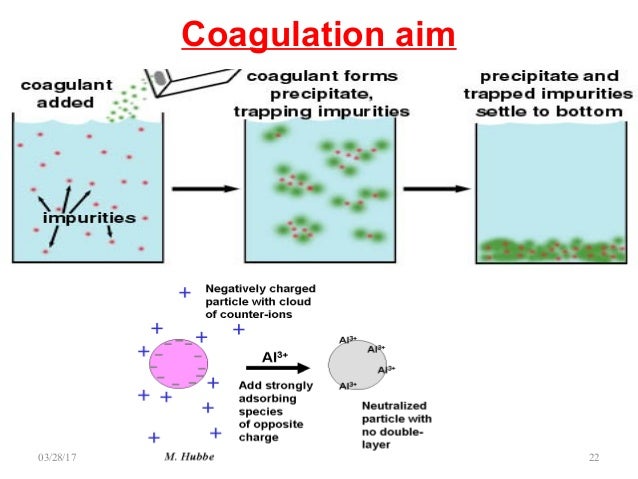
Coagulation water treatment process
- Coagulants. Coagulants are the chemicals that are used to removes tiny particles in water. ...
- Coagulation Mechanism. The colloidal particles carry electrical charges; normally negative charge. ...
- Factors affecting coagulation water treatment. ...
- Coagulation jar test. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is coagulation for water treatment?
Oct 15, 2021 · Ferric sulfate, aluminum sulfate, or ferric chloride, classed as aluminum or iron salts, are common coagulants for water treatment. A coagulant is a chemical that is used to remove suspended solids from drinking water. They are made up of positively charged molecules, which help to provide effective neutralization of water. Advertisement
What are flocculants and coagulants for wastewater treatment?
Coagulants In Wastewater Treatment are Formulated to Enhance Liquid-Solid Separation Coagulants In Wastewater Treatment plays a vital role in the wastewater treatment process, allowing for solids removal and dewatering, water clarification, lime …
Is coagulant and flocculant are same?
Coagulation is a chemical process in which a chemical compound, a “coagulant”, is added to the water, in order to destabilize the suspended particles and promote creation of flocs. A ‘Stable colloidal particle’ is a colloidal particle that remains as a separate entity in the water, i.e. in a dispersed state.
What is the process of water treatment?
Coagulation plays a vital role in the wastewater treatment process, allowing for solids removal and dewatering, water clarification, lime softening, and sludge thickening. With the help of other specialized chemicals and mechanical filtration methods, coagulants help companies maintain a consistent and reliable source of clean water to support ...

What is an example of a coagulant?
Examples of primary coagulants are metallic salts, such as aluminum sulfate (referred to as alum), ferric sulfate, and ferric chloride. Cationic polymers may also be used as primary coagulants.
What are water coagulants?
A coagulant is a chemical that is used to remove suspended solids from drinking water. They are made up of positively charged molecules, which help to provide effective neutralization of water.Oct 15, 2021
What is a coagulant and what is it used for?
Coagulants and flocculation processes are used to remove colloidal impurities: suspended particles such as bacteria, clay, silts, and organic matter from the contaminated water. This produces large flock aggregates that can be removed from the water in subsequent clarification/filtration processes.
What is the most common used coagulant in water treatment *?
aluminum sulfateAluminum and iron salts are the most commonly used inorganic coagulants in the wastewater treatment settings. These include based aluminum metals (aluminum chloride, aluminum sulfate, sodium aluminate) and iron based metals (ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate, ferric chloride) [13, 17, 18].
What does coagulant mean?
Coagulant meaning A substance that brings about coagulation. noun. An agent that causes a liquid or sol to coagulate.
What is the most commonly used coagulant?
Iron and aluminium salts are the most widely used coagulants but salts of other metals such as titanium and zirconium have been found to be highly effective as well.
What is coagulant made of?
The most common coagulants are salts of aluminum or trivalent iron, with aluminum being more commonly used.
How does coagulation work?
Blood clots and coagulation Blood vessels shrink so that less blood will leak out. Tiny cells in the blood called platelets stick together around the wound to patch the leak. Blood proteins and platelets come together and form what is known as a fibrin clot. The clot acts like a mesh to stop the bleeding.
What is the purpose of coagulation and flocculation in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
Is polymer a coagulant?
Polymers (long-chained, high-molecular-weight, organic chemicals) are becoming more widely used. These can be used as coagulant aids along with the regular inorganic coagulants.
What are the advantages of coagulants?
Another advantage is that they do not affect the pH of the treated water. Organic coagulants include polyamines, polyDADMACS, dicyandiamide and melamine formaldehyde. Inorganic coagulants are mostly based on metallic salts, such as iron sulfate and aluminum sulfate.
