What is the maximum dose of radiation tolerated by the brain?
For targets <20 mm, the maximal tolerated dose was >24 Gy (11). The volume of brain receiving ≥12 Gy has been shown to correlate with both the incidence of radiation necrosis and asymptomatic radiologic changes (Table 1). Open in a separate window
What kind of radiation do you get for brain cancer?
Your doctor will decide whether you’ll receive partial or whole brain radiation. You’ll have either external beam radiation therapy or stereotactic radiosurgery depending on your treatment plan. During external beam radiation, a treatment machine will aim beams of radiation directly to the tumor.
What is the success rate of radiation treatment for brain cancer?
The success rate of radiation treatment for brain cancer will depend on the patient’s condition. Most of the time radiation therapy shows good results. Now you should know what tests recommend before brain cancer treatment. What Tests Recommend By Doctor Before Brain Cancer?
What is high-dose-rate radiation therapy?
High-dose-rate radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, is a procedure that involves placing radioactive material inside the body to allow doctors to deliver higher doses of radiation to more specific areas.
How long does radiation treatment last?
Radiation treatments may be given Monday through Friday. For some people, the treatment is given in just one day. For other people, the treatment is given over a number of weeks. Your schedule is based on what your doctor recommends.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to treat cancer. It works by damaging the cancer cells and making it hard for them to reproduce. Your body then is naturally able to get rid of these damaged cancer cells. Radiation therapy also affects normal cells.
What is the phone number to call for radiation therapy?
After 5:00 pm, during the weekend, and on holidays, call 212-639-2000 and ask for the radiation oncologist on call. If you have any questions or concerns, talk with a member of your radiation therapy team. You can reach them Monday through Friday from 9:00 am to 5:00 pm.
How do steroids help with brain tumors?
Steroids reduce brain swelling from the tumor itself or from the effects of radiation therapy . Take steroids only as directed by your doctor. You dose may be changed as needed during your treatment. When your doctor decides it’s safe, you’ll be given a schedule to gradually reduce the dose of the medication.
How to quit smoking after radiation?
Telling your doctor or nurse if you’re in pain. Caring for yourself at home: Quitting smoking, if you smoke. If you want to quit, call our Tobacco Treatment Program at 212-610-0507. Following your radiation therapy team’s instructions to care of your skin.
What happens to your hair during radiation?
During radiation therapy, your skin and hair in the area being treated may change. This may include your forehead, ears, and back of your neck. This is normal. Ask your nurse to point out the areas of your skin and scalp that will be affected.
Can radiation cause brain swelling?
Radiation therapy to the brain may cause brain swelling. If you had neurological symptoms before you began radiation therapy, they could return, or you could have new symptoms. These symptoms may include:
How many people died from radiation?
Of those 134, 28 died from the radiation injuries that they sustained. Although radiation affects different people in different ways, it is generally believed that humans exposed to about 500 rem of radiation all at once will likely die without medical treatment.
How much radiation did the Chernobyl plant receive?
Approximately 134 plant workers and firefighters battling the fire at the Chernobyl power plant received high radiation doses of 70,000 to 1,340,000 mrem (700 to 13,400 mSv) and suffered acute radiation sickness.
Does radiation kill cells?
Moreover, high radiation doses (particularly over a short period of time) have a tendency to kill cells. In fact, high doses can sometimes kill so many cells that tissues and organs are damaged immediately. This, in turn, may cause a rapid whole-body response, which is often called "acute radiation syndrome.".
What is the treatment for brain metastases?
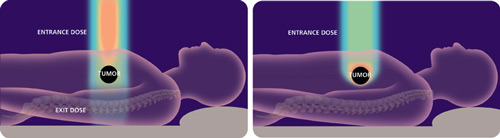
As a result, the preferred conventional radiation therapy treatment for brain metastases has been whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT). WBRT is just what it sounds like—giving radiation to the entire brain, even to healthy tissue. In WBRT, both the healthy brain cells and cancer cells receive X-Ray radiation, but the amount of radiation dose ...
What happens to the brain after cancer?
After primary cancer cells break away from the original site of the cancer, circulate the body through the bloodstream and reach the brain, it is thought that the entire brain is “seeded” with metastases. This may be true even if only a single tumor is found.
How many fractions are given in WBRT?
In addition, WBRT must be spread across many sessions or fractions. Anywhere from five to 30 fractions are given on separate days, ...
Does whole brain radiation help with cancer?
While the intent of whole brain radiation therapy is to limit the growth of metastatic cancer cells, it is well known that this treatment does not provide long term control. [1-2] [1] Kondziolka et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases.
