What is EGD in medical terms?
“Abnormal” EGD results may be due to:
- Celiac disease. This digestive disorder is caused by an atypical immune reaction to gluten that can damage your intestinal lining and prevent it from absorbing nutrients.
- Esophageal rings. ...
- Esophageal varices. ...
- Hiatal hernia. ...
- Inflammatory conditions. ...
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. ...
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome. ...
- Ulcers. ...
- Tumors. ...
What is the doctor looking for in the EGD?
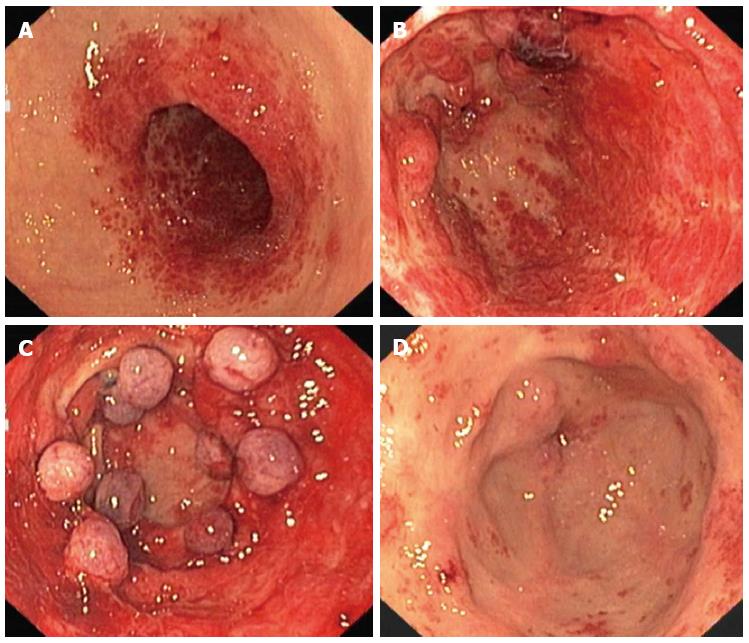
EGD is more accurate than x-ray films for detecting inflammation, ulcers or tumors of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.An upper endoscopy(EGD) allows the doctor to explore the cause of symptoms such as: - Difficulty swallowing,-Abdominal pain,-Vomiting up blood,-Passing blood in the stool.
What is EGD medical term?
An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test in which your doctor uses an endoscope to examine the lining of your esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The esophagus is the muscular tube that connects...
What does EGD mean in medical dictionary?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy: Also known as EGD or upper endoscopy. A procedure that enables the examiner (usually a gastroenterologist) to examine the esophagus (the swallowing tube), stomach, and duodenum (the first portion of small bowel) using a thin flexible tube (a "scope") that can be looked through or seen on a TV monitor.
Why would a doctor order an EGD?
The doctor may perform this procedure to diagnose and treat when possible certain disorders of the upper GI tract. Often it is used to investigate symptoms of abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, prolonged nausea & vomiting, heartburn, unexplained weight loss, anemia, or blood in your bowel movements.
Is an EGD serious?
In general, an EGD is a safe procedure. There's a very slight risk that the endoscope will cause a small hole in your esophagus, stomach, or small intestine. If a biopsy is performed, there's also a small risk of prolonged bleeding from the site where the tissue was taken.
What happens during EGD?
The tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and upper portion of the small intestine. Using the mouth and throat for access, a fiberoptic endoscope equipped with a camera is used to visualize the upper GI tract, obtain a biopsy, or treat gastrointestinal conditions.
What diseases can be detected by an EGD?
What conditions is an EGD used to diagnose?GERD – (gastroesophageal reflux disease)Blocked or narrowed tissue.Ulcers and their accompanying redness and swelling.Benign or malignant tumors.Increased vein size in esophageal tissue.Hiatal hernia, which is when the stomach moves up into the esophagus.More items...•
Do they put you to sleep for an EGD?
During Your EGD: The procedure typically takes between 10 to 30 minutes. You will lie on your left side. An anesthesiologist will administer an intravenous (IV) sedative so you sleep through the procedure. A plastic mouth guard is placed between your teeth to prevent damage to your teeth.
Are you awake during EGD?
You will be awake during the procedure, but you will take medicine to relax you (a sedative) before the test. Someone will have to drive you home afterward. Follow any other instructions your provider gives you to get ready.
How long does a EGD procedure take?
EGD is an endoscopic procedure that allows your doctor to examine your esophagus, stomach and duodenum (part of your small intestine). EGD is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home that same day. It takes approximately 30 to 60 minutes to perform.
What is the prep for an EGD?
