Explore
Apr 14, 2022 · Lumpectomy for DCIS is usually followed by whole breast radiation therapy to lower the risk of [ 6-13 ]: DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) in the treated breast Invasive breast cancer in the treated breast
What is DCIS, and how is it treated?
What is the treatment for DCIS? Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients.
How should DCIS be treated?
Aug 13, 2019 · Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) now represents 20–25% of all ‘breast cancers’ consequent upon detection by population-based breast cancer screening programmes. Currently, all DCIS lesions are treated, and treatment comprises either mastectomy or breast-conserving surgery supplemented with radiotherapy.
How serious is DCIS?
Feb 04, 2022 · Standard treatments for DCIS are: lumpectomy followed by radiation therapy lumpectomy alone, if the DCIS is very small and low-grade mastectomy hormonal therapy, if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive The Oncotype DX Breast DCIS Score Test can help you and your doctor decide if radiation would offer benefits after lumpectomy to remove the DCIS.
Can DCIS be left untreated?
Jun 09, 2021 · Opinions vary about how to treat DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ), but a new study suggests the optimal treatment for most women with this non-invasive breast cancer is surgery plus radiation. “Stage Zero” Breast Cancer: What’s the Optimal Treatment for DCIS? | Columbia University Irving Medical Center

Is DCIS cancer or pre cancer?
DCIS is considered a pre-cancer because sometimes it can become an invasive cancer. This means that over time, DCIS may spread out of the ducts into nearby tissue, and could metastasize. Currently, there's no good way to predict which will become invasive cancer and which won't.
How long does treatment for DCIS take?
Thus far, we have been focused on reducing that risk at all costs and treating DCIS like an early-stage breast cancer: The first step is surgery—usually lumpectomy—followed by radiation treatment for three to four weeks and finally hormone therapy for five years.Jun 9, 2021
How serious is DCIS cancer?
DCIS is non-invasive because it hasn't spread beyond the milk ducts into other healthy tissue. DCIS isn't life-threatening, but if you're diagnosed with DCIS, you have a higher-than-average risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life.Feb 4, 2022
How long does it take DCIS to become cancer?
It assumes that all breast carcinomas begin as DCIS and take 9 years to go from a single cell to an invasive lesion for the slowest growing lesions, 6 years for intermediate growing DCIS lesions, and 3 years for fast-growing DCIS lesions.
Do I need a mastectomy for DCIS?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have breast-sparing surgery, usually followed by radiation therapy. Most women with DCIS or breast cancer can choose to have a mastectomy. You have small breasts and a large area of DCIS or cancer.Jan 21, 2022
What happens if DCIS is left untreated?
The cells in DCIS are cancer cells. If left untreated, they may spread out of the milk duct into the breast tissue. If this happens, DCIS has become invasive (or infiltrating) cancer, which in turn can spread to lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Is DCIS stage 0 cancer?
DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. This means the cells that line the ducts have changed to cancer cells but they have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue.Nov 19, 2021
Why did I get DCIS?
DCIS forms when genetic mutations occur in the DNA of breast duct cells. The genetic mutations cause the cells to appear abnormal, but the cells don't yet have the ability to break out of the breast duct. Researchers don't know exactly what triggers the abnormal cell growth that leads to DCIS.May 20, 2020
How quickly does DCIS spread?
Grade 1 DCIS is almost always ER and PR positive and is a very slow growing form of cancer. It can take years, even decades, to see progression of the disease. In some cases, it may take such a long time to spread beyond the breast duct that it is not an event that will happen during a person's lifetime.Sep 30, 2016
Do all breast cancers start as DCIS?
So DCIS can present in numerous different ways. About 20 percent of all breast cancer, 1 in 5 breast cancers will be a DCIS. And a majority of the time these are what are picked up on a mammogram because it's the earliest signs of a breast cancer.Oct 9, 2018
Can DCIS come back after lumpectomy?
A study has found that for women diagnosed with DCIS considered to have a low risk of recurrence treated with lumpectomy without radiation, the risk of DCIS recurrence or developing invasive disease in the same breast increased through 12 years of follow-up and didn't level off.Nov 2, 2015
What are the chances of getting DCIS in the other breast?
After a DCIS diagnosis in one breast, the average risk of developing either DCIS or invasive breast cancer in the OPPOSITE breast is small -- under 1% each year. The risk is higher for women who have an abnormal breast cancer gene (BRCA1 or BRCA2).Apr 10, 2009
What is the treatment for DCIS?
In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: Lumpectomy only.
What is DCIS on a mammogram?
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging. You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes ...
What is a calcification on a mammogram?
