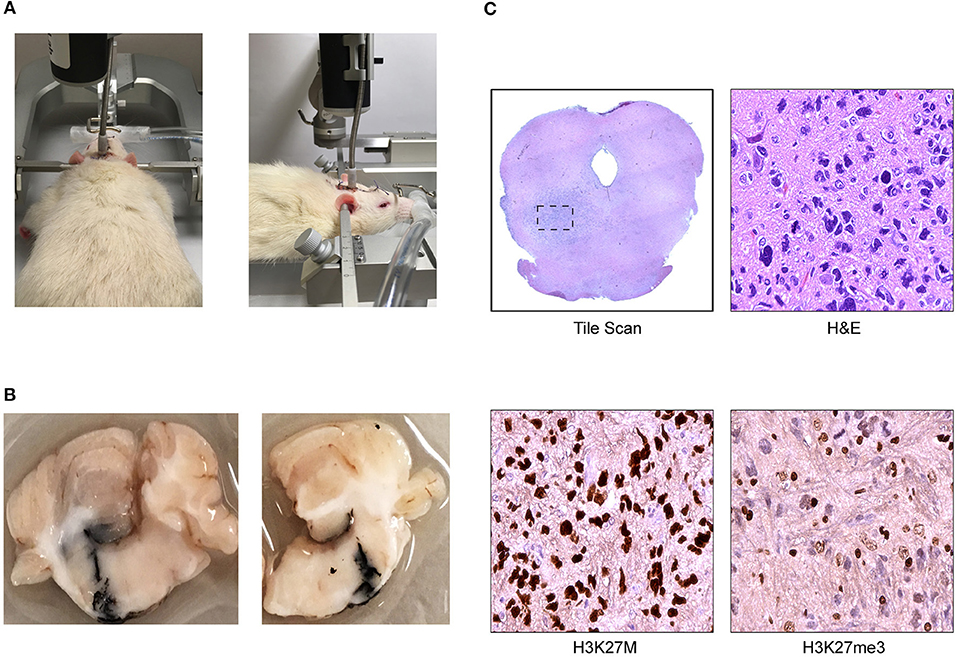
What is CED and how does it work?
What does CED involve? CED involves an operation to implant up to 4 very narrow catheters (hollow tubes) into the brain. The chemotherapy drugs are delivered through these, directly into the tumour. The blood-brain barrier then becomes an advantage, as it helps to keep the drugs within the brain.
Is CED the treatment of choice for the most serious neurological disorders?
Establishing the viability of CED as a recognised treatment of choice for many of the most serious neurological disorders is the current focus of Funding Neuro’s work.
Can CED be used to treat DIPG?
Standard treatment for DIPG is radiotherapy, but this can cause long-term effects, particularly if given to children under 3 years. A technique, such as CED, that can avoid some of these effects is therefore creating interest.
Are there any significant responses to CED clinical trials?
Despite these limitations and uncertainties, significant responses have been observed in all of the CED clinical trials described below.
What is CED therapy?
CED, or convection enhanced delivery, injects agents directly into the tumor. It relies on placing a small catheter in the brain tumor tissue and using a slow rate of infusion. This is the most immediate method for achieving very high concentrations of drug into the tissue WITHOUT any appreciable systemic exposure.
What is the survival rate for glioblastoma?
Glioblastoma Facts & Figures It is estimated that more than 10,000 individuals in the United States will succumb to glioblastoma every year. The five-year survival rate for glioblastoma patients is only 6.8 percent, and the average length of survival for glioblastoma patients is estimated to be only 8 months.
How does convection enhanced delivery work?
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) is a local drug delivery technique that bypasses the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and enhances drug distribution by utilizing hydraulic pressure to deliver infusate directly into a target region.
What is convection enhanced delivery CED?
Convection Enhanced Delivery (CED) is a therapeutic strategy that was developed to facilitate targeted delivery of pharmaceuticals to the brain. The CED procedure involves a minimally invasive surgical exposure of the brain, followed by placement of small diameter catheters directly into the brain tumor.
Can glioblastoma go into remission?
In remission, symptoms may let up or disappear for a time. Glioblastomas often regrow. If that happens, doctors may be able to treat it with surgery and a different form of radiation and chemotherapy.
What triggers glioblastoma?
The causes of glioblastoma are largely unknown. However, it often occurs in people with rare genetic conditions - Turcot syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1 and Li Fraumeni syndrome - due to mutations in a specific gene that causes many of the characteristic features of glioblastoma.
What is convection therapy?
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) is a promising technique that generates a pressure gradient at the tip of an infusion catheter to deliver therapeutics directly through the interstitial spaces of the central nervous system.
What does enhanced delivery mean?
Information about convection enhanced delivery The intervention. Convection enhanced delivery (CED) is a method of administering medicines directly into the brain through a delivery system consisting of small tubes, called catheters, connected to a set of pumps through a metal access port fixed to the skull.
What is Intraparenchymal delivery?
1) Intraparenchymal Delivery of AAV Intraparenchymal, also referred to as intracranial, refers to directly injecting AAV vectors in to the brain parenchyma, or brain tissue.
What is CED in a tumor?
