Recent studies indicate that CMV hyperimmune globulin treatment may reduce the risk of congenital infection and/or neonatal disease when given to pregnant women experiencing a primary CMV infection. Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir are antiviral treatments that may be beneficial to a newborn with symptomatic congenital CMV.
Is there a treatment for cytomegalovirus (CMV) during pregnancy?
There is currently no treatment for CMV infection during pregnancy. Antiviral medications are sometimes used to treat newborns diagnosed with CMV or people with compromised immune systems. How can you avoid getting cytomegalovirus (CMV)?
Can you get CMV if you are pregnant?
For pregnant women. You can pass CMV to your baby. If you are pregnant and have CMV, the virus in your blood can cross through your placenta and infect your developing baby. This is more likely to happen if you have a frst-time CMV infection while pregnant but can also happen if you have a subsequent infection during pregnancy.
Are Obstetricians aware of the latest advances in CMV infection in pregnancy?
Unfortunately, studies have shown most women of childbearing age and surprisingly, many obstetricians, are not aware of the most recent advances in management of CMV infection in pregnancy.
How can I Help my Child with congenital CMV?
Children with congenital CMV should have regular hearing checks. Children with hearing loss should receive services such as speech or occupational therapy. These services help ensure they develop language, social, and communication skills. The earlier your child can get hearing checks and therapies, the more he or she can benefit from them.
Can you treat CMV while pregnant?
There's currently no treatment for CMV in pregnancy, but in most cases the virus does not cause any problems for your baby. Antiviral medicine may be used to treat: babies diagnosed with congenital CMV after they're born. people with a weakened immune system.
How does CMV virus affect pregnancy?
If you get infected with CMV during pregnancy, it may cause pregnancy loss or serious health problems in your baby, including preterm birth or low birthweight, or hearing loss at birth or later in life. CMV is the leading cause of hearing loss in this country, causing 1 in 3 cases of hearing loss.
What if CMV IgG is positive in pregnancy?
Testing for CMV infection is a simple blood test, called a CMV IgG antibody. It will determine if a pregnant woman has had CMV. A positive result indicates a current or past CMV infection. A second blood test, called CMV IgM antibody will help determine if the CMV infection is current or past.
How can I prevent CMV from spreading to my unborn baby?
Can congenital CMV be prevented?wash hands often with soap and running water for at least 15 seconds and dry them thoroughly. ... do not share food, drinks, eating utensils or toothbrushes with young children.avoid contact with saliva when kissing a child.More items...•
What kills CMV virus?
Currently, intravenous ganciclovir or oral valganciclovir are the primary antiviral treatments for CMV. The drugs suppress the virus, says Boger, but they can't eliminate it. In the absence of vaccine for CMV, the best form of prevention is hand-washing.
How do you recover from a CMV virus?
Most people recover in 4 to 6 weeks without medicine. Rest is needed, sometimes for a month or longer to regain full activity levels. Painkillers and warm salt-water gargles can help relieve symptoms.
Can CMV affect future pregnancy?
If a pregnant woman is infected with CMV, she can pass it to her developing baby. This is called congenital CMV, and it can cause birth defects and other health problems.
How do you know if CMV is active?
A blood test can detect the antibodies that the body creates when the immune system responds to CMV's presence. A pregnant person has a minimal risk that reactivation of CMV may affect her developing baby. If a doctor suspects that a pregnant person has CMV, they may suggest an amniocentesis.
Should I worry about CMV?
See your doctor if: You have a weakened immune system and you're experiencing symptoms of CMV infection. For people who have weakened immune systems, CMV infection can be serious or even fatal.
How is CMV spread during pregnancy?
Some women pick up CMV while pregnant. This happens through handling infected children's toys, dirty tissues or soiled nappies. It is also possible to get CMV from having sex, a blood transfusion or an organ transplant. Unborn babies can get CMV from their mothers while in the womb.
Does CMV show up in ultrasound?
