How can I shrink a Bartholin cyst at home?
Soaking in a few inches of warm water — either in a tub or sitz bath — four times a day for a few days may resolve even an infected Bartholin cyst. Taking over-the-counter painkillers, such as naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), acetaminophen (Tylenol), or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), may help with discomfort.
What is the fastest way to cure a Bartholin cyst?
TreatmentSitz baths. Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) several times a day for three or four days may help a small, infected cyst to rupture and drain on its own.Surgical drainage. You may need surgery to drain a cyst that's infected or very large. ... Antibiotics. ... Marsupialization.
How do you get a Bartholin cyst to go down?
soaking the cyst for 10 to 15 minutes in a few inches of warm water (it's easier in the bath) – it's best to do this several times a day for 3 or 4 days if possible. holding a warm compress (a flannel or cotton wool warmed with hot water) against the area. taking painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
Do Bartholin cysts go away naturally?
A Bartholin cyst develops when a blockage occurs in a Bartholin gland in the vagina. This blockage causes a lump that can cause irritation and pain during walking, sitting or sex. Bartholin cysts can resolve on their own over time. If it becomes infected, it may need treated by a healthcare provider.
What is the main cause of Bartholin cyst?
Experts believe that the cause of a Bartholin's cyst is a backup of fluid. Fluid may accumulate when the opening of the gland (duct) becomes obstructed, perhaps caused by infection or injury. A Bartholin's cyst can become infected, forming an abscess.
How long does it take for a Bartholin cyst to burst?
Bartholin gland abscesses usually develop over two to four days and can become larger than 8 cm. They tend to rupture and drain after four to five days.
Is Bartholin cyst caused by stress?
Can a Bartholin's cyst be caused by stress? Stress isn't a known cause of Bartholin's cyst. In fact, the cause of most Bartholin's cysts isn't known, although some cases can be caused by an infection, physical damage to the vagina and area around it, and fluid or mucus build-up around a Bartholin's gland.
How long does a Bartholin cyst last?
It can stay in place for up to 6 weeks. You'll feel better right away after the fluid is gone. But you may need to take pain medication for several days afterward. Keep in mind that a Bartholin's cyst or abscess may come back and need treatment again.
Is Turmeric Good for Bartholin cyst?
Mix about 1/2 a tablespoon of coconut oil with as much turmeric powder as will mix into it. Cover the cyst In a thick layer of the mixture and place a gauze pad over it. Sleep with it on overnight. Turmeric will stain and the oil melts so wear underwear you don't care about and use an old bedsheet.
Can I put apple cider vinegar on my Bartholin cyst?
Apple cider vinegar (ACV): Typically, people who use ACV to treat a Bartholin's abscess dilute it and apply it to the cyst with a cotton ball.
What happens if a Bartholin cyst goes untreated?
If a Bartholin's abscess worsens and goes untreated, the infection could spread to other organs in your body. The infection may enter your bloodstream, a condition called septicemia. This condition is dangerous because the infection can be carried throughout your whole body.
Can a Bartholin cyst go away without bursting?
If a Bartholin abscess bursts, it may resolve on its own in a few days without treatment. However, it is advisable to visit the doctor to avoid the spread of the infection. Your doctor will usually advise you to soak the labia in warm water (sitz bath) and prescribe you antibiotics and pain medications.
What is a Bartholin cyst?
What is a Bartholin’s Cyst? A Bartholin’s cyst is a relatively common vaginal complaint in women. The Bartholin’s glands are situated at either side of the opening of the vagina. The glands are responsible for secreting a fluid that lubricates the vagina.
What is the best oil for Bartholin cyst?
As with apple cider vinegar, the internet is full of anecdotal evidence from women who have successfully treated their Bartholin’s cyst with tea tree oil .
How to treat a cyst in the tub?
A sitz bath can be prepared with warm water filling just a few inches of your bathtub. Simply taking a daily soak is often sufficient to resolve an infected cyst. If you have undergone a surgical procedure to treat your cyst, a frequent soak in a sitz bath is especially important.
Why does Bartholin's cyst form?
