What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Water Treatment Process: Follow Water Through a Surface Water Treatment Plant
- Coagulation. ...
- Flocculation. ...
- Sedimentation (or Clarification) The water continues on to the sedimentation basin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Chlorination Operations. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is the process of water treatment plant?
- Remove specific contaminants
- Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system
- Improve the taste of drinking water
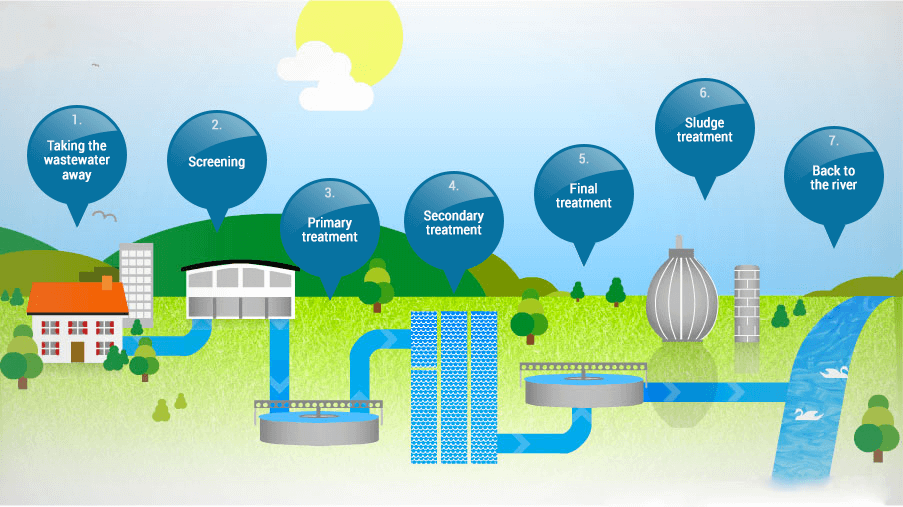
What happens to waste water that leaves your home?
in your home? When the wastewater flushed from your toilet or drained from your household sinks, washing machine, or dishwasher leaves your home, it flows through your community's sanitary sewer system to a wastewater treatment facility. The wastewater from homes, along with wastewater from businesses,
Where does my waste water go?
Don’t flush these items:
- Baby wipes, wet wipes, or any type of special wipes for that matter.
- Eggshells (or any type of shells)
- Napkins
- Hair
- Drugs
- Any kind of plastic
- Dental Floss
- Fats and oils
- Facial Tissues
What happens to the water after it is cleansed by the treatment plant?
After treatment and sufficient disinfection, the water is discharged via a pressurized system of lifts and pipes to the areas in the city where it is needed. A disinfectant residual must be maintained throughout all parts of the system to ensure no waterborne pathogens enter the system and contaminate the water.
What happens at water treatment plants?
A waste water treatment plant cleans sewage and water so that they can be returned to the environment. These plants remove solids and pollutants, break down organic matter and restore the oxygen content of treated water.
What happens to water after it is used?
This is often done with something called a septic tank and drain field. Sewage from a home flows into a large tank that collects the solids, and helpful bacteria in the tank breaks down these solids over time. The liquid flows out to a drain field, where it soaks into the soil and becomes groundwater again.
What is the final process of wastewater treatment?
The last step of primary treatment involves sedimentation, which causes the physical settling of matter. Sedimentation often uses chemicals like flocculants and coagulants.
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
Public water systems often use a series of water treatment steps that include coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
What happens to the treated sludge?
The final destination of treated sewage sludge usually is the land. Dewatered sludge can be buried underground in a sanitary landfill. It also may be spread on agricultural land in order to make use of its value as a soil conditioner and fertilizer.
How is water treated at a wastewater treatment plant?
Carbon filtering removes remaining contaminants and impurities by chemical absorption onto activated carbon. Filtration through sand (calcium carbonate) or fabric filters is the most common method used in municipal wastewater treatment.