CED, or convection enhanced delivery, injects agents directly into the tumor. It relies on placing a small catheter in the brain tumor tissue and using a slow rate of infusion. This is the most immediate method for achieving very high concentrations of drug into the tissue WITHOUT any appreciable systemic exposure.
When was CED first used?
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) is a novel drug delivery method first developed by a research group directed by Edward Oldfield at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders (NINDS) in the early 1990s.
What drugs are being studied for delivery through CED?
Drugs being studied for delivery through CED include conventional chemotherapy drugs, novel small molecule agents and macromolecules such as therapeutic antibodies, immunotoxins, and viral vectors, some of which would otherwise never gain access to the brain.
What are the functions of endothelial cells?
Endothelial cells joined by tight junctions restrict the entry of microscopic objects (e.g., bacteria) and large or hydrophilic molecules into the CSF, while allowing the diffusion of small hydrophobic molecules (O2 , certain hormones, CO2, etc.).
Can CED be used for brain tumors?
Theoretically, any antineoplastic agent can be delivered through CED for the treatment of brain tumors, including standard chemotherapeutic agents and novel macromolecules such as monoclonal antibodies and viral vectors. One unresolved issue is that CED, in its current form, is a surgery and typically performed as a single session. It is unknown how long the infused drugs remain at therapeutic concentrations after a single session of CED. Imaginatively, it is more like a bolus dose, and predictably only a portion of the cancer cells are killed by such a bolus dose and the remaining cancer cells will continue to grow, ultimately resulting in failure of treatment.
Can drugs be injected into the brain?
Drugs can also be injected directly into the CSF, and the drug is usually only able to reach a shallow layer of the brain using this technique. Drug-containing polymers and microchips are a more recent development and they can be embedded at the time of surgical resection of brain tumors.
Is chemo administered locally or systemically?
Blood-Brain Barrier. Chemotherapy may be administered systemically or locally. In systemic chemotherapy, the drug is administered orally or intravenously. An important limitation of systemic chemotherapy in the treatment of brain tumors is the existence of the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
What is a CED in a brain tumor?
CED is an experimental technique for directly infusing drugs into a brain tumor. This increases drug efficacy while reducing side effects to healthy brain tissue and the rest of the body. With CED, a small hole is made in the patient’s skull to insert a cannula (a thin tube) that extends to the site of the tumor.
Can chemotherapy be injected into the brain?
Convection Enhanced Delivery. Using standard chemotherapy on brain tumors is challenging, considering that many of these drugs (administered as a pill, or injected intravenously) do not enter the brain easily. Increasing dosages would not work either, since these medications would reach toxic concentrations in the body before reaching effective ...
CED (Cathode Electro Deposition)
Cathode Electro Deposition is most advanced and environment friendly Water Based coating to be done on metal components.
Electro-Deposition Coating
Electro-deposition of primer coating has become universal for a modern automotive paint shop. In ED, charged particles from the paint emulsion move to Anode (AED) or Cathode (CED) under electrical forces. The direct current established through the bath makes the pigment and resin base of the paint wander towards the body surfaces.
Treatment Methods
Dr. Benjamin Caplan’s practice is highly sought out for those considering medicinal cannabis as a treatment plan due to his expertise in the area. He creates a personalized treatment plan for each patient based on individual needs and goals.
Vaporization
One common misconception concerning the administration of medicinal cannabis through inhalation is that it utilizes a flame. This should actually be avoided because combustion unnecessarily introduces harmful toxins.
Edible
For many patients, ingestion is the preferred method of medicinal cannabis consumption. The usage of edible products and/or tinctures allows patients to be treated without the necessity of inhalation.
What is a CED cycle?
A CED cycle is considered "completed" when CMS removes a requirement for study participation as a condition of coverage for one or more indications of an item or service. For CED under an NCD, the publication of the final decision is the effective date for the close of a CED cycle performed under that NCD.
When was the CMS CED released?
CMS released an updated guidance document on November 20, 2014 that describes coverage with evidence development (CED). CMS, as part of the national coverage determination (NCD) may determine coverage of an item or service only in the context of a clinical study.
Diagnosis
The doctor will ask questions about your medical history, do a physical exam and order routine blood tests. He or she may suggest one or more diagnostic tests as well, including:
Treatment
Treatment for coronary artery disease usually involves lifestyle changes and, if necessary, drugs and certain medical procedures.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Lifestyle changes can help you prevent or slow the progression of coronary artery disease.
Alternative medicine
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of unsaturated fatty acid that's thought to reduce inflammation throughout the body, a contributing factor to coronary artery disease. However, some studies haven't found a benefit. More research is needed.
Preparing for your appointment
If you know you have symptoms of or risk factors for coronary artery disease, you're likely to see your primary care doctor. Eventually, you may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist).

Catheter Design For Ced
Tip Configuration
Monitoring Drug Distribution
Predicting and Planning Ced Distribution
Safety of Ced in The Brainstem
Therapeutic Efficacy of Ced
Ced Clinical Trials For The Treatment of Brain Tumors
- Theoretically, any antineoplastic agent can be delivered through CED for the treatment of brain tumors, including standard chemotherapeutic agents and novel macromolecules such as monoclonal antibodies and viral vectors. One unresolved issue is that CED, in its current form, is a surgery and typically performed as a single session. It is unknown ho...