Types of Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors
There are 2 main types of therapy. You may get both types. They include:
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
There are several types of EBRT. The goal is to target the tumor and limit damage to nearby healthy brain cells. To limit the harm, your healthcare provider may use special types of EBRT such as:
Brachytherapy
For this treatment, the radiation is placed very close to or inside the tumor. This is done during surgery. The radiation the implants give off travels a very short distance. This helps limit the effect on nearby healthy tissue.
Brain Radiation Side Effects
Generally, side effects from radiation treatment are grouped into two categories:
Radiation necrosis
Sometimes dead brain tissue forms at the site of the radiation. This is called radiation necrosis. The mass of dead brain tissue comes from both cancer cells and healthy cells. Radiation necrosis can take anywhere from months to years to develop.
Risk of future cancer
Radiation can damage the DNA in healthy cells. As a result, you have a small risk of a second brain cancer after brain radiation. This second cancer usually occurs many years later. Talk to your radiation oncologist about the risks and benefits of radiation therapy.
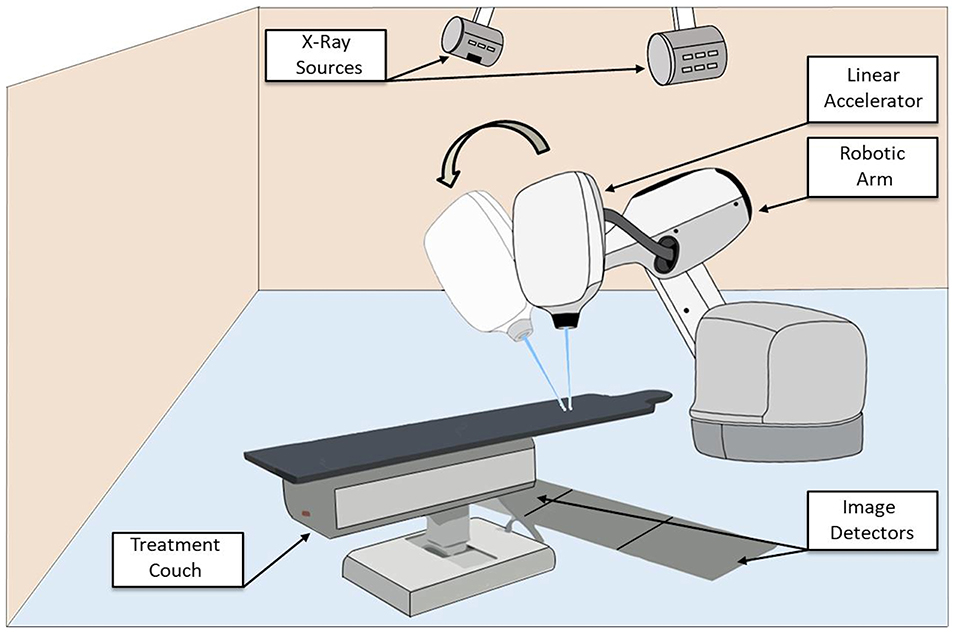
The Radiation Team
Treatment planning for radiation therapy includes mapping to pinpoint the exact location of the brain tumor using X-rays or other images.
What is the unit used to measure the total amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to?
Gray (Gy) is the unit used to measure the total amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to. This can also be recorded as centigray (cGy), which is 0.01 of a single Gy unit.
How long does radiation therapy last?
Standard treatment with radiation therapy lasts for five to eight weeks, depending on the specific type of cancer being treated, and is at the discretion of the oncologist supervising the therapy.
Why is radiation therapy important?
By Yolanda Smith, B.Pharm. Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. When radiation therapy is used to kill cancerous cells in the body , it is important to measure the dose correctly to avoid unnecessary damage to normal cells in the body. Radiation is not selective to tumor cells and therefore targets any cells that are in the process ...
Why is patient positioning important during radiation treatment?
The exact position of the patient during the radiation treatment is of utmost importance to ensure that the correct dose of radiation is emitted to the intended area of the body. It is common practice for skin to be marked to indicate where the treatment should be focused.
Why do you need a mold for radiation?
Additionally, areas of the body that do not contain tumor cells should be subjected to as little radiation as possible, often necessitating blocks or shields to protect other parts of the body .
Is radiation selective to tumor cells?
Radiation is not selective to tumor cells and therefore targets any cells that are in the process of replication when the therapy is applied. This thereby stresses the importance of administering the correct dose in order to ensure optimal efficiency with minimal side effects. Image Credit: Roman Zaiets / Shutterstock.com.
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
What is the most common drug used for radiation therapy?
The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy. Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
How long does it take for radiation to show up in the brain?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How to take care of your mouth during radiation?
Here are some tips that may help you manage mouth problems: Avoid spicy and rough foods, such as raw vegetables, dry crackers, and nuts.