What are the steps of wastewater treatment plant?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
Where does wastewater go after treatment?
The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it's used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What are the steps of water treatment?
The water treatment process to deliver safe and wholesome water to customers includes many steps. Coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection are the water treatment processes that make up a conventional surface water treatment plant. These water treatment processes ensure that the water consumers receive is safe to drink and aesthetically pleasing.
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
The goal of the SWTR is to reduce illnesses related to pathogens in drinking water. These pathogens include coliform, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium .
How do clarifiers work?
The large flocs will settle out of suspension via gravity. Clarifiers can remove a very large percentage of the suspended materials in water. In some plants, clarifiers remove as much as 90% of the suspended solids load. Particles that do not settle will be removed by filtration in the next treatment step.
How does water temperature affect coagulation?
Water temperature also impacts the coagulation process because it effects the viscosity of water. Both alum and ferric salts form flocs at a slower rate as the water temperature decreases.
Why is a coagulant injected into water?
A coagulant chemical is injected to neutralize these small negative charges and then the water is rapidly mixed. The rapid mixing disperses the coagulant and also increases the interaction of these small particles.
What is the process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration?
The water treatment process of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration remove the pathogens. The disinfection water treatment process inactivates them. The small particles in water may consist of silt and clay, color bodies, precipitated iron or manganese oxides, and even bacteria and algae. Together, these particles make the water ...
When to backwash a plant?
A filter may be backwashed when the head loss, which is the pressure build up, reaches a certain level. The system’s domestic water supply permit may also specify that a filter be backwashed following a certain length of time, regardless if that target head loss is achieved.
What happens when chemicals are added to water?
Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water. The positive charge of these chemicals neutralizes the negative charge of dirt and other dissolved particles in the water. When this occurs, the particles bind with the chemicals and form larger particles, called floc. Sedimentation.
How does a water treatment unit work?
Even though EPA regulates and sets standards for public drinking water, many Americans use a home water treatment unit to: 1 Remove specific contaminants 2 Take extra precautions because a household member has a compromised immune system 3 Improve the taste of drinking water
What is the process of boiled water?
Distillation is a process in which impure water is boiled and the steam is collected and condensed in a separate container, leaving many of the solid contaminants behind. Disinfection. Disinfection is a physical or chemical process in which pathogenic microorganisms are deactivated or killed.
What are the steps of water treatment?
Today, the most common steps in water treatment used by community water systems (mainly surface water treatment) include: Coagulation and flocculation are often the first steps in water treatment. Chemicals with a positive charge are added to the water.
What is a water softener?
Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water. A water softener typically uses sodium or potassium ions to replace calcium and magnesium ions, the ions that create “hardness.”. Distillation Systems.
What is the most common type of water treatment system?
The most common types of household water treatment systems consist of: Filtration Systems. A water filter is a device which removes impurities from water by means of a physical barrier, chemical, and/or biological process. Water Softeners. A water softener is a device that reduces the hardness of the water.
Why is chlorine added to water?
After the water has been filtered, a disinfectant (for example, chlorine, chloramine) may be added in order to kill any remaining parasites, bacteria, and viruses, and to protect the water from germs when it is piped to homes and businesses.
What is the goal of wastewater treatment?
The essential goal of wastewater treatment is generally to allow human and business effluents to be disposed of without chance to human fitness or unacceptable harm to the herbal environment. Irrigation with wastewater is each disposal and usage and indeed is an effective form of wastewater disposal (as in slow-charge land treatment).
Why is water important?
Water is essential for health, hygiene and the productivity of our community. The water treatment process may vary slightly at different locations, depending on the technology of the plant and the water it needs to process, but the basic principles are largely the same.
What is the process of removing particles from water?
The process is not simple and begins with coagulation and flocculation. This particular process is responsible for removing all of the natural particles that accompany water from the actual water source. Coagulants, when added to the water, can make the debris stick together. An example of a typical coagulant is aluminum sulfites ...
