Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a collection of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the fermentation used industrially to produce food and drink products, as well as home fermentation, uses anaerobic digestion.
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater Treatment Plant Digesters : quasar energy group Wastewater Treatment Plant Digesters The energy hidden in wastewater is an untapped resource with the potential to offset 12% of the US electric demand. That’s thousands of POWER PLANTS ready to be turned on.
How does a digester work?
In large wastewater treatment plants, anaerobic digestion breaks down organic waste. The process produces digester gas from the decomposition of sewage sludge from primary or secondary clarifiers. Wastewater digester gas is a methane-rich byproduct that can be an energy source. A digester gas flow meter can monitor digester gas applications.
How does the digester work?
Existing Infrastructure – Many wastewater treatment facilities in the Pacific Southwest (US Region 9) and across the country, use anaerobic digesters to reduce the volume of the biosolids (sewage sludge) before they are taken off site. The anaerobic digesters produce biogas which is either flared or used onsite as an energy source.
What is a sludge digester?
Oct 10, 2020 · Anaerobic digester mixing systems can play an important role in the treatment of wastewater; in fact, digester wastewater treatment can be both a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to treat sludge, sewage, and beyond.

What is a digester and how does it work?
That's thanks in part to digesters, which help dairy farmers make cow poop something we can all use. Micro-organisms break down organic materials like cow manure or food waste in a process called anaerobic digestion. This happens in a closed tank, where there's no oxygen, called a digester.Sep 30, 2019
What does a wastewater digester do?
In large wastewater treatment plants, anaerobic digestion breaks down organic waste. The process produces digester gas from the decomposition of sewage sludge from primary or secondary clarifiers. Wastewater digester gas is a methane-rich byproduct that can be an energy source.
What is the purpose of a digester?
Digesters can help farmers manage nutrients, reduce odors, and generate additional farm revenue. Dairy, swine and poultry are the primary animal types for farms with digesters. On-farm digesters can also accept outside food waste as a feedstock.Jun 8, 2021
What are the two types of digesters?
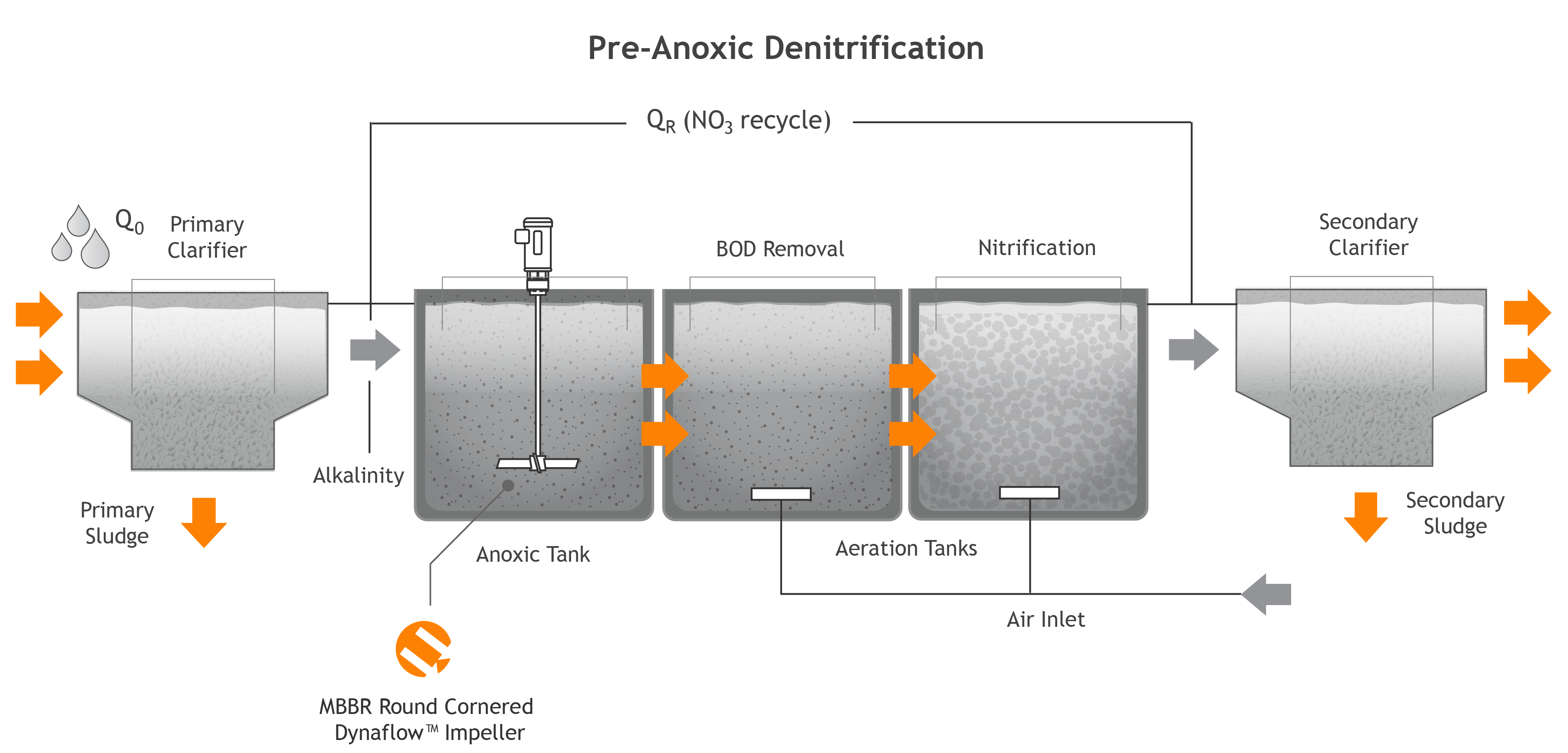
Two common types of suspended media digesters are the Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Digester or UASB Digester (Figure 10) and the Induced Blanket Reactor or IBR Digester (Figure 11).