Ultrasound can show some of the issues caused by congenital CMV, such as slow growth, small head size, large placenta, and changes in brain structure. However, many babies with congenital CMV will not show any signs of infection on ultrasound.
How long does CMV stay active?
How long can an infected person carry CMV? CMV remains in the body throughout a lifetime. Infected people may occasionally shed the virus in urine or saliva. Several studies have found that from three to 11 percent of normal adults and up to 50 percent of healthy children shed the virus in either urine or saliva.
How might I become infected with CMV during pregnancy?
CMV is spread by direct contact with an infected person's bodily fluids, such as saliva, urine, feces, semen, vaginal secretions, blood, tears, and breast milk.
How many chances of getting CMV while pregnant?
However, if you become infected for the first time during pregnancy, the chance of passing the virus to your baby is much higher. About 1 to 4 percent of previously uninfected women have a first (or primary) CMV infection during pregnancy. Among these women there's about a 30 to 50 percent chance that the baby will become infected in the womb.
What is cytomegalovirus?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a member of the herpes virus family. As the most common intrauterine infection, 1 out of every 200 babies is born with CMV, a condition known as congenital CMV. Pregnant women who have CMV can pass it to their baby through the placenta three different ways: primary infection, becoming reinfected with a different CMV strain, or via reactivation of the virus already in the body.
How much risk of CMV infection to a baby?
Fortunately, the risk of passing the virus to your baby during a recurrent infection is very low (the CDC estimates it to be about 1 percent) and the risk of serious complications is even lower. So if you got your first CMV infection at least six months before you conceived, the risk to your baby from CMV is very small.
What is the congenital CMV?
The cytomegalovirus (CMV) is an infectious disease that's a member of the herpes family. While most pregnant women who become infected with CMV will recover on their own, they can transmit the virus to their baby in the womb. As a result, babies who are born with the infection have a condition known as congenital CMV. Most babies with congenital CMV won't show signs or experience symptoms, but a small percentage become very ill and have long-term health issues. These babies will need treatment and extra monitoring to ensure their illness doesn't become worse. If you're pregnant, it's important to practice good handwashing and limit your time around very young children, who carry high levels of the virus.
What is the most common virus that is passed on to a baby during pregnancy?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a member of the herpes virus family. It's the virus most frequently passed on to babies during pregnancy. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, about 1 percent of babies are born with the infection, a condition called congenital CMV. Most babies with congenital CMV have no problems from the condition.
What to look for in an ultrasound if you have CMV?
If you become infected with CMV during pregnancy, your provider may order extra ultrasounds to look for abnormalities in your baby that may have been caused by CMV. Some things she may look for in an ultrasound are placental thickening, enlargement of the liver, spleen, and organs, and microcephaly (small head). If an abnormality is confirmed, your provider may recommend doing an amniocentesis, which involves taking a sample of amniotic fluid, to determine whether your baby has been infected.
What are the risks of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection during pregnancy?
The majority of babies who are infected with CMV during pregnancy never show any signs of infection at birth. For the few who do, symptoms may include:
How is cytomegalovirus (CMV) treated?
There is currently no treatment for CMV infection during pregnancy. Antiviral medications are sometimes used to treat newborns diagnosed with CMV or people with compromised immune systems.
What is cytomegalovirus (CMV)?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common virus that’s related to the herpes virus (which causes the chickenpox and cold sores). It generally comes and goes without mild, if any, symptoms in healthy children and adults.
What are the symptoms of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in new moms?
The symptoms of CMV in new moms are the same as during pregnancy. For most, that means having no symptoms at all. However, you may experience:
What percentage of babies have CMV?
Research suggests about 80 to 90 percent of babies with congenital CMV are asymptomatic at birth and have very low chances of long-term complications. The odds of long-term complications increase significantly in babies who are infected early on in pregnancy and in newborns who experience symptoms at birth.
How long does it take for CMV symptoms to go away?