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications (shown left) are more likely to be noncancerous (benign). Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications (shown right) may indicate cancer.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are studying new strategies for managing DCIS, such as close monitoring rather than surgery after diagnosis. Whether you're eligible to participate in a clinical trial depends on your specific situation. Talk with your doctor about your options.
Can alternative medicine cure DCIS?
Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress.
Can you have a mastectomy with DCIS?
Most women with DCIS are candidates for lumpectomy. However, mastectomy may be recommended if: You have a large area of DCIS.
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
What is a Lumpectomy for DCIS?
Lumpectomy for DCIS is usually followed by whole breast radiation therapy to lower the risk of [ 6-13 ]: DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) in the treated breast. Invasive breast cancer in the treated breast.
Why is DCIS called in situ?
It’s called “in situ” (which means “in place”) because the cells have not left the milk ducts to invade nearby breast tissue. DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma. You may hear the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS. DCIS is treated to try to prevent the development of invasive breast cancer.
How do pathologists determine the hormone receptor status of a DCIS tumor?
A pathologist determines the hormone receptor status of the DCIS by testing the tissue removed during a biopsy. Hormone receptor-positive (estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive) DCIS tumors express hormone receptors. This means they have a lot of hormone receptors..
Can a lumpectomy be done with DCIS?
If there’s little spread of DCIS within the ducts, a choice can be made between mastectomy or lumpectomy. With lumpectomy, the surgeon removes only the abnormal tissue in the breast and a small rim of normal tissue around it. The rest of the breast is left intact.
Can you get DCIS without radiation?
Because DCIS might progress to invasive breast cancer, almost all cases of DCIS are treated. Surgery (with or without radiation therapy) is recommended to treat DCIS. After surgery and radiation therapy, some people take hormone therapy. Learn more about treatments for DCIS. Learn about the risk of invasive breast cancer after treatment for DCIS.
Can DCIS progress to breast cancer?
DCIS is non-invasive, but without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive cancer over time. Left untreated, it’s estimated 20-50 percent of DCIS cases may progress to invasive breast cancer [ 1-5 ]. Health care providers cannot predict which cases of DCIS will progress to invasive breast cancer ...
How is DCIS diagnosed?
If a doctor sees the calcifications on your mammogram, he or she will recommend more tests, which could include a breast biopsy. During the biopsy, a doctor or other health care provider takes samples of cells or tissues from your body. The cells are examined by a pathologist — a doctor who checks for signs of disease in body tissues.
What is the treatment for DCIS?
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy — another surgery — to remove all of the cancer.
What should I expect after a DCIS diagnosis?
The outlook after DCIS diagnosis, Sun says, is encouraging. “With continued, rigorous monitoring, the prognosis for DCIS is excellent,” she explains. “Your doctor will recommend a regular screening schedule to guard against recurrence in the original breast, and to monitor the other breast for any signs of malignancy.
What is DCIS in mammography?
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently. Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside ...
How long does it take to survive DCIS?
It’s important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment. These treatments instead reduce the risk of breast cancer down the road.
Can hormone therapy be used for DCIS?
However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits. The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the study’s findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS.
Is DCIS a pre-invasive cancer?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, ...
Can DCIS be overtreated?
Since treatment of DCIS after surgery doesn’t improve survival, there is a growing concern that DCIS may be overtreated if the benefit of these treatments is outweighed by their impact on quality of life.
What is DCIS 2021?
January 21, 2021. Breast cancer screening with mammography or other tools (such as MRI) has increased the rates of diagnosis of very early breast cancers knowns as DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ).
How long does breast cancer last after a DCIS?
This study showed that increased cancer risk persisted for more than 15 years after a diagnosis of DCIS, and that more intensive therapy than lumpectomy alone — whether with mastectomy, radiation therapy, or endocrine therapy — reduced the risk of invasive breast cancer among women with DCIS. The lowest risk of invasive breast cancer was in women ...
Does DCIS increase the risk of breast cancer?
Overall, the researchers found that having DCIS more than doubled the risk of developing invasive breast cancer and increased the risk of dying of breast cancer by 70%, compared with the general population.
Is DCIS invasive?
As opposed to invasive breast cancers, DCIS cancers are confined to the local area and have not spread to deeper tissues or elsewhere in the body. With increased rates of diagnosis, there has been considerable controversy about the true risks of DCIS and the best treatments, with some suggesting that women are being overtreated for a condition ...
Should DCIS patients continue to have breast cancer?
While no details on surveillance strategies, such as regular mammograms or other exams, were presented in this study, based on these results, patients with DCIS should continue active surveillance for breast cancer for decades after their diagnosis.