While the exact cause of a Bartholin’s cyst is uncertain, experts believe they are caused by a fluid backup which obstructs the gland. This may be caused by injury or infection. When the cyst becomes infected, it can cause an abscess to form.
What happens if a cyst gets infected?
However, if the fluid in the cyst gets infected, pus can collect and cause an abscess to develop. If the cyst is infected, a visit to the doctor is recommended and a course of antibiotics is usually prescribed.
What happens if you leave a Bartholin cyst untreated?
If a Bartholin’s cyst is left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications like infection. The cyst can fill up with pus and bacteria and become an abscess. If an abscess bursts within the body, severe complications can occur and you are at a much greater risk of septicaemia (blood poisoning).
Why does my vagina have a cyst?
The cyst is believed to be caused by the obstruction of the glands causing a back up of fluid. A Bartholin’s cyst is oftenj painless but pain and infection can occur.
How to diagnose Bartholin cyst?
To diagnose a Bartholin cyst, a doctor will do a physical exam to look at the vagina. If the cyst produces discharge, your doctor may test the fluid for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or other bacterial infections. In women older than age 40, doctors may perform a test called a biopsy to rule out cancer of the vulva.
What are the symptoms of a Bartholin cyst?
If a Bartholin cyst forms an abscess (infection), symptoms may include pain, change in size with swelling, drainage, redness and fever. Larger cysts that aren't infected may cause symptoms including: Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
What is a cyst in the vagina?
A Bartholin cyst develops when a blockage occurs in a Bartholin gland in the vagina. This blockage causes a lump that can cause irritation and pain during sitting, walking or sex.
Where are the Bartholin glands located?
The Bartholin glands are two small glands located on either side of the opening of the vagina. The glands produce mucus that helps lubricate (moisten) the vagina. A Bartholin cyst occurs when a blockage happens in the openings of one of these glands, causing the mucus to build up and form a lump. Bartholin cysts occur in about 3% of all women.
How to treat a cyst that is small and doesn't appear infected?
However, your doctor may recommend watching it for growth. If the area has signs of infection and is painful, your doctor may recommend self-care treatments including sitting in a warm bath a few times a day for several days.
Can Bartholin help with abscess?
If symptoms persist or the cyst grows, then you may be developing a Bartholin's abscess. Your doctor may want to drain the abscess or give you antibiotics.
Is Bartholin cyst a non-profit?
The chance of developing a Bartholin cyst decreases after menopause. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission.
Why does Bartholin's cyst form?
Experts believe that the cause of a Bartholin's cyst is a backup of fluid. Fluid may accumulate when the opening of the gland (duct) becomes obstructed, perhaps caused by infection or injury. A Bartholin's cyst can become infected, forming an abscess.
What happens if you have a Bartholin cyst?
A Bartholin's cyst or abscess is common. Treatment of a Bartholin's cyst depends on the size of the cyst, how painful the cyst is and whether the cyst is infected. Sometimes home treatment is all you need.
What is a lump on the side of the vagina?
A tender, painful lump near the vaginal opening. Discomfort while walking or sitting. Pain during intercourse. Fever. A Bartholin's cyst or abscess typically occurs on only one side of the vaginal opening.
How do you know if you have a Bartholin cyst?
Symptoms. If you have a small, noninfected Bartholin's cyst, you may not notice it. If the cyst grows, you might feel a lump or mass near your vaginal opening. Although a cyst is usually painless, it can be tender. A full-blown infection of a Bartholin's cyst can occur in a matter of days.
What is the name of the gland that secretes fluid to lubricate the vagina?
The Bartholin's (BAHR-toe-linz) glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. These glands secrete fluid that helps lubricate the vagina. Sometimes the openings of these glands become obstructed, causing fluid to back up into the gland. The result is relatively painless swelling called a Bartholin's cyst.
How to treat a lump in the vagina?
Call your doctor if you have a painful lump near the opening of your vagina that doesn't improve after two or three days of self-care — for instance, soaking the area in warm water (sitz bath). If the pain is severe, make an appointment with your doctor right away.
Where is the cyst on the vagina?
Bartholin's cyst. Bartholin's cyst. The Bartholin's glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. They secrete fluid that helps lubricate the vagina. Sometimes the ducts of these glands become obstructed and fluid backs up, forming a cyst.