Although CMV often comes and goes without any obvious symptoms, you may experience CMV symptoms including: These symptoms usually go away on their own within around three weeks. Rarely, CMV can lead to mononucleosis (a condition caused by certain viruses that causes extreme fatigue among other symptoms).
How many babies are born with CMV?
About one in 200 babies is born with congenital CMV (or a CMV infection at birth). Of the approximately 1 to 4 percent of people who get CMV during pregnancy, about 1 in 3 pass the infection on to their babies.
How Is CMV Infection Treated During Pregnancy?
If you have CMV infection with symptoms, you may consult a doctor who may provide you with medications for symptomatic relief. You may also observe other general practices observed during viral infection, such as adequate rest and fluids with a healthy diet.
What Are The Risks Of CMV Infection During Pregnancy?
A pregnant woman may contract CMV infection from someone with an active infection. The following factors may increase the risk of CMV infection in pregnancy (6) (7).
What Causes CMV Infection?
The CMV infection spreads by coming into close contact with a person with an active infection. It may be passed during sexual activity or when you come in contact with infected body fluids such as saliva, urine, blood, tears, urine, or stool (1).
What Is The Risk Of CMV Transmission To The Fetus?
The risk of vertical transmission is lowest in the first trimester of pregnancy. In case the fetus acquires infection at this time, the risk of developing serious congenital malformations is highest. As pregnancy advances ( third trimester ), the risk of fetal transmission increases, but the odds of the baby having serious birth defects are less (4). This may be due to the increased passing of maternal antibodies to the fetus with advancing gestational age. Infection may also be passed through vaginal secretions during birth and via breast milk after that.
What Is Cytomegalovirus Infection?
Cytomegalovirus infection is a common perinatal infection and could also lead to a CMV infection in babies due to maternal transmission (2) (3). Similar to other herpes viruses, the CMV shows characteristics of latency and reactivation. It means once you get infected, the virus stays dormant in the body forever.
What is the risk to my baby if I have a CMV infection during pregnancy?
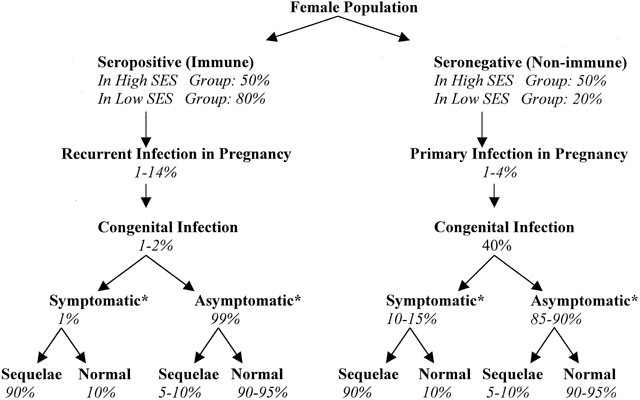
Approximately 40% of women who experience a primary CMV infection during pregnancy will transmit the CMV infection to their baby, and approximately 60% will not. The reason why some women transmit CMV to their baby and some women do not is not known. Most babies born congenitally infected with CMV will appear normal at birth. However, approximately 10% of babies born congenitally infected as a result of their mother's primary CMV infection during pregnancy will have symptoms in the womb or at birth. Newborns with symptomatic congenital CMV disease at birth may have a variety of signs and symptoms in many organ systems, and also may experience disabilities long term in hearing, vision, cognition and motor development. In some babies with severe congenital CMV disease, the congenital CMV infection is fatal. Therefore a maternal primary CMV infection may carry a significant risk to the unborn baby. Women who experience a recurrent CMV infection also may transmit CMV to their baby, but the occurrence is much, much lower ( 0.1% or less) than after a primary CMV infection (40%), and serious symptoms rarely occur in the fetus or newborn born congenitally infected as a result of a maternal recurrent infection.
What are the signs and symptoms of CMV during pregnancy?