How do clarifiers work?
The clarifier works by permitting the heavier and larger particles to settle to the bottom of the clarifier. The particles then form a bottom layer of sludge requiring regular removal and disposal. Clarified water then proceeds through several more steps before being sent for storage and use.
What do digester eggs do?
Part of the upgrade to the plant, the largest in all of New York City, the eggs are actually enormous stainless steel vessels which utilize the same bacteria found in the human gastronintestinal tract to “digest”, break down, and sterilize the estimated 315 million gallons a day of sewage that enters the plant.Jul 25, 2010
How many types of digester are there?
Wet digesters.TypesExamplesConventional digestersBatch reactor, plug flow reactor (PFR), continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR)Sludge retention digestersAnaerobic contact reactor, upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor, upflow solid reactor (USR), expanded granular sludge bed (EGSB) reactor1 more row
Why is a digester heated?
The methanogenic bacteria in the digester are very sensitive to temperature change, and thermal shocks will reduce the level of methane production. Therefore, it is essential to monitor digester temperature and retain the correct temperature window using heating in order to prevent reduced digester performance.Nov 9, 2021
What is digester gas?
Digester gas means any gaseous by-product of wastewater treatment typically formed through the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste materials and composed principally of methane and CO2.
What are digesters used for?
Anaerobic digesters are commonly used in various industrial applications to produce biogas, including: 1 Farms use digesters to exercise manure management for an energy source and co-generation 2 Brewers use digesters in wastewater treatment for pollution prevention and create biogas for use in their boilers reducing natural gas consumption 3 Distillers use digesters to convert their waste to energy and control pollution
What is anaerobic digester?
Anaerobic digesters are commonly used in various industrial applications to produce biogas, including: Farms use digesters to exercise manure management for an energy source and co-generation. Brewers use digesters in wastewater treatment for pollution prevention and create biogas for use in their boilers reducing natural gas consumption. ...
What is the gas produced by anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion at WW treatment plants produces wastewater digester gas, which is a methane-rich byproduct that can be an energy source. Digester gas is a form of biogas. The composition of wastewater digester gas varies, though the primary constituents are methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Trace amounts of nitrogen gas (N2), oxygen gas ...
What is sludge digested?
The digested sludge is de-watered, dried up and used as sewage sludge fertilizer while the gases produced are used as fuel or for driving gas engines. The supernatant liquor is re-treated at the treatment plant along with the raw sewage. The tanks in which sludge digestion is carried out are called sludge digestion tanks.
What are the products of decomposition of sewage sludge?
The products of decomposition are acid carbonates, organic acids with gases as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide.
What is anaerobic digestion?
There are two distinct uses of Anaerobic Digestion in Wastewater Treatment: 1 As a treatment process in its own right for primary sewage treatment/ organic industrial effluent, as known as a “UASB” 2 As a method of treating the sludge produced by Wastewater Treatment Plants.
Where are wastewater treatment facilities located?
Located in Urban Areas – Wastewater treatment facilities are often located in dense, urban areas, where compost facilities are not. It makes logical sense for a highly populated area to ship organic waste to a nearby anaerobic digester where the energy content is recovered and the volume reduced.
How is sewage sludge disposed of?
The remaining sewage sludge after digestion can be disposed of sustainably , and without the heavy metals and other substance it may contain causing the problems which can occur when it is spread on land. This is done by a process known as “pyrolysis and/ or gasification”.
What happens during the first stage of fermentation?
In this stage, the organic acids and nitrogenous compounds of the first stage are liquefied i.e., transformed from large solid particles to either a soluble or finely dissolved form. The process is brought about by hydrolysis using extra cellular enzymes. It is during this period, that the intermediate products of fermentation in other words, acid carbonates and ammonia compounds, accumulate and the resulting gasification into H2 and CO2 is at a minimum. The pH value rises a little to about 6.8, odor is extremely offensive and the decomposing sludge entraps gases of decomposition, becomes foam and rises to the surface to form scum. This stage is known to last much longer than the proceeding stage of acidification and hence also termed as acid regression.
What is the stage of methane gasification?
It is the stage when more resistant materials like proteins and organic acids are broken up. Large volumes of methane gas of high calorific value, along with comparatively smaller volumes of carbon dioxide are evolved. The pH value goes to the alkaline range i.e., above 7 and a tarry odour appears. Gasification finally becomes very slow; the sludge becomes well adjusted and is stable enough for disposal. This stage in the digestion of sludge is also termed as alkaline fermentation.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion is the biological degradation of organic matters in the absence of oxygen and converts the chemical energy in organic carbon to biogas. Typically, anaerobic digestion has been used for wastewater sludge treatment and reduction, agricultural manure management, and food waste management. To accomplish more sustainable resource ...
Is wastewater a renewable resource?
To accomplish more sustainable resource recovery and reduce overall energy footprint, wastewater can be regarded as renewable resource to convert embedded chemical energy to biogas. And as a result, anaerobic digestion can play a significant role in energy recovery from wastewater.