- Exposed wood can be treated with an insecticide/wood preservative such as Boracare. These products will last the life of the wood.
- Foundational walls and piers can be treated with a termiticide ( Termidor SC) at the soil level: Dig a trench in the soil adjacent to the structure, 6 inches ...
- Concrete Slabs should be treated with Termidor SC. ...
What are the barriers to treatment entry?
Dec 06, 2021 · A full barrier termite treatment is the most effective way to protect your home from these pests. The process involves drilling 8mm holes to your foundation in areas that concrete meets the structure, trenching to the foundation in the soil areas and filling them with liquid termiticide, and then sealing them up again.
What are the barriers to mental health treatment?
Jan 17, 2018 · A total of 110 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility, and papers were excluded based on 4 criteria: 1) the study focused on adherence-enhancing interventions; 2) the study focused upon adherence to a non-medication, such as diet or exercise; 3) barriers to adherence were not provided in the paper; and 4) scale of adherence was the ...
What are physical barriers?
Most of the adherence research has focused on the patients' hurdles to adherence, instead of the responsibility the physician has for assuring adherence to treatment. Objective: The purpose of this review is to identify barriers to medication adherence and refocus how we describe those barriers in terms of physician behavior hurdles.
What is a barrier to access?
Injection drug users identified barriers to treatment that included items such as an unspecified fear of treatment, bad previous treatment experience(s), and an aversion to specific types of treatment, usually methadone maintenance (Appel et al., 2004). The BTI Fear of Treatment factor included fear of what might happen during treatment, embarrassment, fear of people in …
What is a barrier treatment?
What type of termite treatment is best?
- Taurus SC: Most Popular.
- Bifen XTS: Best Fast-acting.
- Spectracide Terminate: Best Bait.
- Termidor Foam: Best Direct Chemical Treatment.
- BioAdvanced Termite Killer: Best for DIY.
What are the different types of termite treatments?
- Liquid soil-applied termiticides.
- Termite baits.
- Building materials impregnated with termiticides.
- Wood treatments.
What is the best treatment to prevent termites?
- Keep It Dry: Divert rainwater away from your home and be sure to repair any leaks. ...
- Wood: Scrap wood and firewood should be discarded or stored away from buildings. ...
- Seal It: Seal any structural cracks or crevices in the walls or foundation of your building.
Do termites come back after treatment?
What kills termites permanently?
Can termites be treated without tenting?
Can you treat termites without fumigation?
Baiting systems, spot treatments, liquid termiticides (Termidor), soil treatment, wood treatment, orange oil, and even heat or cold treatments are all methods that have been used as alternatives to fumigation to varying degrees at success.
What are the signs of termites in your home?
- Mud 'tubes' ...
- Power at your house repeatedly short circuits. ...
- Noticeable floor or ceiling damage. ...
- Swarms of flying insects outdoors. ...
- Cracked paint or plaster on walls.
How successful is termite treatment?
What can I spray on wood to keep termites away?
Spraying borate onto any wood prior to priming and painting is an excellent way to prevent termites, carpenter ants, and some wood destroying fungi from attacking your house. Products like Bora-Care are simple to apply, you just dilute with water and spray on any wood you want to keep termites off of.Sep 16, 2013
What kills termites naturally?
What is the paradigm of barriers to treatment?
A useful paradigm for viewing barriers to treatment is Andersen's conceptualization of health care utilization (Andersen, 1995; Andersen & Newman, 1973). In its most recent iteration, Andersen stresses that characteristics of the health care system, as well as individual determinants (predisposing static characteristics, enabling/inhibiting factors, and situational need factors), interact to influence health care utilization, including substance abuse treatment. Specific influences in each of these areas may serve as barriers or obstacles to obtaining treatment (Cunningham, Sobell, Sobell, Agrawal, & Toneatte, 1993).
