies are provoked by the drugs causing an allergic reaction.
What is antibody dependent cellular toxicity?
Antibody-dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC): Sometimes Antibody is attached to Antigen on the cell surface will bring this complex near to NK cells or other phagocytic cells possessing the Fc-Receptor and leads to antibody dependant cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Opsonization and phagocytosis:
What is an antigen?
Antigen: It is present or is a part of the cell membrane. It may be: Exogenous Ag: Microbes, parasites, drugs. Intrinsic Ag: Autoimmune diseases, and these are self-Ag. Antibody: This is mainly due to IgG and occasionally IgM. Rarely IgA can give this reaction.
What type of reaction is good pasteur syndrome?
Kidney: – Type II reaction gives anti-glomerular-basement membrane nephritis (anti-GBM nephritis) and Good Pasteur’s syndrome. There are antibodies against the collagen type IV, which is the major component of the glomeruli’s basement membrane. In 50% of the cases, it binds the complement and is usually IgG.
What drugs destroy platelets?
Platelets: – The platelets are destroyed in ITP (idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura) and drugs like sedormid and quinidine. Autoantibodies to platelets are seen in 70% of the cases of ITP. It is increased removal of platelets from the circulation; this is mediated primarily by the splenic macrophages.
What type of reaction is a type I hypersensitivity reaction?
Type I hypersensitivity reactions can be seen in bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, food allergy, allergic conjunctivitis, and anaphylactic shock.
What is a hypersensitivity reaction?
Hypersensitivity reactions (HR) are immune responses that are exaggerated or inappropriate against an antigen or allergen. Coombs and Gell classified hypersensitivity reactions into four forms.
Which type of antibody mediates anaphylactic response?
Antibodies including IgE, IgM, and IgG mediate them. [1] Type I or Anaphylactic Response. The anaphylactic response is mediated by IgE antibodies that are produced by the immune system in response to environmental proteins (allergens) such as pollens, animal danders, or dust mites.
What is type 1 hypersensitivity?
History and Physical. In type I hypersensitivity reactions, there is a history of atopy or a patient suffering from an allergic condition (e.g., bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, or food allergy). It may be associated with recurrent infections caused by viruses and bacteria.
What is an arthus reaction?
Arthus reaction is a local reaction seen when a small quantity of antigens is injected into the skin repeatedly until detectable levels of antibodies (IgG) are present. If the same antigen is inoculated, immune complexes develop at the mentioned local site and in the endothelium of small vessels.
What is the name of the disorder that causes double vision and weakness in the upper arms?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder caused by antibodies to post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors that interfere with neuromuscular transmission. It is characterized by extreme muscular fatigue, double vision, bilateral ptosis, deconjugate eye movements, difficulty swallowing, and weakness in the upper arms.
Which antibody is used in type III hypersensitivity reactions?
The method that uses fluorescent antibodies has also been used in type III hypersensitivity reactions to demonstrate the presence of immune complexes in the intima and media of the arterial wall, as well as IgG and C3 deposits in kidney, joints, arteries, and skin.