Medication
On the Horizon: More Hope for Treating Huntington’s Disease
- Resveratrol ( 27, 28, 29, 30, 31)
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) ( 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37)
- Vitamin E (26, 37)
- Ethyl-EPA ( 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43)
- Idebenone (26, 44)
- Unsaturated fatty acids ( 45)
Therapy
Treatment
- Medications for movement disorders. Drugs to control movement include tetrabenazine (Xenazine) and deutetrabenazine (Austedo), which have been specifically approved by the Food and Drug Administration to suppress the involuntary jerking ...
- Medications for psychiatric disorders. ...
- Psychotherapy. ...
- Speech therapy. ...
- Physical therapy. ...
- Occupational therapy. ...
Self-care
- Stage I: (0 to 8 years from illness onset)
- Alternate Stage I: Defiance.
- Alternate Stage II: Perseverance.
- Stage III: (5 – 16 years from illness onset)
- Alternate Stage III: Compassion.
See more
Prescriptions
- Chorea. Oral medications used to reduce chorea are taken daily or several times per day. ...
- Mood Changes. Depression is the most common mood symptom associated with Huntington’s disease, although anxiety can occur as well.
- Psychiatric Symptoms
- Complications. ...
Are there any natural treatment for Huntingtons disease?
What types of treatment are there for the Huntingtons disease?
What is the life expectancy of someone with Huntington disease?
How can Huntington disease be treated?

What treatments are used for Huntington's disease?
No treatments can alter the course of Huntington's disease. But medications can lessen some symptoms of movement and psychiatric disorders....Occupational therapyHandrails at home.Assistive devices for activities such as bathing and dressing.Eating and drinking utensils adapted for people with limited fine motor skills.
What is the most common treatment for Huntington's disease?
Xenazine (tetrabenazine) is the only medication specifically approved for Huntington's chorea. Others, such as antipsychotics and benzodiazepines, have also demonstrated a benefit and can be used off-label. Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and prevent falls through tailored exercises for the patient.
Can Huntington's disease be prevented or treated?
Can you prevent Huntington's disease (HD)? HD is caused by having a mutation on the HTT gene. You can't change your genes or prevent the disease from developing. Currently, there isn't a treatment that can slow or stop the progression of HD.
Are there any new treatments for Huntington's disease?
The journal Nature Medicine has identified a phase 3 study of pridopidine as a treatment for Huntington's disease as one of 11 clinical trials that will shape medicine in 2022.
Can gene therapy cure Huntington's disease?
There's currently no cure for Huntington's disease, but there are types of gene therapy approaches that may offer hope for managing or slowing symptoms.
How does physical therapy help Huntington's disease?
What physical therapy can do. Although the exercises recommended for Huntington's patients train different areas of the body, all aim to prevent falls, promote correct walking and body control, build coordination, and encourage a positive and confident attitude toward the body.
Why can't Huntington's disease cured?
The disease is genetic, which means it is inherited from your parents. There is no cure, and it is fatal. People are born with the defective gene that causes the disease. But symptoms usually don't appear until middle age.
Is Huntington's disease painful?
A large worldwide study on the prevalence of pain in Huntington's Disease (HD). The outcomes are pain interference, painful conditions and analgesic use. The prevalence of pain interference increases up to 42% in the middle stage of HD. The prevalence of painful conditions and analgesic use decrease as HD progresses.
What triggers Huntington disease?
Huntington's disease is caused by a faulty gene that results in parts of the brain becoming gradually damaged over time. You're usually only at risk of developing it if one of your parents has or had it. Both men and women can get it.
How close is a cure for Huntington's?
There is no cure, and symptoms on average begin in the mid-40s (it then usually takes around 15 years to kill). Indeed, for more than 100 years after the disease was characterised, those at 50:50 risk of inheriting it had no way of ending the uncertainty until the symptoms started.
What is Huntington's disease?