Nothing to eat or drink at least 8 hours before the procedure. Medication can be taken 4 hours before examination with little sips of water. DO NOT TAKE ANY ANTACIDS OR CARAFATE BEFORE THE PROCEDURE or any of the medications mentioned. Wear loose comfortable clothing.
How long does it take to get results from an EGD test?
EGD results are immediate, while pathology results may take up to two weeks to obtain results.
How do you stay calm during an endoscopy?
General relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation and mindfulness are also fantastic ways to keep yourself relaxed.
Do they always take biopsy during endoscopy?
Your doctor might use upper endoscopy to obtain a biopsy (small tissue samples). A biopsy helps your doctor distinguish between benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) tissues. Remember, biopsies are taken for many reasons, and your doctor may take a biopsy even if he or she does not suspect cancer.
What does EGD mean?
Persistent nausea or vomiting. Swallowing difficulties. Upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Chest pain (without evidence of heart disease) Bloody stool. Your doctor may also order EGD for: Periodic screening, if your doctor thinks you are at risk for developing a digestive disorder.
Why do we use EGD?
EGD: Why It’s Performed. EGD is used to evaluate a number of digestive disorders. It is a popular diagnostic option because patients generally tolerate it well and it causes minimal discomfort. Your gastroenterologist may use EGD to evaluate: Abdominal pain.
How long does it take to get an EGD?
EGD is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home that same day. It takes approximately 30 to 60 minutes to perform.
What to do during an EGD?
When you arrive for the EGD, you will register and give a medical history. We will insert an intravenous line in order to administer fluids and sedatives. During the EGD, your doctor will: Anesthetize your throat with a topical anesthetic to suppress the gag reflex. Administer pain medication and a sedative.
How to get rid of a swollen esophagus?
Administer pain medication and a sedative. Place a plastic mouthpiece between your teeth to prevent damage to the endoscope. Insert the endoscope; as you swallow, the swallowing motion guides the endoscope through your esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
What is EGD used for?
As a diagnostic tool, EGD is also useful when it's the easiest and safest way to obtain a biopsy. During the procedure, your doctor may collect one or more tissue samples so they can be examined under a microscope. 4. Conditions that may be diagnosed or treated with EGD include: 2. Peptic ulcer.
What is an EGD?
Recovery. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), often referred to as an upper endoscopy, is an invasive procedure that can help in evaluating and managing several conditions that involve the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract—which is composed of the esophagus, stomach, and upper portion of the small intestine.
Where is EGD done?
An EGD is typically done in an endoscopy suite, which is a special procedure room. It may be located in the hospital, a surgical center, or an outpatient clinic. You should be prepared to spend several hours at your EGD appointment and to rest for the remainder of the day after your procedure.
Why do you need an EGD?
Purpose of an EGD. An EGD may be done for diagnostic or therapeutic reasons, depending on your condition . Your doctor may recommend an EGD if you have any of the following symptoms: 4. Visualizing the lumen can help identify their cause, which may be otherwise unclear based on presentation alone.
What is fiber optic endoscope?
Using the mouth and throat for access, a fiberoptic endoscope equipped with a camera is used to visualize your upper GI tract, obtain a biopsy, or treat gastrointestinal conditions. Illustration by Emily Roberts, Verywell.
When is an upper endoscopy used?
This makes an upper endoscopy a useful adjunct when used along with imaging tests. EGD is also considered when the medical history and physical examination suggest the possibility of a lesion in the lumen that could not be well-visualized with a less invasive test (like an imaging test).
How often do you have to swallow after an endoscope?
When you are adequately relaxed, you will be asked to swallow once or twice during the initial period of insertion of the endoscope. The tube will not interfere with your ability to breathe and is only mildly uncomfortable following the initial insertion.
What is EGD test?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (the duodenum).
Where is EGD done?
EGD is done in a hospital or medical center. The procedure uses an endoscope. This is a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end. The procedure is done as follows: During the procedure, your breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen level are checked. Wires are attached to certain areas of your body and then to machines ...
What is the term for a condition in which food or liquid from the stomach leaks backwards into the
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (a condition in which food or liquid from the stomach leaks backwards into the esophagus) Hiatal hernia (a condition in which part of the stomach sticks up into the chest through an opening in the diaphragm) Mallory-Weiss syndrome (tear in the esophagus)
How long does a gag reflex test last?
After the test is finished, you will not be able to have food and liquid until your gag reflex returns (so you do not choke). The test lasts about 5 to 20 minutes.
What is the mouth guard used for?
A mouth guard is used to protect your teeth and the scope. Dentures must be removed before the procedure begins. You then lie on your left side. The scope is inserted through the esophagus (food pipe) to the stomach and duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine.