How does water sit in a tank?
Water is allowed to sit thus enabling the sediments to settle down to the bottom of the holding takes. The sediments that have settled down are cleared away periodically. The water is then made to move over weirds thus allowing the cleanest water at the top to move into the next array of tanks for further processes. The next phase is that of filtration.
How are coagulants introduced into water?
These coagulants are introduced in the water when it enters the treatment plant. The water is then passed through flocculation basins where slow mixing takes place. This mixing makes sure that thorough coagulation takes place. Once coagulation is completed, the water is pumped into a sedimentation basin. Water is allowed to sit thus enabling the ...
How does water pass through a carbon filter?
Once the water reaches the filtration phase, it is made to pass through differing coarseness of sand. Particles keep on getting trapped as the coarseness of the sand filter decreases. In the end, the water is made to pass through an active carbon filter. Once the filtration is over, the water is disinfected. There are three approaches that can be ...
What are the three methods of disinfecting water?
Once the filtration is over, the water is disinfected. There are three approaches that can be employed; chlorination, ozone treatment, and ultraviolet treatment . These approaches can be used either individually or in combination. Once all of these steps are completed, water is pumped out to be used by the population.
What are the resources used in water treatment?
The local water treatment plants usually rely on natural resources for procuring water, however; that is not always the case. The resources include river, dam, and well. The water that is obtained from these sources is treated thus making it safe for humans to consume at a mass level.
Does filtration remove bacteria?
However, filtration helps remove the bacteria as well. Most of the water treatment plants make use of a sand filter. The sand filter is low-tech but is a very efficient way of carrying out water purification. Once the water reaches the filtration phase, it is made to pass through differing coarseness of sand.
Screening
Most sewer systems operate by gravity flow, which pulls wastewater toward the treatment plant. It first enters the plant at the headworks and passes through the preliminary treatment called screening where large objects are trapped and removed for landfill disposal.
Aeration and Sedimentation
The wastewater leaving primary treatment then enters the secondary treatment process which is a two-phase process. In the first phase, also called aeration, the wastewater is mixed with air and cultivated microorganisms that consume suspended organic matter such as food particles, human waste, and other organic matter.
Disinfection
The fairly clean water from the secondary treatment process is sent through a filtration system to remove any fine particles remaining, and then it is ready for disinfection. The most common form of disinfection is chlorine inside a chlorine contact chamber, but other disinfection methods also work such as ozone, ultraviolet light, and peroxide.

Coagulation
Flocculation
Sedimentation
- The water continues on to the sedimentationbasin, or clarifier, after the flocs have been formed. The goal of this stage of the treatment process is to reduce the amount of solids in the water before the water is filtered in the next treatment step. The large flocs will settle out of suspension via gravity. Clarifiers can remove a very large percentage of the suspended materials in water. I…
Filtration
- The final water treatment process in removing particulates is filtration. The sedimentation process will have already removed a large percentage of the suspended solids. Sedimentation is unable to remove many small particles in water though. Filtration will remove these microorganisms and other suspended material that did not settle out previously.
Disinfection
- As discussed previously, the surface water treatment rule requires both the filtration and disinfection of surface water sources. The water must be disinfected now that it has been filtered.
Chlorination Operations
- Chlorination was one of the first drinking water disinfection methods. It is still the most commonly used disinfection method used today. The filtered water is injected with either liquid sodium hypochlorite, gaseous chlorine, or solid calcium hypochlorite. Chlorine is a strong oxidant. It is used to both disinfect and also to remove color, taste and odor compounds, iron and manganes…
Conclusion
- In order to meet the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule, a water system must both remove and inactivate the pathogens in the water. This process begins with coagulation, which destabilizes the particles in the water. Then, during flocculation, the destabilized particles bump into each other and form larger and larger flocs. These larg...