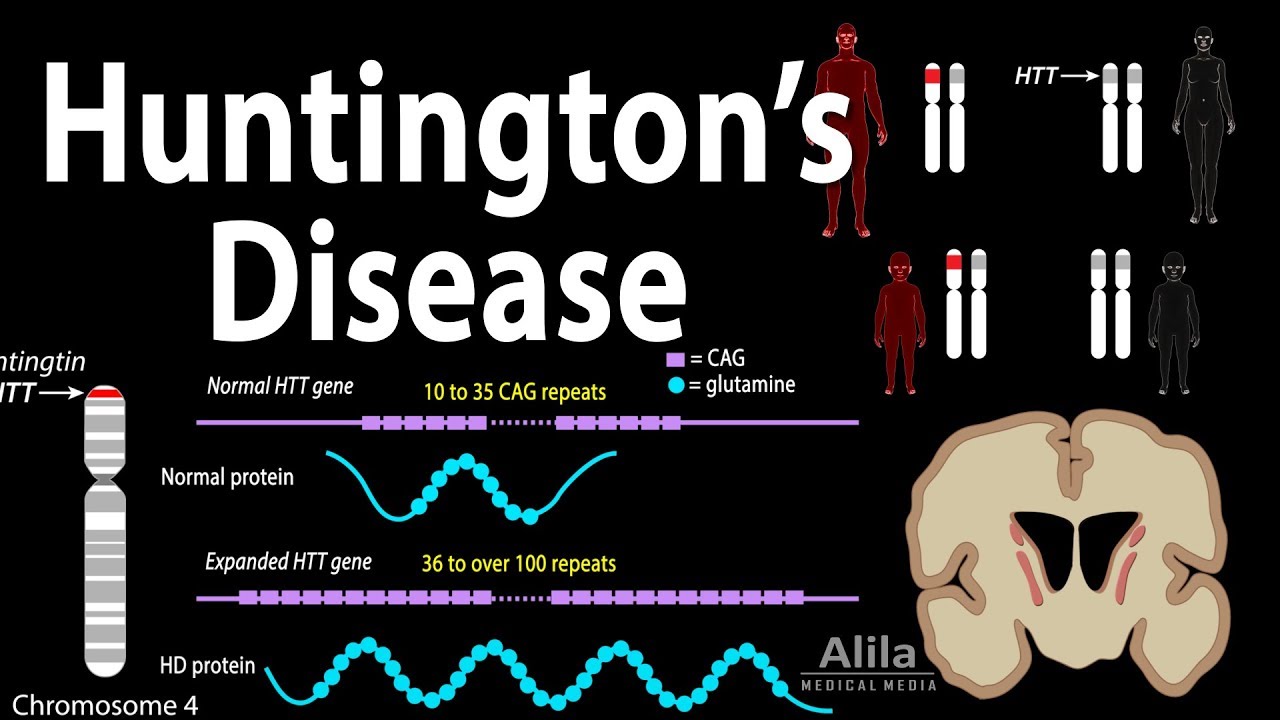
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a hereditary, progressive neurodegenerative disease clinically characterized by abnormal involuntary movements, behavioral disturbance, cognitive dysfunction, and psychiatric disease. The disease is caused by a CAG (glutamine) trinucleotide expansion in exon 1 of the huntingtin (htt) gene at the location 4p16.9 [1]. The normal function of httis not known, but it may be involved in internal cell signaling, maintenance of cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein, and preventing neuronal toxicity [2]. Early evidence suggests that the binding of the Ras homologue enriched in striatum protein to mutant htt(mhtt) may be necessary to cause cellular toxicity [3]. However, why the protein causes cellular toxicity in adulthood is not well understood. There is evidence suggesting that the interaction of the group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors and mhttprotein may be at the root of delayed onset [4].
What is the best treatment for dystonia?
For patients with the akinetic form of HD (Westphal variant), antiparkinsonian medications, such as levodopa, dopamine agonists, and amantadine, may be beneficial [103–106]. Botulinum toxin injections can also be considered for focal dystonia associated with HD, both typical presentation and Westphal variant. Even in patients with chorea, underlying dystonia and/or bradykinesia may be present and needs to be addressed.
What is the best medication for chorea?
Other medications that are commonly considered when treating chorea include dopamine anta gonists, benzodiazepines, and glutamate antagonists. Dopamine antagonists (neuroleptics) are perhaps the most commonly considered agents in the management of chorea and psychosis in patients with HD, but few double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of these agents have been published [75–77]. None of the typical neuroleptics have been found to be effective in reducing chorea in placebo-controlled trials. However, in a study of haloperidol in 10 patients, oral doses of 1.5–10.0 mg/day corresponded with at least a 30 % reduction in chorea compared with baseline [78]. The quantity and quality of these efficacy data need to be taken into account when considering the risks of using typical neuroleptics, particularly tardive dyskinesia. Apathy and akathisia, other potential adverse effects of the dopamine receptor blockers, can be particularly problematic in patients with HD, as they may not have the insight to recognize these problems or may wrongly attribute the symptoms to HD.
How to treat behavioral dyscontrol?