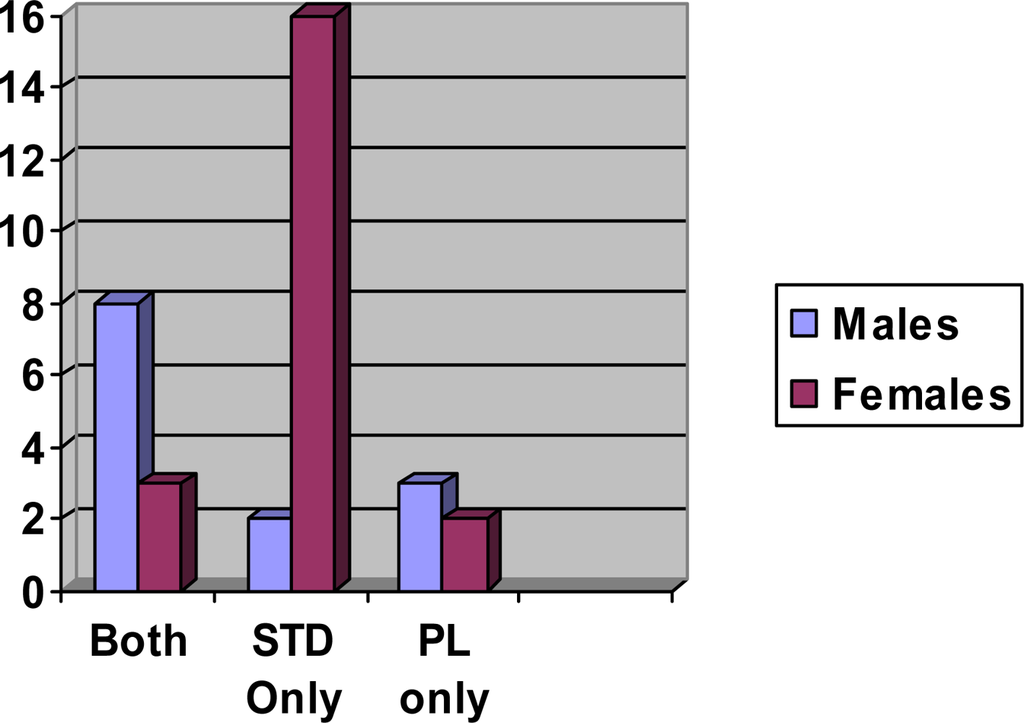
How many barriers to treatment were identified in the BTI?
This study sought to develop a psychometrically valid inventory for identifying substance abusers' views of barriers to treatment. The 59-item Barriers to Treatment Inventory (BTI) was administered to 312 substance abusers at a centralized intake unit (CIU) immediately following their assessment and before they had the opportunity to link with treatment. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were used to determine the factorial structure and reliability of the BTI. In addition to the development of a useful instrument, the study sought to gain further understanding of the relationship between individual barriers and higher order constructs. The relationship between constructs and predisposing client characteristics was also examined.
What is a BTI?
The BTI is an instrument with good reliability that can be used by substance abusers and assessment staff as a useful tool for helping identify barriers to treatment entry. Further research with other substance abuse populations, especially treatment nonattenders, may broaden its usefulness. Acknowledgments.
What is the focus of the BTI?
The focus of this study is the BTI. The BTI contains items drawn from the extensive literature on barriers to treatment and from items found in the Allen Barriers to Treatment Instrume nt (ABTI) ( Allen, 1994; Allen & Dixon , 1994), as well as other barrier lists (Grant, 1997; Tucker et al., 2004). Approximately 100 items from these sources were considered for inclusion in the BTI. Items were reviewed by senior clinical staff for relevance to the current population and setting. Fifty-nine items were selected for inclusion in the instrument.
What are the barriers to treatment for injection drug abuse?
Injection drug users identified “wanting to conceal addiction from a spouse” and having to care for a sick family member as their most frequent barriers to treatment (Appel et al., 2004). Lack of insurance/Medicaid and the time demands involved in finding and using drugs were also mentioned, as was a diverse “treatment” category that included: fear of treatment, bad treatment experiences, and aversion to a specific type of treatment. Outpatient alcohol and drug abusers identified inability to share problems with others and stigma as the two major barriers in both groups (Cunningham et al., 1993).
What is the determinant of barrier constructs?
Court referral was the determinant most frequently related to barrier constructs.. Being court-referred to the CIU predicted higher scores on Absence of Problem and greater Fear of Treatment, as well as on two system-based barriers (Time Conflict and Poor Treatment Availability). Previous treatment experience was only associated with recognition of a substance abuse problem. Subjects whose self-identified primary problems were heroin, crack, or marijuana were more likely to identify a problem and to have a support network that encouraged treatment. Alcohol as a self-reported primary problem was not associated with any of the barrier factors.
How long does it take to complete the BTI?
The BTI is read to subjects by a research assistant, taking an average of 15 minutes to complete. Subjects are asked to indicate on a five-point scale how much they believe that each barrier would affect their entry into treatment. The five-point scale includes: 1 = disagree strongly; 2 = disagree; 3 = uncertain; 4 = agree; and 5 = agree strongly.
