Acls cardioversion afib Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter (continued) Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter If ≤48 hours: — DC cardioversion or amiodarone or others If >48 hours: — Anticoagulate × 3 wk, this IS a shockable rhythm Apply defibrillator pads (or paddles) and shock the ] Synchronized cardioversion
Full Answer
How long are the guidelines for atrial fibrillation?
Although the guidelines for atrial fibrillation are about 170 pages long, there are some basic decisions outlined in the treatment guidelines that every AFib patient should understand. How will I prevent stroke?
When is atrial fibrillation a problem for ACLS?
For ACLS, atrial fibrillation becomes a problem when the fibrillation produces a rapid heart rate which reduces cardiac output and causes symptoms or an unstable condition.
What is the appropriate voltage for cardioversion of unstable atrial fibrillation?
The appropriate voltage for cardioverting unstable atrial fibrillation is 120-200 J. Cardioversion of stable atrial fibrillation should be performed with caution if the arrhythmia is more than 48 hours old and no anticoagulant therapy has been initiated due to the risk of emboli that can cause MI and stroke.
What are the treatment options for atrial fibrillation (AFIB)?
For the purposes of ACLS atrial fibrillation is treated when the arrhythmia/tachyarrhythmia produces hemodynamic instability and serious signs and symptoms. For the patient with unstable tachycardia due to a tachyarrhythmia, immediate cardioversion is recommended. Drugs are not used to manage unstable tachycardia.

How do you treat atrial fibrillation in ACLS?
Medications that are used in the treatment of new onset stable atrial fibrillation include diltiazem (calcium channel blocker) or metoprolol (beta-blocker). These medications are given to control rate. Depending on the severity of the patient's symptoms, these medications can be given intravenously or orally.
What is the first line treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are first-line agents for rate control in AF. These drugs can be administered either intravenously or orally. They are effective at rest and with exertion. Intravenous diltiazem or metoprolol are commonly used for AF with a rapid ventricular response.
What is the recommended approach to treatment of atrial fibrillation?
Cardioversion. Cardioversion may be recommended for some people with atrial fibrillation. It involves giving the heart a controlled electric shock to try to restore a normal rhythm. Cardioversion is usually carried out in hospital so the heart can be carefully monitored.
What is the standard of care for atrial fibrillation?
The AHA/ACC/HRS guideline recommends treating AF with an antiarrhythmic drug, to maintain sinus rhythm. Once risks have been assessed (class I recommendation), choices include amiodarone, dofetilide, dronedarone, flecainide, propafenone, and sotalol, depending on underlying heart disease and comorbidities.
What is PAF with RVR?
A-fib with RVR is the common term for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. A common disorder that involves a rapid heart rate, it requires medical attention and, in many cases, hospitalization.
How do you stop AFib immediately?
6 Ways to Stop an AFib EpisodeEngage in deep, mindful breathing. ... Get some exercise. ... Valsalva maneuver. ... Practice yoga. ... Put some cold water on your face. ... Contact a health professional.
When do you start rate control in AF?
Current guidelines define adequate rate control in atrial fibrillation as maintenance of the ventricular rate response between 60 and 80 beats/min at rest and between 90 and 115 beats/min during moderate exercise.
How do you manage AFib with RVR?
Drugs called beta-blockers. They control your heart rate. Your doctor will get them to you in your vein (they'll call this intravenously) if you have AFib with RVR....The most commonly used drugs are:Esmolol (Brevibloc)Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol)Propranolol (Inderal, Innopran)
What two treatments may help a patient with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation treatment may involve: Medications. Therapy to reset the heart rhythm (cardioversion) Surgery or catheter procedures....Medications used to treat atrial fibrillation include:Beta blockers. ... Calcium channel blockers. ... Digoxin. ... Anti-arrhythmic medications. ... Blood thinners.
Is amiodarone used for AFib?
Article Sections. Amiodarone is a potent antiarrhythmic agent that is used to treat ventricular arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. The drug prevents the recurrence of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias and produces a modest reduction of sudden deaths in high-risk patients.
How long does atrial fibrillation last?