What is the purpose of coagulation?
Coagulation is a chemical process in which a chemical compound, a “coagulant”, is added to the water, in order to destabilize the suspended particles and promote creation of flocs. A ‘Stable colloidal particle’ is a colloidal particle that remains as a separate entity in the water, i.e. in a dispersed state.
What is precipitation coagulation?
Precipitation coagulation – Addition of relatively large doses of coagulants, usually aluminum or iron salts, results in their precipitation, due to solubility limitation. The colloid particles get trapped in the precipitant as it settles down and settle down with it.
What is the pH of a coagulant?
Therefore, each coagulant has an optimal pH range in which it works best. For example, Alum works best at a pH of 5.8-6.5, Aluminium chlorohydrate (ACH) works at a pH range of 6.5-7.5.
What are the four mechanisms of coagulation?
Coagulants act in four different mechanisms, that can act individually or simultaneously: 1 Compression of the double layer. 2 Electrostatic adsorption. 3 Adsorption and bridging. 4 Precipitation, or sweep-coagulation.
What is a coagulant in water?
A coagulant is used in colored, low pH or alkaline and low turbidity water. The optimum pH it generates helps in water purification. The coagulate dose used in purification produces a hydrolysis process that generates a pH suitable for coagulation.
Why is coagulant important?
The importance of a coagulant is: To destabilize the acidity of the fluid and cause flocs formation. Purify the fluid by removing unwanted a ctive metallic or non-metallic elements. An inappropriate coagulant dose might lead to corrosion due to acidity, hence one must follow guidelines by the governing authority.
What is a coagulant in water treatment?
Water treatment coagulants are comprised of positively charged molecules that, when added to the water and mixed, accomplish this charge neutralization. Inorganic, organic, or a combination of both coagulant types are typically used to treat water for suspended solids removal. When an inorganic coagulant is added to water containing ...
What is the most widely used class of organic coagulation chemicals?
Polyamine and PolyDADMAC. These are the most widely used classes of organic coagulation chemicals. They function by charge neutralization alone, so there is no advantage to the sweep-floc mechanism. Polyamines will generally treat higher turbidity raw water (approximately >20 NTU) effectively.
What are some examples of flocculants?
Examples of ChemTreat flocculants include low-, medium-, and high-molecular weight polymers.
Is aluminum sulfate a chemical?
It is manufactured as a liquid, and the crystalline form is dehydrated from the liquid. Alum is one of the most commonly used water treatment chemicals in the world.
Is aluminum chloride the same as alum?
Generally, aluminum chloride works similarly to alum, but is usually more expensive, hazardous, and corrosive. Because of this, it is normally a distant second choice to alum. ChemTreat has aluminum chloride available as a liquid.
What is a sweep floc?
This sweep-floc precipitate readily adsorbs organic materials such as oil and grease. The precipitate generally dewaters to low moisture concentration, making this choice of coagulant particularly well-suited to unit operations that generate hazardous sludge, such as DGF and IGF units in oil refineries. This self-precipitating chemistry is generally significantly more expensive to use than inorganic coagulant chemistry, but it can be economical when sludge removal and disposal costs are factored in.
Is ferric chloride a coagulant?
Ferric chloride is generally the least expensive inorganic coagulant, because it is generated as a waste material from steel-making operations (waste “pickle liquor”). However, it is by far the most corrosive and hazardous inorganic coagulant, and its use is limited to facilities equipped to handle it safely.
What is a coagulant aid?
Coagulant aids are used to improve the settling characteristics of floc produced by aluminium or iron coagulants. The coagulant aid most used for a number of years was activated silica; other aids included sodium alginates and some soluble starch products.
What is the most commonly used coagulant?
1.Aluminium coagulants. Aluminium sulphate is the most widely used aluminium coagulant. It is available in a number of solid grades such as block, kibbled or ground and is also available as a solution. In waterworks practice aluminium sulphate is frequently but incorrectly referred to as ‘alum’.
What is the process of removing suspended solids from water?
The process of removal of suspended solids in water by use of chemical agents is known as coagulation. Coagulation is carried out for the filtration and purification of water.
What is the best coagulant for cold water?
Sodium aluminate. Another widely used types of coagulants is sodium aluminate. Sodium aluminate is prepared from aluminium oxide stabilised with caustic soda; it is used with aluminium sulphate to coagulate very cold waters which would not coagulate successfully with aluminium sulphate alone.
Is aluminium hydroxide soluble in water?
The aluminium hydroxide floc is insoluble over relatively narrow bands of pH, which may vary with the source of the raw water. Therefore pH control is important in coagulation, not only in the removal of turbidity and colour but also to maintain satisfactory minimum levels of dissolved residual aluminium in the clarified water.