What is an EGD?
What is EGD? Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, or EGD, is an endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum (the uppermost part of the small intestine) for hiatal hernias, ulcers, bleeding sources, tumors or other problems. The procedure can also offer a number of therapeutic interventions such as control of bleeding, manometry, ...
What is an EGD test?
Oftentimes, EGD tests are ordered after an x-ray or other, less invasive test shows signs of an abnormality that may need further examination. During the EGD, a surgeon can actually remove small growths or cancers detected—so that the patient will not have to under another medical procedure.
How long before EGD can you eat?
To empty your upper GI tract, simply stop eating food and drinking beverages for 8 to 12 hours before the EGD. Also note that you will not be able to eat or drink anything for a couple of hours after the EDG, as well, because if you eat while sedated you might choke without feeling or noticing it.
What is the procedure called when you have a GI?
Together, the three procedures are referred to as EGD, or Upper Endoscopy. The EGD procedure is usually done by a GI doctor (gastroenterologist).
What is the name of the procedure that looks inside the stomach?
The procedure’s medical name is actually a combination of the names of three different procedures that are usually performed collectively: Esophagoscopy —looking inside the esophagus for hiatal hernias, polyps, strictures, etc. Gastroscopy —looking inside the stomach for ulcers, polyps, inflammation, etc.
What is an EGD?
An upper GI endoscopy or EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in your upper GI (gastrointestinal) tract. The upper GI tract includes your food pipe (esophagus), stomach, and the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum). This procedure is done using a long, flexible tube called an endoscope.
What is upper GI endoscopy?
An upper GI endoscopy can be used to diagnose and treat problems in your upper GI tract. It is often used to find the cause of unexplained symptoms such as: Trouble swallowing (dysphagia) Unexplained weight loss. Upper belly pain or chest pain that is not heart-related.
What is asked during an upper GI endoscopy?
Generally, an upper GI endoscopy follows this process: You will be asked to remove any clothing, jewelry, or other objects that may interfere with the procedure.
What is the pain of a stomach endoscopy?
Upper belly pain or chest pain that is not heart-related. Continuous vomiting for an unknown reason (intractable vomiting) Bleeding in the upper GI tract. An upper GI endoscopy can be used to identify disorders or problems such as: GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) Narrowing (strictures) or blockages.
Is it necessary to drive home after an endoscopy?
This may be recommended in certain situations, such as when dilation is being performed. It is not needed for a standard upper endoscopy. You will be awake during the procedure, but you will take medicine to relax you (a sedative) before the test. Someone will have to drive you home afterward.
Can Crohn's disease be treated with an endoscopy?
Crohn's disease of the upper GI tract. Infections of the upper GI tract. An upper GI endoscopy can also treat problems in the upper GI tract. The procedure can be used to:
What is an EGD?
An EGD is performed to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. It may be performed for diagnosis or treatment of digestive disorders. The doctor may recommend an EGD for patient with symptoms such as. Persistent pain in the upper abdomen. Chronic heartburn.
What is EGD screening?
EGD is also performed as a regular screening procedure for people . at risk for upper GI diseases. with existing GI disorders. with liver cirrhosis. The doctor may perform an EGD for treatments such as. Removal of foreign bodies.
What is GERD in GI tract?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease ( GERD) Narrowing of esophagus due to abnormal tissue growth (esophageal rings) Swollen veins in the esophagus (esophageal varices) Esophageal tears. Tumors or cancer in the GI tract.
What is the name of the condition where the stomach backs up into the esophagus?
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is a condition in which the acidified liquid contents of the stomach backs up into the esophagus. The symptoms of uncomplicated GERD are: heartburn, regurgitation, and. nausea.
How does a doctor insert an endoscope?
The doctor inserts the endoscope through the mouth and passes it through the esophagus and stomach to the duodenum.
Where is the endoscope in the mouth?
A flexible tube with a lighted camera (endoscope) is introduced through the mouth or nose passing through the esophagus and stomach up to the top part of the small intestine (duodenum). An EGD is also known as an upper endoscopy.
What does it feel like to have an EGD?
Feeling full with small quantity of food. Nausea and vomiting. Vomiting blood. Anemia and weight loss. Blood in stool. Feeling of food stuck in the throat. EGD is also performed as a regular screening procedure for people.
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
EGD; endoscopic examination of the interior of the esophagus, stomach, and initial portion of the duodenum. The procedure usually is done for diagnostic purposes and permits removal of samples of tissue for further study. In some cases the procedure is done to locate and remove a foreign object that has become lodged in the esophagus.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
An imaging test that involves visually examining the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and upper duodenum with a flexible fiberoptic endoscope.