How to diagnose Bartholin's cyst?
To diagnose a Bartholin's cyst, your doctor may: Ask questions about your medical history. Perform a pelvic exam. Take a sample of secretions from your vagina or cervix to test for a sexually transmitted infection. Recommend a test of the mass (biopsy) to check for cancerous cells if you're postmenopausal or over 40.
How to drain a cyst that is infected?
Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz bath) several times a day for three or four days may help a small, infected cyst to rupture and drain on its own. Surgical drainage. You may need surgery to drain a cyst that's infected or very large. Drainage of a cyst can be done using local anesthesia or sedation.
How long does a catheter stay in place for cyst drainage?
The catheter stays in place for up to six weeks to keep the incision open and allow complete drainage. Antibiotics.
Do you need antibiotics for cysts?
But if the abscess is drained properly, you may not need antibiotics. Marsupialization.
Can Bartholin's cyst be treated?
Often a Bartholin's cyst requires no treatment — especially if the cyst causes no signs or symptoms. When needed, treatment depends on the size of the cyst, your discomfort level and whether it's infected, which can result in an abscess.
How to get rid of Bartholin cyst?
The most effective way to get rid of a persistent Bartholin cyst is via surgical drainage. You can see your family doctor, who may do it themselves (if they are experienced with the procedure). Alternatively, they may refer you on to another physician to have the procedure performed.
What to do if Bartholin cyst persists?
Alternatively, if the cyst persists, you may opt for medical treatments such as pain medications, surgical drainage, marsupialization, and/or antibiotics if your cyst is concurrently infected. After treating your Bartholin cyst, it is equally important to take steps to ensure proper recovery and full healing. Steps.
How does the Bartholin gland work?
The gland's primary function is to secrete mucus through the Bartholin duct to create vulvar and vaginal lubrication. If the opening of the duct becomes obstructed, the mucus accumulates, causing swelling next to the obstruction. There are a variety of strategies you can try to get rid of a Bartholin cyst.
Why do you need a catheter for Bartholin cysts?
This is usually only done for cases of recurrent Bartholin cysts. The purpose of the catheter is to keep the cyst open, so that any further fluid that accumulates can drain out immediately. Keeping the cyst open prevents fluid buildup and, as such, allows the cyst to naturally heal.
How to remove Bartholin gland?
If you have a particularly bad cyst, or have had recurrent cysts, one of the "last resort" treatments is to have your Bartholin gland completely removed surgically, or removed via a laser procedure. Both of these are simple procedures that do not require an overnight hospital stay.
What to do if you suspect a Bartholin cyst?
If you suspect that you may have a Bartholin cyst, it is important to see your family doctor for a pelvic exam to confirm the diagnosis. In addition to a pelvic exam, your doctor will likely test for STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
Is Bartholin cyst asymptomatic?
This is more complicated to treat than a simple cyst, so it is best to be proactive. If you are under 40 and you the cyst is asymptomatic (no pain, fever, etc.), then often no medical intervention is necessary. If you notice signs of a fever alongside your Bartholin cyst, see your doctor for treatment.
How to diagnose Bartholin cyst?
To accurately diagnose a Bartholin’s cyst, the doctor might do the following: Ask important questions about your medical history. Conduct a pelvic examination. Get samples of your secretions from the cervix or the vagina to check for any sexually transmitted infections.
Why does a cyst form in the ducts of the Bartholin gland?
A Bartholin’s cyst occurs when the duct found in the Bartholin’s gland is blocked. When this happens, a fluid filled cyst develops. Sometimes the cyst might be caused by an infection, but it is not exactly an infection. The Bartholin’s glands, known as major vestibular glands are a pair of glands that are located between the vagina and the vulva.
Why do Bartholin cysts form?
Research shows that the course of the Bartholin cysts is an accumulation of lubrication fluid. This generally happens when the glands become obstructed . The obstruction may be caused by an infection or an injury. Sometimes the cyst might become infected, forming an abscess.
How long does it take for a Bartholin cyst to develop?