When symptoms do occur, they most commonly are fever, sore throat, swollen lymph glands and extreme fatigue. Rarely, a rash, cough or diarrhea may occur. These symptoms are not specific for CMV infection and may be cause by other conditions. And, unfortunately, often the first time a pregnant woman is aware of CMV is when she has a baby who is diagnosed with congenital CMV infection. Therefore, blood tests are needed to accurately diagnose a CMV infection during pregnancy.
What does a low CMV IgG avidity index mean?
A low CMV IgG avidity index indicates the primary CMV infection occurred less than 4 months prior to the blood test, and a high CMV IgG avidity index indicates a CMV infection occurred 4 months ago or longer. A CMV IgG avidity test is not recommended if the CMV IgM antibody is negative, and the test cannot be performed if ...
What is the test for CMV infection?
Testing for CMV infection is a simple blood test, called a CMV IgG antibody. It will determine if a pregnant woman has had CMV. A positive result indicates a current or past CMV infection. A second blood test, called CMV IgM antibody will help determine if the CMV infection is current or past.
What is the most common congenital infection?
Cytomegalovirus ( CMV) is the most common virus most people have never heard of! It is the most common congenitally acquired virus, and about 1 out of every 100 to 150 newborns is born congenitally infected with CMV. It is common in both children and adults. Between 50 to 80 percent of women of childbearing age have caught CMV and between 1 and 5 percent of pregnant women will catch CMV for the first time during their pregnancy. Most CMV infections are "silent" and harmless, but in pregnant women, CMV can be transmitted to the fetus, with sometimes devastating effects to the unborn baby and newborn. Therefore, it is important if you are pregnant, or know someone who is pregnant, to be "CMV Aware" and "CMV Cautious". Women who are pregnant should discuss CMV with their obstetrician. Testing for CMV infection is a simple blood test. And, there are interventions available to help. Unfortunately, studies have shown most women of childbearing age and surprisingly, many obstetricians, are not aware of the most recent advances in management of CMV infection in pregnancy. Because many of the questions I received from my first blog post were about CMV infection during pregnancy, I decided to post some basic information that I hope you find helpful:
How common is CMV in pregnant women?
It is common in both children and adults. Between 50 to 80 percent of women of childbearing age have caught CMV and between 1 and 5 percent of pregnant women will catch CMV for the first time during their pregnancy. Most CMV infections are "silent" and harmless, but in pregnant women, CMV can be transmitted to the fetus, ...
Does CMV affect the fetus?
Prenatal treatment of the pregnant mother with CMV hyperimmune globulin (CMV enriched antibody) may reduce the transmission of CMV to the fetus and reduce or reverse some of the effects of CMV on the fetus.
What is national CMV?
National CMV is here to help guide you as you begin this journey, providing information and resources to better understand what comes next. More than that, National CMV is about providing connections to other parents who understand what you're going through and can give advice, support, and unconditional love. Most importantly, National CMV can connect you with doctors who can provide more information about treatments that may help. For more information, contact us here.
What tests are needed for CMV?
At birth, your child should have baseline laboratory tests completed to determine what organs in the body have been affected by CMV, including the following: * complete blood count . * platelet count. * liver function test. * computerized tomography (CT) brain scan.
Does Valganciclovir help with CMV?
Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir may prevent hearing loss and improve head and brain growth. They can also help combat immediate medical concerns caused by CMV, such as thrombocytopenia (low platelets), organ failure (most commonly spleen and/or liver), hepatitis, and pneumonitis. If you are a pregnant woman who has been diagnosed with CMV ...
Can CMV help a baby?
Are there any treatments that can help my baby? Yes. Recent studies indicate that CMV hyperimmune globulin treatment may reduce the risk of congenital infection and/or neonatal disease when given to pregnant women experiencing a primary CMV infection.
Can a child with CMV have special needs?
If a child has delayed hearing or vision problems, early detection can help their development. Because a child with congenital CMV may have special needs, their growth and development should be followed carefully. Routine immunizations (shots) are recommended for all children born with congenital CMV.
