
Medication
Jul 19, 2021 · Shortness of breath. Over time, CAD can weaken the heart muscle. This may lead to heart failure, a serious condition where the heart can’t pump blood the way it should. Learn the facts about heart disease, including coronary artery …
Procedures
Mar 24, 2022 · Coronary artery disease affects the larger coronary arteries on the surface of the heart. Another type of heart disease, called coronary microvascular disease, affects the tiny arteries in the heart muscle. Coronary microvascular disease is more common in women. The cause of coronary heart disease depends on the type.
Self-care
Jun 01, 2021 · Without treatment, CAD will get worse and can suddenly cause a fatal heart attack, or can cause a heart attack that results in lifelong complications and a diminished quality of life. If you experience angina or symptoms of what seems to be a heart attack, you need to get emergency medical attention. When to Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
Nutrition
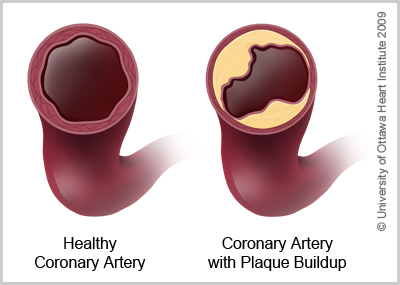
Mar 01, 2022 · The plaque buildup can narrow the blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow through. Plaques can also break or rupture, causing a blood clot to form. When a clot blocks blood from getting to the heart, it damages the heart muscle and causes a heart attack. CAD is usually diagnosed at the onset of symptoms, like chest pain.
What happens if you leave coronary artery disease untreated?
If left untreated, CAD can lead to other heart conditions, some of which are life-threatening: Cardiogenic shock: This life-threatening emergency can develop after severe injury to heart muscle function. This type of injury includes a heart attack or a dangerous arrhythmia (irregular heart rhythm).
How long can you live with coronary artery disease?
In terms of absolute years spent with heart disease, Figure 2 shows that at every age the average woman can expect to live with heart disease more years than the average man. At age 50, the average woman can expect to live 7.9 years with heart disease, while the figure for the average man is 6.7 years.
Is coronary artery disease a death sentence?
Coronary artery disease — an accumulation of fatty deposits in the inner layer of the coronary arteries — does not have to be a death sentence, especially with early diagnosis and the right treatment.Jun 10, 2019
How quickly does coronary artery disease progress?
Although atherosclerosis is believed to progress over many years, it has been increasingly noted to progress over few months to 2-3 years in few patients without traditional factors for accelerated atherosclerosis.
Can you live a full life with coronary artery disease?
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is treatable, but there is no cure. This means that once diagnosed with CAD, you have to learn to live with it for the rest of your life. By lowering your risk factors and losing your fears, you can live a full life despite CAD.
How serious is coronary artery?
Narrowed arteries can cause chest pain because they can block blood flow to your heart muscle and the rest of your body. Over time, CAD can weaken the heart muscle. This may lead to heart failure, a serious condition where the heart can't pump blood the way it should.Jul 19, 2021
What is the difference between coronary artery disease and heart disease?
Coronary artery disease is a narrowing or blockage of your coronary arteries usually caused by the buildup of fatty material called plaque. Coronary artery disease is also called coronary heart disease, ischemic heart disease and heart disease.Jun 21, 2021
What is the most common cause of coronary artery disease?
The most common cause of CAD is vascular injury with cholesterol plaque buildup in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. Reduced blood flow occurs when one or more of these arteries becomes partially or completely blocked.
Is heart failure painful?
Abstract. Background: Patients with advanced heart failure (HF) have high rates of pain and other symptoms that diminish quality of life.
What are the stages of coronary artery disease?
There are four heart failure stages (Stage A, B, C and D). The stages range from "high risk of developing heart failure" to "advanced heart failure."...Stage CShortness of breath.Feeling tired (fatigue).Less able to exercise.Weak legs.Waking up to urinate.Swollen feet, ankles, lower legs and abdomen (edema).Jan 21, 2022
What happens when the right coronary artery is blocked?
A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. The classic signs and symptoms of a heart attack include crushing pressure in your chest and pain in your shoulder or arm, sometimes with shortness of breath and sweating.Jun 5, 2020
What does a blocked artery feel like?
The symptoms of an artery blockage include chest pain and tightness, and shortness of breath. Imagine driving through a tunnel. On Monday, you encounter a pile of rubble. There is a narrow gap, big enough to drive through.Dec 3, 2020
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Treatment for coronary artery disease usually involves lifestyle changes and, if necessary, drugs and certain medical procedures.
Overview
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Symptoms
- Lifestyle changes can help you prevent or slow the progression of coronary artery disease. 1. Stop smoking.Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease. Nicotine constricts blood vessels and forces your heart to work harder, and carbon monoxide reduces oxygen in your blood and damages the lining of your blood vessels. If you smoke, quitting is one of the best ways to r…
Causes
- Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of unsaturated fatty acid that's thought to reduce inflammation throughout the body, a contributing factor to coronary artery disease. However, some studies haven't found a benefit. More research is needed. 1. Fish and fish oil.Fish and fish oil are the most effective sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish — such as salmon, herring and light canned t…
Risk Factors
- If you know you have symptoms of or risk factors for coronary artery disease, you're likely to see your primary care doctor. Eventually, you may be referred to a heart specialist (cardiologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and to know what to expect from your doctor.
Complications
- Coronary artery disease develops when the major blood vessels that supply your heart become damaged or diseased. Cholesterol-containing deposits (plaques) in your coronary arteries and inflammation are usually to blame for coronary artery disease. The coronary arteries supply blood, oxygen and nutrients to your heart. A buildup of plaque can narrow these arteries, decreasing bl…
Prevention