Behavioral dyscontrol can be a severely disabling symptom of HD causing distress to the patient, family, and caregivers. Environmental approaches and cognitive interventions are the mainstay of treatments, but pharmacological agents can augment addressing disruptive behaviors. Depression, anxiety, aggressive, impulsive, and obsessive–compulsive behaviors are also frequently treated pharmacologically and require behavioral intervention, but caution should be used to avoid oversedation and apathy, already common in patients with HD. Although not well-studied, cognitive approaches to treat behavior may be more effective than pharmacotherapy for some aspects of the disease [40]. There have been few clinical trials to examine the effect of agents for cognition in HD such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and atomoxetine. None of the trials to date have demonstrated significant improvement [41–43]. Recent advances in the cognitive aspect of HD have focused on finding improved methods of diagnosing and tracking changes over time [44].
How is HD diagnosed?
HD is diagnosed based on the presence of typical motor findings commonly in the setting of a family history of the disease. There may be other manifestations of HD at the time of presentation or prior to diagnosis based on personality changes or behavioral and cognitive symptoms. A DNA test showing abnormal CAG expansion in the httgene can be used to confirm the diagnosis in symptomatic individuals. With proper genetic counseling and at the patient’s request, DNA analysis can be performed in individuals at risk for developing HD under the care of experienced clinicians.
Is there a treatment for chorea?
Although there is no established treatment to delay the onset or forestall the progression of HD, symptomatic treatment of chorea based on the neurochemical pathology known may be beneficial in some individuals, as it may have a favorable effect on motor function, quality of life, and safety [5–7]. Clinicians may also consider treatment for dystonia, other movement disorders, and non-motor aspects of HD.
Does chorea require a long term treatment?
Overall, there is not enough evidence available to guide long-term symptomatic treatment in HD, and double-blind and long-term studies assessing various treatment strategies in HD are needed [55]. Despite the lack of evidence, an American Academy of Neurology Guidelines publication was recently released recommending consideration of tetrabenazine (TBZ), amantadine, or riluzole if chorea requires treatment [46]. A Cochrane review of studies for the symptomatic treatment of HD examined 22 trials that involved 1254 different participants [56]. Nine trials had a crossover design and 13 were conducted in parallel. The studies examined were of relatively short duration, ranging from 2 to 80 weeks. The number of trials examining various pharmacological interventions included antidopaminergic drugs (n = 5), glutamate receptor antagonists (n = 5), and energy metabolites (n = 5). Based on available evidence, the authors of the Cochrane review concluded that only TBZ showed clear efficacy for the control of chorea, but “no statement can be made regarding the best medical practice for the control of motor and non-motor symptoms in HD”.
What is the best treatment for Huntington's disease?
Movement problems, such as chorea, for example, are a common Huntington’s symptom. Xenazine (tetraben azine) is the only medication specifically approved for Huntington’s chorea. Others, such as antipsychotics and benzodiazepines, have also demonstrated a benefit and can be used off-label.
What is Huntington's disease?
Treatments for Huntington’s disease. Huntington’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, caused by inheritable mutations in the huntingtin ( HTT) gene. The mutation produces a toxic form of the HTT protein that aggregates in and ultimately kills nerve cells.
What is gene silencing therapy?
Gene silencing therapies act to reduce the levels of toxic HTT protein being produced. It is hoped that this could slow the progression ...
What are some examples of anti-inflammatory treatments for Huntington's disease?
Examples of experimental anti-inflammatory therapies include VX15/2503 and laquinimod. Neuroprotective therapies aimed at reducing nerve cell death in the brain are also an option. Examples include Huntexil (prodopidine) and SBT-20.
What is the best treatment for a person with a psychiatric disorder?
Occupational therapy and speech therapy can also help deal with communication issues that may arise due to the disease affecting the muscles of the mouth and throat. Psychiatric problems may be managed using anti-depressants, antipsychotics, and mood-stabilizing medications.
How does physical therapy help with falls?
Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and prevent falls through tailored exercises for the patient. This can be complemented by occupational therapy that helps the patient establish coping strategies and identify ways to make his or her life easier, either through simple changes or the introduction of assistive devices. Occupational therapy and speech therapy can also help deal with communication issues that may arise due to the disease affecting the muscles of the mouth and throat.
Can Huntington's disease slow the progression of the disease?
It is hoped that this could slow the progression of the disease, and not just manage the symptoms. Neuroinflammation is an abnormal immune response that is common in Huntington’s disease and can lead to further damage and cell death in the brain.
What kind of doctor is needed for Huntington's disease?
To effectively manage Huntington’s disease you will need a neurologist, psychiatrist, social worker and geneticist.
What is the treatment for psychiatric symptoms?
Symptomatic treatment for psychiatric, behavioral, and cognitive symptoms are variable and include SSRIs, antipsychotics, and other treatments.