How to prevent CMV infection in pregnant women?
Good hygiene practices and avoiding intimate contact with young children (e.g., kissing on the mouth and sharing utensils ) have been suggested as an approach to prevent maternal primary CMV infection during pregnancy, but remains an unproven method of reducing the risk of congenital CMV infection.
What is the rate of CMV transmission in pregnancy?
Congenital CMV transmission rates are as high as 50% in women who acquire primary CMV infection during pregnancy, and less than 2% in women with nonprimary infection.
What is the primary source of CMV?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a DNA herpesvirus that is common worldwide. The two known main sources of primary CMV infection during pregnancy are through sexual activity and contact with young children. Primary infection occurs in approximately 1 to 4% of pregnancies, and is mostly asymptomatic in immunocompetent adults.
Can antiviral treatment be used for CMV?
Antiviral treatment prenatally and postnatally has not proven effective at preventing congenital or postnatal CMV infection, and is not recommended for routine clinical care. However, antiviral treatment when initiated in the first month of life for symptomatic congenital CMV infection is recommended for improved neurodevelopmental ...
What is the CMV in pregnancy?
Occupational Health Clinic. Posted in. Keeping You Safe At Work, Occupational Health Clinic, Resource Articles. Cytomegalovirus, or CMV, is a herpes virus that most women of child-bearing age have already acquired. If you become infected with CMV while you're pregnant, there is a one-in-three chance ...
Can you get CMV before you get pregnant?
If you are infected with CMV before you become pregnant, that risk is reduced to about one-in-100. Pregnant women who are healthy are not at special risk for disease from a CMV infection. Most babies with congenital (meaning from birth) CMV never have health problems.
Can a baby get CMV?
However, in some babies congenital CMV causes health problems when the baby is born or later in the baby's life. There is no vaccine to prevent CMV infection.
What is the treatment for CMV?
Babies who show signs of congenital CMV at birth may be treated with medicines called antivirals. Antivirals may decrease the severity of health problems and hearing loss but should be used with caution due to side effects.
How to prevent CMV?
You can avoid getting a child’s saliva in your mouth by, for example, not sharing food, utensils, or cups with a child. Also, you should wash your hands after changing diapers. These cannot eliminate your risk of getting CMV, but may lessen the chances of getting it.
How many babies are born with CMV?
About 1 out of every 200 babies is born with congenital CMV. About 1 out of 5 of these babies will have birth defects or other long-term health problems.
What services should a child with congenital CMV receive?
Children with congenital CMV should have regular hearing checks. Children with hearing loss should receive services such as speech or occupational therapy. These services help ensure they develop language, social, and communication skills. The earlier your child can get hearing checks and therapies, the more he or she can beneft from them.
Can you get CMV while pregnant?
If you are pregnant and have CMV, the virus in your blood can cross through your placenta and infect your developing baby. This is more likely to happen if you have a frst-time CMV infection while pregnant but can also happen if you have a subsequent infection during pregnancy.
What to do if your baby has CMV?
If your baby is diagnosed with congenital CMV, be sure to have his or her hearing and vision checked regularly to identify any early onset of hearing or vision loss. Early diagnosis is critical to experiencing long-term developmental successes.
What is the best treatment for CMV?
Emerging research shows that antiviral drugs, Ganciclovir or Valganciclovir, may help newborns born with symptomatic congenital CMV . These antiviral treatments may prevent or lessen the severity of hearing loss and may improve head and brain growth.
How long does ganciclovir last?
Treatments generally last from 6 weeks to 6 months and are administered orally or through an IV or PICC line. Both Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir can have serious side effects, so be sure to consult with a doctor before beginning treatment and during the antiviral treatment period.
Does cytogam help with congenital infection?
Recent studies indicate that Cytomegalovirus Immune Globulin Intravenous (CMV-IGIV), or Cytogam, treatment may lessen or reduce the risk of congenital infection and /or neonatal disease when given to pregnant women experiencing a primary CMV infection.