What is the barrier to adherence to a treatment plan?
Patients feeling overwhelmed with the treatment plan is another significant barrier to adherence. Treatment plans may contain a long list of supplements or many aspects of the treatment to follow at different times throughout the day. Practitioners commonly report that their patients express feelings of being overwhelmed, ...
What are the barriers to adherence for Fullscript?
Fullscript practitioners have reported cost, readiness to change, and feeling overwhelmed as the top barriers to adherence for patients.
What is Fullscript educational?
At Fullscript, we are committed to curating accurate, and reliable educational content for practitioners and patients alike. Our educational offerings cover a broad range of topics related to integrative medicine, such as supplement ingredients, diet, lifestyle, and health conditions.
What are the barriers to adherence?
Through our research, the top barriers to adherence for patients were identified as cost, readiness to change, and feeling overwhelmed. Understanding and addressing these factors when building a treatment plan is an important consideration for improving patient adherence, satisfaction, and potentially clinical outcomes.
Is integrative medicine covered by insurance?
In integrative medicine, the cost of appointments and supplements is often not covered by private insurance plans, or patients choose to pay out of pocket. Due to the severity or chronicity of their health concerns, patients often end up engaging with numerous different practitioners to find solutions, which only further increases treatment costs.
Is non-adherence a patient centered problem?
Despite the many contributing factors, non-adherence has been traditionally considered a patient-centered problem. Therefore, interventions to improve adherence have primarily focused on patient factors and have largely ignored the other dimensions. ( 9 ) ( 10 ) ( 16 ) ( 17)
Does treatment adherence rate decline over time?
Generally, treatment adherence rates decline for all patients over time, and the likelihood of this is influenced by many different factors, such as practitioner and patient education, cost, feasibility, and patient readiness to change. ( 13)
What are the barriers to getting help for mental health?
A recent study demonstrated that lack of awareness, social stigma, cost, and limited access are some of the most prominent factors standing in the way of people pursuing mental health ...
What are the barriers to mental health?
For as much as mental health awareness and advocacy continues to build momentum, there are still formidable barriers to cross. And, unfortunately, it’s the individuals and families of people in need of mental health treatment that experience these challenges the most. Lack of awareness, social stigma, cost, and limited access are some of the most prominent factors standing in the way of people pursuing mental health treatment. Let’s take a closer look at how these obstacles impact access to much-needed mental health treatment and resources.
What is futures recovery?
At Futures Recovery Healthcare, we understand the issues and challenges that stand in the way of people receiving the help they desperately deserve and need . No one should have to wait and worry about getting help for a mental health disorder. Our Futures Mental Health division tirelessly works together to help individuals and families find and secure treatment and support for a wide range of mental health disorders in a safe and judgment-free environment.
Can you control your mental health if you only tried?
“You could control your mental illness…if you only tried.” Sadly, this is something that people with mental illness hear often. Stigmas such as this add to the shame and embarrassment felt by those struggling with a mental health disorder, so much so, in fact, that they will avoid seeking treatment for their condition.
What are the most basic barriers?
Attitudinal barriers. Attitudinal barriers are the most basic and contribute to other barriers. For example, some people may not be aware that difficulties in getting to or into a place can limit a person with a disability from participating in everyday life and common daily activities.
What is the WHO definition of barriers?
Here is the WHO definition of barriers: “Factors in a person’s environment that, through their absence or presence, limit functioning and create disability. These include aspects such as:
How many barriers are there to disability?
Often there are multiple barriers that can make it extremely difficult or even impossible for people with disabilities to function. Here are the seven most common barriers. Often, more than one barrier occurs at a time.
What are programmatic barriers?
Programmatic barriers limit the effective delivery of a public health or healthcare program for people with different types of impairments. Examples of programmatic barriers include:
What are the barriers to understanding for people with cognitive impairments?
Oral communications without accompanying manual interpretation (such as, American Sign Language). The use of technical language, long sentences, and words with many syllables may be significant barriers to understanding for people with cognitive impairments.
What are some examples of communication barriers?
Examples of communication barriers include: Written health promotion messages with barriers that prevent people with vision impairments from receiving the message. These include. Use of small print or no large-print versions of material, and. No Braille or versions for people who use screen readers.
What is a physical environment that is not accessible?
a physical environment that is not accessible, lack of relevant assistive technology (assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices), negative attitudes of people towards disability, services, systems and policies that are either nonexistent or that hinder the involvement of all people with a health condition in all areas of life.” 1. ...