What is the best treatment for DCIS?
Mastectomy. This type of surgery removes as much of the breast tissue as possible. If DCIS is present in more than one place in your breast, or if there is a large area of DCIS, mastectomy may be the best option for your treatment.
What is a DCIS?
The bottom line. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a preinvasive breast cancer that has a very high cure rate . DCIS generally doesn’t have any symptoms and is most often detected during a mammogram. Depending on the size and location of the affected cells, treatment of DCIS may involve a lumpectomy or mastectomy.
What is a biopsy of DCIS?
The report that comes back from the pathologists in the lab may contain some unfamiliar terms, like the ones described below: A biopsy will also be able to determine the hormone receptor status of the DCIS cells. Many times, DCIS will have receptors that respond to the hormones estrogen or progesterone.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses high energy beams to damage the DNA of cancer cells. This helps to destroy the abnormal cells. Radiation therapy is a localized type of treatment, which means it only targets the specific area that’s being radiated. This helps limit the damage to healthy cells.
Is DCIS a stage 0 cancer?
Because these abnormal cells haven’t spread beyond the milk duct to the surrounding tissue, it has a high cure rate. DCIS is considered a stage 0 or preinvasive cancer. In other words, it’s a precursor to breast cancer.
Is chemo needed for DCIS?
Also, since the abnormal cells are only found in your breast duct, chemotherapy is never needed for DCIS. Let’s take a closer look at some treatment options you and your healthcare team may decide to use, ...
Can DCIS cause breast cancer?
In some cases, DCIS may cause symptoms such as: discharge coming from a nipple that isn’t milk. a small lump. Most breast symptoms or changes aren’t caused by cancer, but tests are often needed to rule out the possibility of abnormal breast cells.
How to remove DCIS?
DCIS can often be removed via a lumpectomy— a surgery that spares the surrounding breast tissue. (In some cases, if DCIS has infiltrated multiple ducts or a tumor has grown large enough, removing the entire breast via mastectomy may be recommended.)
What is DCIS diagnosed with?
“Typically, the mammogram finds a calcification—a small cluster of cells with abnormal shapes and sizes—and then it is diagnosed after a biopsy, ” says Dr. Meyers.
How does DCIS affect breasts?
DCIS occurs when cells in one of those milk ducts have mutated and multiplied to look like cancer cells. About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS.
What is DCIS in breast cancer?
DCIS occurs when cells in one of those milk ducts have mutated and multiplied to look like cancer cells. About one in five newly diagnosed breast cancers is DCIS. Because those cells usually stay confined to the duct and do not spread to surrounding tissue, DCIS is also known as stage 0 breast cancer or sometimes pre-cancer. ...
How many DCIS cases were diagnosed in the 1990s?
In the 1990s, only about 15,000 to 18,000 DCIS cases were diagnosed per year, she says; now, that number has grown to more than 60,000, according to the American Cancer Society. “That’s because so many women are now getting mammograms, and the technology is so good, that we pick up very small lesions,” says Dr. White.
What happens after a woman is diagnosed with DCIS?
After a woman is diagnosed with DCIS and has the abnormal growth removed via surgery, the next step is to assess her risk of a recurrence or a more invasive cancer.
When do DCIS rates increase?
According to the American Cancer Society, DCIS rates increase with age, and peak around age 70 to 79.
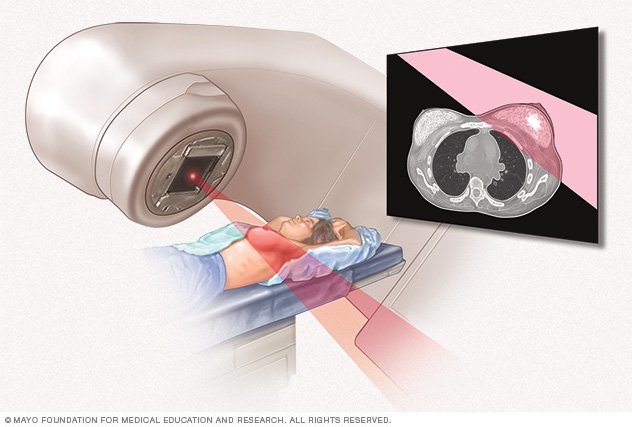
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: 1. Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy 2. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: 1. Lumpectomy only 2. Lumpec...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress. If you're distressed, you may have difficulty sleeping and find yourself constantly thinki…
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to: 1. Learn enough about DCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis and your pathology results. Use this information to research your treatment options. Look to reputable sources of information, such as the Nationa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual changes in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic mammogram images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound …