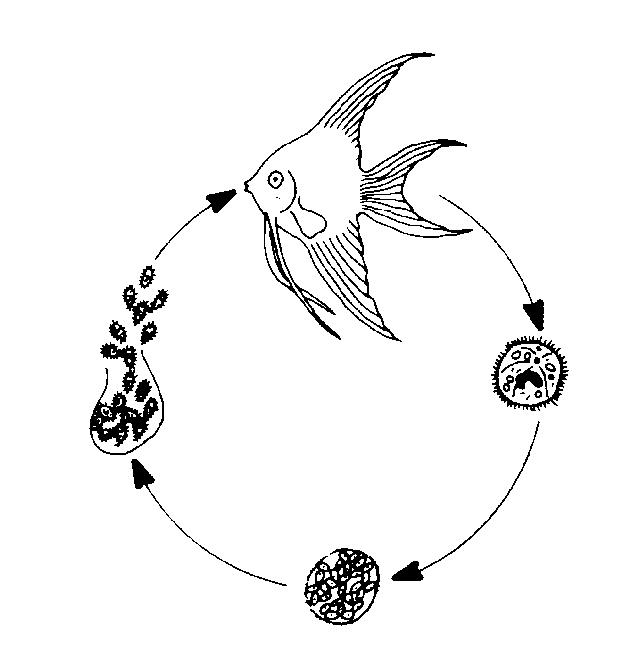
What is the life cycle of Ich in a tank?
Jul 28, 2021 · During this time, the theront is most susceptible to treatment. The Cycle Starts All Over Again Once the theront locates a host, it only takes five minutes for it to burrow into the skin while during gill invasion, the parasite can become enclosed by a …
What is the prognosis of Ich disease?
The Life Cycle Of Marine Ich. The life cycle of Marine Ich consists of four unique stages in which the parasite takes on five different forms: Trophont; Protomont; Tomont; Tomite; Theront; During each stage, the parasite performs a different function that helps ensure its own survival. 1) Infection. The free-swimming Theronts search for a host to prey upon. This is a sensitive stage …
Can Ich disease be controlled?
Aug 21, 2018 · Only the infective theront stage is susceptible to treatment. Repeating the appropriate chemical treatment will disrupt the life cycle and control the outbreak. Daily cleaning of the tank is also beneficial because tomonts attached to organic matter can be physically removed from the environment.
What is Ich disease?
Aug 26, 2013 · ICH LIfe Cycle Information provided in the Fish Lore link below: Ich Fish Disease Natural Treatment: When dealing with ICH, the entire tank should be treated. If 1 fish has the parasite then chances are good that the entire tank is infected. If you move the ill fish to a Quarantine tank, then you will probably have to treat 2 tanks.Personally I use the increased heat …

What is Ich life cycle?
Is Ich hard to treat?
How fast does Ich treatment work?
How long does it take for white spot treatment to work?
Can I feed my fish while treating ICH?
Can Melafix treat ICH?
How long does Ich treatment last?
How long till Ich falls off fish?
How long after Ich can I add fish?
How does white spot treatment work?
What is the best treatment for white spot?
- low-dose corticosteroid creams, like 1-percent hydrocortisone cream.
- Elidel cream, a nonsteroidal formula.
- ultraviolet light treatment in combination with topical medications.
- bleaching the skin surrounding large white patches to blend them.
- tattooing over white patches.
What causes white spots on aquarium fish?
How long does it take for Ich to complete its life cycle?
At warm temperatures (75–79°F), the life cycle is completed in about 3 to 6 days. At these temperatures, chemical treatments should be applied daily and a minimum of 3 to 5 treatments is required.
What is the best treatment for Ich?
Formalin. If fish are maintained in a tank system, formalin is often used to treat "Ich". Formalin is not the ideal treatment for ponds, but it works well in tanks. Vigorous aeration is required because every 5 mg/L of formalin removes 1 mg/L of oxygen from the water.
What are the stages of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis?
Although Ichthyophthirius multifiliis has a direct life cycle, it is fairly complex and has three distinct life stages: 1) the on-fish, feeding trophont; 2) the environmental, reproducing tomont; and 3) the infective, fish-seeking theront (see Figure 1). The trophont invades and encysts between the thin outer layers of the fish host's skin and gills in order to feed on those tissues. Because of the covering by this epithelial tissue and mucus, the trophont stage is protected from chemical treatment. Once the trophont is mature, it stops feeding, leaves the fish, and becomes a tomont. The tomont quickly secretes a gelatinous-walled outer cyst that allows it to stick to surfaces in the environment. The tomont begins to divide quickly, forming hundreds of new "daughter" parasites (tomites) within a single cyst. This can occur in a day or less at warmer water temperatures. The gelatinous wall of the tomont cyst protects it and the daughter tomites from chemical treatment. The tomites begin to develop and become theronts within the tomont cyst. Following a period of days (warm water temperatures) or weeks (cool water temperatures), the theronts bore out of the tomont cyst and become free-swimming, infective parasites in search of a fish host. These infective theronts must find a live fish to complete the parasite's life cycle. This free-swimming phase is unprotected and, therefore, highly susceptible to chemicals. Treatment protocols should be designed to target this theront stage.
What is the white spot disease?
1. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis is a large, ciliated protozoan that causes "Ich" or "white spot disease.". This disease is a major problem to freshwater aquarists and commercial fish producers worldwide. All species of freshwater fish are considered susceptible, and the parasite has been found in all areas of the world in both cultured ...
What causes white spots on fish?
Ichthyophthirius multifiliis is a large, ciliated protozoan that causes "Ich" or "white spot disease." This disease is a major problem to freshwater aquarists and commercial fish producers worldwide. All species of freshwater fish are considered susceptible, and the parasite has been found in all areas of the world in both cultured and wild fish. These large parasites cause the characteristic white spots that are often seen on the skin and fins of infected fish. The disease is highly contagious and spreads rapidly from one fish to another without the need for additional hosts (direct life cycle). Although often considered a "warm water" disease, outbreaks often occur when water temperatures are changing, especially in the spring when water temperatures are increasing. The disease is particularly severe when fish are crowded. While many protozoans reproduce by simple division (one parasite "splits" into two), a single "Ich" organism can multiply into hundreds of new parasites in one generation, making early detection and treatment of this parasite crucial. The organism is unusual in that it is an obligate parasite, which means that it cannot survive unless live fish are present. "Ich" is capable of causing massive mortality within a short period of time. An outbreak of "Ich"is a true emergency situation and requires immediate treatment; if left untreated, this disease may result in 100% mortality.
How to tell if fish have an ich infection?
The classic sign of an "Ich" infection is the presence of small white spots on the skin or fins (Figure 2). These spots are caused as the adult parasite (trophont) penetrates and creates a space in the outer layers of the fish's body surfaces (epithelium) in order to feed on the fish and move around.
What chemical is used to treat Ich?
In general, copper sulfate and formalin are both effective against "Ich" when applied at the correct dose in a repetitive manner as described above.
What is copper sulfate used for?
Copper sulfate isused as an indefinite treatment(i.e., applied to the water andallowed to remain without subse-quent dilution of the treatment). The treatment rate is determinedby the total alkalinity concentra-tion of the water being treated; thetreatment rate of copper sulfate inppm is equal to the total alkalinitydivided by 100. For example, ifthe total alkalinity of a pond were85 ppm, then the treatment ratefor copper sulfate would be 85 Ö100 = 0.85 ppm. In a pond, thepounds of copper sulfate neededin this example would be:
What is potassium permanganate?
Potassium permanganate(KMnO4) (often referred to asÒpotassiumÓ) is an oxidizingagent that oxidizes organic mate-rials in water, including proto-zoan parasites or external bacterialiving on the surface of fish. It isusually used as an indefinitetreatment in ponds at a ratedependent on the amount oforganic material in the water. Two(2) ppm of KMnO4is the mini-mum dose required to be effectiveagainst external parasites such asIch, while waters rich in nutrientswith a heavy algal bloom need agreater amount of KMnO4for aneffective treatment. (An author isaware of one case where 20 ppmKMnO4was needed to reach aneffective treatment level.) Apotas-sium permanganate demand testis often used by aquatic biologistsand Extension specialists to deter-mine the most effective, but safe,treatment rate.
What is a marine ich?
Marine Ich (Cryptocaryon irritans) is best described as salt or sugar-like “sprinkles” on the body or fins. Sometimes however, the parasite can harbor inside the gills – out of sight. Behavioral symptoms such as flashing, scratching, twitching and heavy breathing are other indicators of ich.
What does it mean when a fish has a white spot?
A white spot on a fish can be Lymphocystis (a harmless virus), or something more serious like Brooklynella, Uronema or the beginnings of a bacterial infection. If a fish is completely covered in sprinkles, then this could mean Marine Velvet Disease (Amyloodinium) – a potential tank killer.
How to tell if fish has ich?
Easiest way to diagnose Ich is to look carefully at your fish. If you see little, white, slightly raised salt like spots on the fish’s fins or body, your fish has Ich.
Can Ich go away?
Ich will not go away by itself. It must be treated or can be deadly to your fish. It may start on the body, but at some point will infest the gills; you will remember from the earlier paragraphs how dangerous this is. It also stresses the fish greatly which depresses the fish’s immune system; that combined with the open wounds caused by the burrowing parasites can result in opportunistic diseases such as fungal or bacterial infections. Occasionally the stress of the infestation alone will cause the fish to perish, despite proper treatment, which why prevention is so important.
Why do fish have gills?
Not only because the infestation causes loss of electrolytes and fluids from the skin damage, causing the fish to have difficulty regulating water loss, but Ich often infests the gills. The layer of gill cells thickens in response to the parasites, and the amount of oxygen getting into the fish is reduced.
Do clown loaches have parasites?
Many wild caught fish, such as clown loaches which have yet to be bred in any quantity in captivity, usually arrive with parasitical infestations. Keeping fish healthy, with proper food and good water quality is also important, as Ich is opportunistic itself, and a stressed fish often has a depressed immune system.
Why is it important to keep fish healthy?
Keeping fish healthy, with proper food and good water quality is also important, as Ich is opportunistic itself, and a stressed fish often has a depressed immune system. This makes the fish more susceptible and less able to fight off the infection itself.
Is water change bad for salt?
Obviously, it is not an issue for the high temperature treatment. However, water changes are NOT necessarily a bad thing; in fact, by doing water changes and gravel vacs, you are removing some of the theronts swimming in the water and the tomonts encysted in the substrate and reducing the overall levels of parasites in your system.
How long does a parasite live?
The complete parasitic life cycle ranges from 14 to 16 days. Higher temperatures accelerate the cycle while lower temperatures will extend the parasitic activities. The three day duration of the tomite stage is the only stage in which the parasite is vulnerable and can be treated with medication.
Where do trophozoites form?
The mature parasite (trophozoites) forms pustules in the skin in order to feed (visible as white spots). Once the pustule ruptures, the trophont settles at the bottom of the tank. Secreting a coating it forms a protective capsule (cyst).
Is ich a disease?
Both Freshwater and Marine species are susceptible to the disease however it is not known to affect invertebrates. Ich is one of, if not the most common disease. It is also responsible for the majority of disease related deaths in the aquarium. Ich can be identified by its distinctive white dot appearance.
How to prevent ich in aquarium?
Prevention of Ich is the most effective route in making sure Ich never exposes itself in your aquarium. Taking steps to avoid the disease will greatly reduce the need for curing ich. This can be done in a number of ways: Using a quarantine tank. The importance of a quarantine tank cannot be stressed enough.
Can fish be quarantined?
Fish should always be quarantined in a seperate aquarium before being introduced to the display tank. However, sometimes this just isn’t possible. When making your decision to start an aquarium, you should anticipate the possibility of fish diseases such as ich. Ich is very commonly encountered in the aquarium hobby.
What is the disease of fish?
Ich (also known as ick) is a very common disease affecting tropical fish. Both Freshwater and Marine species are susceptible to the disease however it is not known to affect invertebrates. Ich is one of, if not the most common disease. It is also responsible for the majority of disease related deaths in the aquarium.
How to tell if a fish has ich?
Ich can be identified by looking for a number of symptoms. Fish will have white, round dots attached to their gills and/or body. These white dots are usually between 0.5 to 1.5mm in size. Affected fish may try to scratch themselves on rocks and hardscape in the aquarium.
How hot can a fish get?
It is recommended to increase the temperature to at least 86 degrees (30 celcius) from its current state. It is not recommended to exceed 90 degrees (32 degrees celcius). Most tropical fish will be able to withstand temperatures around 86 degrees for shorter periods of time.
Is salt good for ich?
There is constant debate to the legitimacy of using salt when curing Ich. Salt is often hailed as an excellent additive for freshwater fish diseases. In personal experience salt has had little impact when curing Ich. More importantly, some fish such as Cories can be very sensitive to salinity changes.