Most of the time these cysts are painless, but they can be tender. However, a full blown Bartholin cyst infection can develop in just a matter of days. When the cyst becomes infected, the patient will experience the following: A tender and sometimes very painful lump close to the vaginal opening.
What is the function of the Bartholin glands?
Functions of the Bartholin glands. The main purpose of the glands is to produce lubrication after stimulation. Together with the vestibular glands, the Bartholin glands help in sexual intercourse by decreasing friction. The lubrication produced goes from the Bartholin’s glands ducts into the lower entrance of the vagina.
What to do if cyst is drained?
Antibiotics . If the doctor determines that the cyst is infected, or the patient has a sexually transmitted infection, a dose of antibiotics will be prescribed. However, if the cyst is drained well, the patient doesn’t require the antibiotics. .
What happens when you get a Bartholin cyst?
When a blockage happens in the ducts, the lubrication accumulates, making the tubes expand, and the result is a Bartholin’s cyst. When someone gets the cyst, the chances of getting an infection in the area are high, and an abscess can also develop. According to the National Health Service in the United Kingdom, ...
What is a Bartholin cyst?
In a woman’s body, Bartholin glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. The function of these glands is to secrete fluid that lubricates the vagina. These glands are present in the posterior part of the vagina. They are homologous to the bulbourethral glands present in males.
Signs and symptoms of Bartholin cyst
The Bartholin cyst is painless as it is merely the accumulation of fluid. If you have a non-infected, small Bartholin cyst, then they might not notice it or fail to diagnose it as it does not cause any signs or symptoms. However, if the cyst is not detected or treated at an early stage, it will grow.
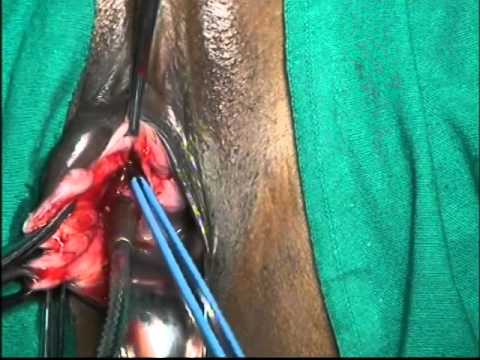
How to Burst A Bartholin Cyst at Home
You can easily drain small and painless Bartholin cysts at home. There are a few easy procedures that any individual can follow at home without medical personnel. An individual can quickly learn these procedures by watching popping a Bartholin cyst video.
Causes of Bartholin cyst
Bartholin cyst occurs due to the obstruction of the opening of Bartholin’s gland. Infections or injuries may obstruct the opening of the Bartholin gland. Various types of bacteria may cause infection, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.
Complications of Bartholin cyst
There is a possibility of recurrence of Bartholin’s cyst even after it is treated. For this reason, a person who has suffered from this can again face the same problem. If a person learns how to burst a Bartholin cyst at home, then they can easily get rid of it every time it occurs.
Diagnosis
If the Bartholin’s cyst is painless and small, you cannot notice it as there is no change in the body. This results in delayed diagnosis of the cyst. But if the cyst is painful, then you can detect it quickly. When you feel pain or uneasiness, consult the doctor as soon as possible and get a check-up.
Conclusion
A person should not hesitate to perform this procedure at home. It is usual to feel tense to achieve such a procedure without the help of medical personnel, but one should keep in mind that it is a straightforward procedure. Before performing this procedure, one should attain sufficient knowledge about how to burst a Bartholin cyst at home.
What happens if a Bartholin duct is blocked?
If a Bartholin duct gets blocked, fluid builds up in the gland and it creates a cyst. These cysts can typically be pea sized to marble size and are generally not treated as long as there are no unpleasant symptoms. They can also go away by themselves unless they are so large they cause discomfort.
Is Bartholin cyst treatment safe?
However, this is an inexpensive and very safe treatment to test. It’s certainly much less painful and intrusive than the standard medical treatments which many times don’t help at all. WHERE TO GET TREATED . One of our awesome followers said that Planned Parenthood would treat a Bartholin cyst.
Is bartholin cyst painful?