What is the treatment for chorea?
Symptomatic treatment for chorea involves medications that deplete dopamine (such as tetrabenazine) or block dopamine (such as antipsychotics). Symptomatic treatment for psychiatric, behavioral, and cognitive symptoms are variable and include SSRIs, antipsychotics, and other treatments.
What is the first treatment for Huntington's disease?
If you have severe muscle stiffness that causes pain or inhibits your movements, medication adjustment is usually the first type of treatment, because some of the antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of Huntington’s disease can cause muscle stiffness. 6 . Physical therapy may help as well.
How to reduce the effects of your condition?
You can reduce the effects of your condition with some at home strategies. As your motor control and coordination decline, you can optimize your safety by doing things like avoiding stairs, using a walker, and having supportive handrails while you shower.
What is the best medication for chorea?
Oral medications used to reduce chorea are taken daily or several times per day. Xenazine (tetrabenazine) and Austedo (deutetrabenazine) are both approved for reducing chorea in Huntington’s disease. 1 These medications are believed to work by interaction with neurotransmitters in the brain.
Can you take multiple medications for Huntington's disease?
You might need several different medications to manage each of the different symptoms, and sometimes one or more of your medications may exacerbate the effects of Huntington’s disease, so they have to be dosed carefully.
Is Huntington's disease reversible?
Caring for Someone Who Has Huntington's Disease. Huntington’s disease is not reversible, but some of the effects can be managed and controlled to improve the quality of life for those who have the disease and for their loved ones. Treatments can help manage involuntary muscle movements and psychosis . It is never too soon to begin talking ...
Can Huntington's disease cause anxiety?
Depression is the most common mood symptom associated with Huntington’s disease, although anxiety can occur as well. These symptoms can be treated with antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications, with careful monitoring of side effects and consideration of potential drug interactions. 2
What are the symptoms of Huntington's disease?
As a neurological condition, Huntington's causes symptoms that typically fall into one of three categories: physical/movement changes, cognitive changes, and emotional/behavioral changes. HD is also one of several conditions that cause dementia to develop.
Do people with Huntington's disease need help?
Most importantly, people with HD and their families have a risk for isolation. Know that there are resources and support available to encourage you and help you determine your next steps. If you're not sure what to do or need help, the Huntington's Disease Society of America has local chapters as well as online support groups that can encourage you, answer your questions or walk with you or just be a listening ear as you live with HD.
Can you manage HD?
HD has a wide range of symptoms that may develop , some of which can be successfully managed with medications and non-drug approaches. Before delving into treatments, understanding symptoms as part of the disease can also help cope with them and take a more active role in your own or a family member's care.
Is there a cure for HD?
While there is no cure available for HD at this time , there are a few medications and complementary approaches that may help relieve some symptoms for a time. Keep in mind that you should not use complementary or supplementary substances without checking with your physician, as some can have significant negative side effects or drug interactions with your other medications.
What are the movement disorders associated with Huntington's disease?
The movement disorders associated with Huntington's disease can include both involuntary movement problems and impairments in voluntary movements, such as: Involuntary jerking or writhing movements (chorea) Muscle problems, such as rigidity or muscle contracture (dystonia) Slow or abnormal eye movements.
When does Huntington's disease start?
Huntington's disease symptoms can develop at any time, but they often first appear when people are in their 30s or 40s. If the condition develops before age 20, it's called juvenile Huntington's disease. When Huntington's develops early, symptoms are somewhat different and the disease may progress faster.
What to do if your parent is at risk for genetic testing?
If an at-risk parent is considering genetic testing, it can be helpful to meet with a genetic counselor. A genetic counselor will discuss the potential risks of a positive test result, which would indicate that the parent will develop the disease.
How many copies of each gene are there in Huntington's disease?
Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that a person needs only one copy of the defective gene to develop the disorder. With the exception of genes on the sex chromosomes, a person inherits two copies of every gene — one copy from each parent.
How do you know if you have Huntington's disease?
See your doctor if you notice changes in your movements, emotional state or mental ability. The signs and symptoms of Huntington's disease can be caused by a number of different conditions. Therefore, it's important to get a prompt, thorough diagnosis.
Where are Huntington's embryos implanted?
The embryos are tested for presence of the Huntington gene, and only those testing negative for the Huntington gene are implanted in the mother's uterus. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Huntington's disease care at Mayo Clinic.
Does Huntington's disease cause weight loss?
In addition to the above disorders, weight loss is common in people with Huntington's disease, especially as the disease progresses.

Diagnosis
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment