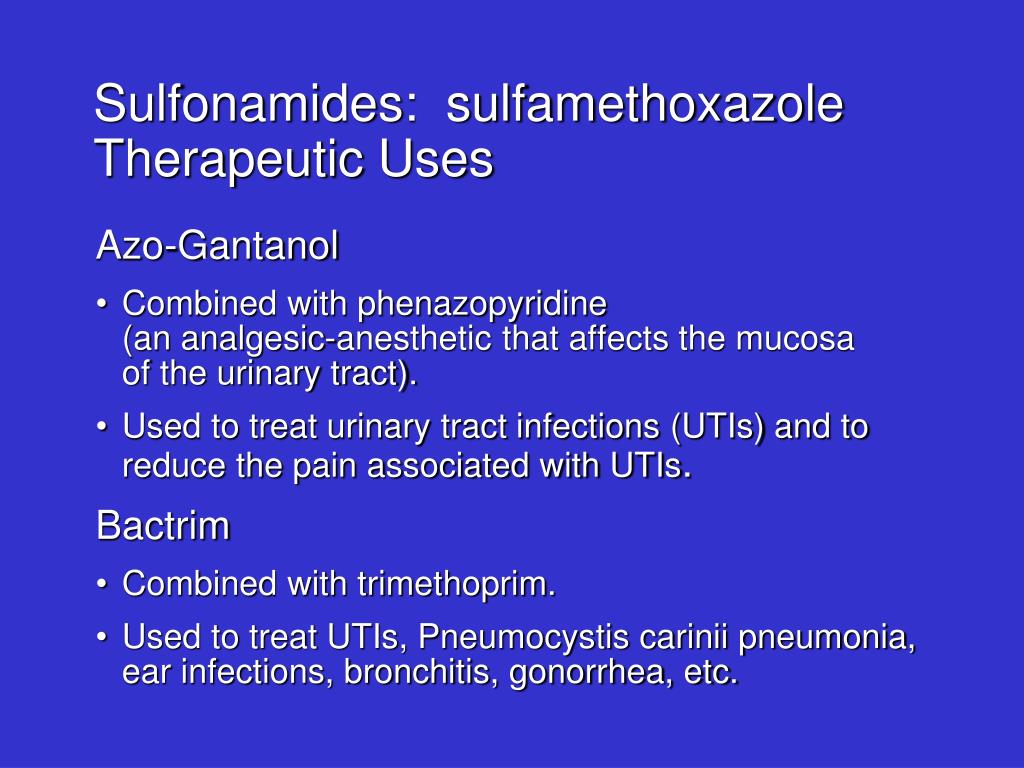
Preferred Therapy: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the preferred agent for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis in individuals with HIV infection and studies have shown that either a double-strength tablet or a single-strength tablet taken daily is effective in preventing Pneumocystis pneumonia.
What is Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis?
About Pneumocystis Pneumonia Prophylaxis: Involves the taking of medicine for the purpose of preventing Pneumocystis Pneumonia - a fungal lung infection occurring in persons with impaired immune systems. The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Do antibiotics prevent Pneumocystis infections?
Any chemoprophylaxis administered for the prevention of Pneumocystis infections versus placebo, no intervention, or an antibiotic(s) with no activity against Pneumocystis pneumonia. We also included trials that compared different antibiotics for the prevention of Pneumocystis infections.
How are approaches to Pneumocystis infection changing?
Approaches to the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis infection are changing with the increased use of anti- Pneumocystis prophylaxis in both AIDS and non-AIDS immunocompromised hosts and by improvements in antiviral therapies for HIV.
What is a documented Pneumocystis infection?
Documented Pneumocystis infections, defined as documentation of Pneumocystis from a properly obtained specimen (bronchoalveolar lavage, induced sputum, or biopsy) in a patient with clinical manifestations compatible with PCP.
What is the preferred regimen for primary prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia?
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) is the recommended prophylactic agent for PCP (AI). One double-strength TMP-SMX tablet daily is the preferred regimen (AI), but one single-strength tablet daily45 is also effective and may be better tolerated than the double-strength tablet (AI).
What is the treatment for Pneumocystis?
Treatment and Outcomes PCP must be treated with prescription medicine. Without treatment, PCP can cause death. The most common form of treatment is trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX), which is also known as co-trimoxazole and by several different brand names, including Bactrim, Septra, and Cotrim.
When do you give Pneumocystis prophylaxis?
For recipients of solid organ transplant, guidelines recommend primary prophylaxis for a minimum of 6 months after transplant. Some patients, such as lung and small bowel transplant recipients or those with a history of PCP infection or chronic cytomegalovirus infection, have indications for lifelong prophylaxis.
Which one of the following medications provides sufficient prophylaxis for both Pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasma encephalitis?
Recommended Regimens for Primary Prophylaxis [17] Note that all recommended regimens for Toxoplasma encephalitis prophylaxis are also effective for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis. Preferred Therapy: Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is the preferred agent for Toxoplasma encephalitis prophylaxis in individuals with HIV.
When do you start PJP prophylaxis steroids?
However, the American Thoracic Society provides a low evidence-based recommendation to consider PCP prophylaxis during the time period of treatment with >20 mg/day of prednisone for longer than 1 month. Additionally, there is 1 recent noteworthy article that can guide the approach to this clinical issue.
What is primary and secondary prophylaxis?
Definition. Opportunistic infections are intercurrent infections that occur in people infected with HIV. Prophylaxis aims to avoid either the first occurrence of these infections (primary prophylaxis) or their recurrence (secondary prophylaxis, maintenance treatment).
Drugs used for Pneumocystis Pneumonia Prophylaxis
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What are the two compounds studied most extensively for prophylaxis against PCP?
REGIMENS FOR PROPHYLAXIS. The two compounds studied most extensively for prophylaxis against PCP have been trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, given orally, and pentamidine, given as an aerosol. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole.
What is the most common presenting manifestation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)?
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), the most common presenting manifestation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), is a major and recurring cause of morbidity and mortality for persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In recent years, important advances have been made in understanding which patient ...
Is prophylaxis a primary or secondary?
Prophylaxis is categorized as secondary if the goal is to prevent subsequent episodes for a person who has already had at least one episode of PCP. Risk of an Initial Episode of PCP.
Is trimethoprim a parenteral pentamidine?
However, such conventional therapy as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or parenteral pentamidine is often complicated by adverse reactions that may require termination of the therapy (2), and the mortality for first episodes of PCP is still 5%-20%. Thus, prevention of PCP is a preferred alternative to treating patients for successive episodes ...
TARGET POPULATIONS FOR ANTI- PNEUMOCYSTIS PROPHYLAXIS
A natural reservoir of P. carinii has not been demonstrated.
TARGETS FOR ANTIMICROBIAL DEVELOPMENT
Some features of the life cycle of the organism are relevant to a discussion of the antimicrobial agents used for prophylaxis and therapy (Table (Table1). 1 ). Three forms of the organism have been identified: the trophozoite, cyst, and sporozoite (or intracystic body) forms.
ANIMAL MODELS AND IN VITRO CULTIVATION OF P. CARINII
Continuous cultivation of P. carinii in vitro for purposes of testing of its susceptibility to antimicrobial agents has not been consistently achieved ( 23, 34, 85, 101 ). Although data suggestive of the activities of certain agents against P.
ANTIMICROBIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY
The emergence of resistance of P. carinii to the commonly used therapeutic agents has not been demonstrated in vitro for human-derived organisms or in animal models of Pneumocystis infection. Techniques that can be used to demonstrate the resistance of P. carinii to antimicrobial agents in vitro are not generally available ( 23 ).
PROPHYLACTIC STRATEGIES FOR PNEUMOCYSTIS
In the pre-AIDS era, the prevention of P. carinii pneumonia was associated with time-limited antimicrobial agent use in the setting of prolonged neutropenia or corticosteroid use due to cancer chemotherapy.
BREAKTHROUGH INFECTION
Breakthrough infection is uncommon in patients taking TMP-SMX, for which systemic absorption is routinely adequate ( 114 ). All other prophylactic agents may be considered second-line agents.
VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
The development of vaccines for the prevention of Pneumocystis pneumonia has been hindered by the inability to define for the organism invariant antigens which generate protective immunity, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Patients with P.