A Bartholin cyst is very painful and difficult to treat and many women have had little success with traditional medicine. Well, we’ve got a Bartholin Cyst home treatment that is inexpressive and easy to do and it works. This treatment was used by someone I know personally and I followed along with them during the entire duration of their condition.

Overview
- The Bartholin's (BAHR-toe-linz) glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. These glands secrete fluid that helps lubricate the vagina.Sometimes the openings of these glands become obstructed, causing fluid to back up into the gland. The result is relatively painless swelling called a Bartholin's cyst. If the fluid within the cyst becomes infected, you may develop …
Treatment
- Home treatment of Bartholin's cysts and abscesses involves sitz baths, which promote drainage. Special sitz bath basins are available, but the simplest method is to sit in the bathtub in a few inches of warm water. The water should not be so hot as to burn the skin, but it should be fairly warm. These soaks should be done for 10-15 minutes at a time, 3-4 times daily. This treatment i…
- Often a Bartholin's cyst requires no treatment — especially if the cyst causes no signs or symptoms. When needed, treatment depends on the size of the cyst, your discomfort level and whether it's infected, which can result in an abscess.Treatment options your doctor may recommend include: 1. Sitz baths. Soaking in a tub filled with a few inches of warm water (sitz b…
Causes
- Experts believe that the cause of a Bartholin's cyst is a backup of fluid. Fluid may accumulate when the opening of the gland (duct) becomes obstructed, perhaps caused by infection or injury.A Bartholin's cyst can become infected, forming an abscess. A number of bacteria may cause the infection, including Escherichia coli (E. coli) and bacteria that cause sexually transmitted infecti…
- Bartholin's abscesses can be caused by any of a number of bacteria. These include bacterial organisms that cause sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea as well as bacteria normally found in the intestinal tract, such as Escherichia coli. It is common for these abscesses to involve more than one type of organism.
Symptoms
- If you have a small, noninfected Bartholin's cyst, you may not notice it. If the cyst grows, you might feel a lump or mass near your vaginal opening. Although a cyst is usually painless, it can be tender.A full-blown infection of a Bartholin's cyst can occur in a matter of days. If the cyst becomes infected, you may experience: 1. A tender, painful lump near the vaginal opening 2. Dis…
Management
- If the cyst is small and not causing a problem no action should be taken. The exception is in patients over 40 years of age in whom histology must be obtained to exclude malignancy. If there are no features of infection, antibiotics are not required and culture is usually sterile. Simple incision of the cyst often results in recurrence and is not recommended.For an abscess, incisio…
Prevention
- There's no way to prevent a Bartholin's cyst. However, safer sex practices — in particular, using condoms — and good hygiene habits may help to prevent infection of a cyst and the formation of an abscess.
Diagnosis
- Sometimes cultures are taken to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection and to check for sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. These cultures simply involve taking a swab either from the material drained from the abscess or from another area such as the cervix. Results of these tests are not available until about 48 hours later, so they do …
- To diagnose a Bartholin's cyst, your doctor may: 1. Ask questions about your medical history 2. Perform a pelvic exam 3. Take a sample of secretions from your vagina or cervix to test for a sexually transmitted infection 4. Recommend a test of the mass (biopsy) to check for cancerous cells if you're postmenopausal or over 40If cancer is a concern, your doctor may refer you to a g…
History
- 1. Small cysts may be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally - for example, when performing a routine cervical smear. 2. Onset of an abscess is rapid over a matter of days or even hours. 3. There is initially labial oedema before a swelling forms. 4. The swelling may be very painful. The woman may find it uncomfortable to walk or sit. There may be superficial dyspareunia. 5. If the c…
Epidemiology
- Cysts or abscesses are usually unilateral. Bartholin's cysts occur in about 3% of women.They most commonly present in women of childbearing age. If they present after the age of 40 a malignant cause must be considered, although this is rare.
Prognosis
- There is a high rate of recurrence which varies from 0-38%, depending on the type of surgery used. Recurrence is highest after incision and drainage and is low after marsupialisation.Complications after marsupialisation include haematoma, dyspareunia and infection.Complications after balloon catheter insertion include infection, abscess recurrence, bleeding, pain from having the catheter …