Persistent atrial fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation that lasts longer than seven days in duration, requiring intervention or treatment to manage. If these persistent episodes of atrial fibrillation occur with an uncontrolled and rapid ventricular rate, remodeling may occur within the heart that may lead to dilated cardiomyopathy.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is a cardiac arrhythmia also known as AFib, or AF. During atrial fibrillation, electrical signals within the atria have deteriorated. This deterioration results in a cardiac rhythm change, such that the heart operates in a disorganized manner where the atria fibrillate, or quiver. The signals from the atria are then sent to the ventricles in a similarly disorganized way, which leads to irregular ventricular contractions.
What is considered a candidate for cardioversion?
A patient is a candidate for cardioversion if they are experiencing symptomatic tachycardia with a heart rate of 150 beats per minute or more and the patient is considered symptomatically and hemodynamically unstable. However, it is important to note that patients may be symptomatic at heart rates less than 150 beats per minute, particularly if they have existing cardiovascular disease, other risk factors, or potential contributory causes as described above. The healthcare provider must have an understanding of when cardioversion should be utilized, which medications are indicated for cardioversion, how to prepare the patient for cardioversion, and how to operate the cardioverter. The ACLS Electrical Cardioversion Algorithm should be followed to initiate cardioversion in a patient.
What is stable tachycardia?
Stable tachycardia occurs when the patient has an increased heart rate (more than 100 beats per minute) without any signs of hemodynamic instability; systems within the body remain uncompromised. A patient with stable tachycardia does not have any underlying cardiac electrical factors that would cause the identified rhythm. With stable tachycardia, there is time to evaluate and determine treatment options. Unstable tachycardia occurs when the patient’s markedly rapid heart rate and uncoordinated cardiac contractions contribute to symptoms or hemodynamic instability, due to decreased cardiac output. With unstable tachycardia, it is imperative to move quickly when evaluating and managing the patient’s condition to prevent clinical deterioration of the patient. Patients with atrial fibrillation may present with symptoms or be asymptomatic. If a heart rate is less than 150 beats per minute, it is widely thought that any symptoms present are unlikely to be caused by tachycardia unless the patient has altered ventricular function.
Why is atrial fibrillation irregular?
In atrial fibrillation, there is a rapid heart rate without any regular or predictable rhythm pattern, which is why it is known as an arrhythmia that is irregularly irregular.
How to determine block in AV node?
Blocking in the AV node can be determined by counting the number of flutter waves prior to each QRS complex. For example, if there are two flutter waves prior to a QRS complex, then it is considered a 2:1 block
What is the primary assessment of cardiac life support?
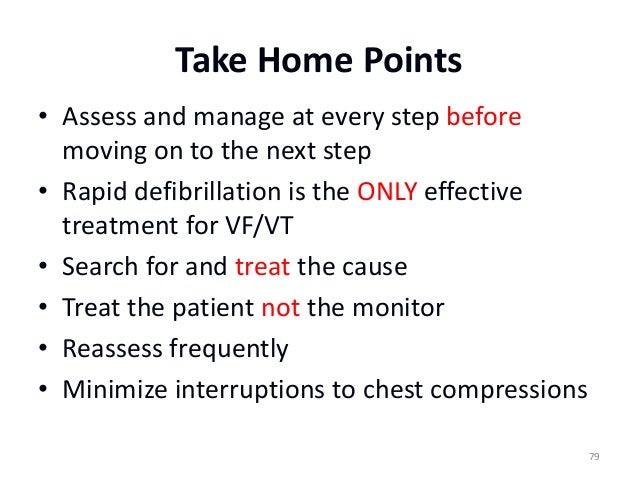
To initiate and guide care of the patient, the healthcare provider should utilize the Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) Primary Assessment. Elements of the ACLS Primary Assessment include evaluating the patient’s airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and potential exposure. The healthcare provider should take actions using the ACLS Primary Assessment, including managing the patient’s airway, supplying supplemental oxygen if needed, identifying the patient’s cardiac rhythm, and monitoring vital signs. In addition, it should be determined if the patient has any neurological deficits, and clothing should be removed to perform a visual assessment of the patient for medical alert identification, or potential trauma, burns, or bleeding. Intravenous (IV) access should be obtained, in addition to a 12-lead ECG, if possible. Following the ACLS Primary Assessment, the healthcare provider should utilize the ACLS Secondary Assessment, evaluating H’s and T’s for potential causes of the patient’s condition and gathering a focused medical history.
Assessment and Monitoring
AF often initially presents in a paroxysmal (PAF) form, defined by self-termination within 7 days, while persistent AF requires termination by pharmacological or direct-current electric cardioversion.
Treatment
ACLS Certification teaches that t he goal of atrial fibrillation treatment is three-fold: to control the rate, to control the rhythm, and to prevent stroke.
Conversion and Long-Term Treatment
Besides medication, other measures can be taken to convert AF. One of these methods is synchronized cardioversion. By administering a shock, the hope is that the SA node will reassert itself and the patient will convert into a normal sinus rhythm. Patients will require sedation, as cardioversion is quite painful.
What is the best treatment for AFIB?
3. Beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers are the preferred drug treatment for AFib when there is no evidence of heart failure (e.g., no pulmonary edema by chest x-ray; no “crackles” on lung exam). Digoxin may be given if AFib is due to heart failure or if a patient is experiencing heart failure. 4.
How much does it cost to treat AFIB?
According to the Centers for Disease Control it costs more than $6.65 billion each year to treat the more than 5 million Americans that have AFib. As the condition grows more widespread, chances are good that you may have to perform a lifesaving intervention for a patient with AFib.
What are the symptoms of AFIB?
Common symptoms of AFib include: chest pain or palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness and possibly loss of consciousness, peripheral edema, jugular vein distention, and possibly pulmonary edema.
How does catheter ablation work?
This procedure is performed by an electrophysiologist and involves inserting a wire through a vein in the leg or arm and threading it to the heart. Radio wave energy is then sent through the wire to destroy abnormal tissue that may be disrupting the normal flow of electrical signals.
How long are the guidelines for AFIB?
The guidelines spell out what is proven most helpful to the greatest number of people. Although the guidelines for atrial fibrillation are about 170 pages long, there are some basic decisions outlined in the treatment guidelines that every AFib patient should understand.
Why are medical guidelines written?
Medical guidelines are written by a panel of experts to document the science that helps healthcare providers choose the right treatments. The guidelines spell out what is proven most helpful to the greatest number of people.
What does ACLS stand for?
ACLS is an acronym that stands for Advanced Cardiac Life support . ACLS teaches healthcare professionals advanced interventional protocols and algorithms for the treatment of cardiopulmonary emergencies. These include primary survey, secondary survey, advanced airways, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, tachycardias, bradycardias, and stroke. The treatment protocols have been established through collaborative clinical research and later published by the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR).
When to follow instructions of AED?
Follow instructions of the AED until the arrival of medical transport.
How many beats per min should a pacer be set at?
Set the pacer 10-20 beats per min above the patient’s intrinsic heart rate or 60 beats per min if there is no intrinsic heart rate.
What are the two principles of airway and breathing?
Airway & Breathing. There are two important principles when evaluating the airway and breathing. First, is the airway patent or obstructed. Second, is there possible injury or trauma that would change the providers method of treating an obstructed airway or inefficient breathing. Patent/obstructed.
What is the AF2019 AHA/ACC/HRS?
AF2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused pdate of the 2014 uideline for anagement of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
What is GUIDELIES ADE SIMPLE AF201?
GUIDELIES ADE SIMPLE AF201 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 01 uideline for anagement of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
What anticoagulants are recommended for high risk patients?
Oral anticoagulants recommended for high risk patients now include edoxaban.
Is the term "nonvalvular AF" still used?
2014 2019 The term “nonvalvular AF”is no longer used
What is the ACLS Bradycardia algorithm?
The ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm contains the steps you will need to follow when you encounter a patient who has symptomatic bradycardia. Learn when to treat bradycardia, and when not to treat it.
What is the BLS algorithm?
The BLS CPR Algorithm describes the sequence of steps for performing high-quality CPR when only one rescuer is available to help the victim. It is suitable for use in adults and children above the age of 1.
What is the PALS wide QRS?
The PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm describes the management of a pediatric patient who has a wide QRS waveform by ECG and is adequately perfusing his tissues.
What is the PALS sequence algorithm?
The PALS Sequence Algorithm describes the basic response to pediatric cardiopulmonary emergency. It covers the initial assessment in the primary assessment sequence.
Can a bystander administer naloxone?
New in 2015, bystanders may administer naloxone to victims who are apparently suffering from an op ioid overdose. Unresponsive victims encountered outside a hospital may benefit from timely administration of naloxone given by trained lay providers.
Is cardiac arrest handled differently?
Cardiac arrest that occurs in the hospital is handled differently than it is in other adults in some important ways.