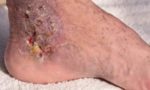
What are the consequences of untreated diabetes?
- Increased thirst or hunger
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Skin infections
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
What happens when diabetes is left untreated?
- The digestive tract, as well as the urinary bladder, fails to work appropriately. ...
- Your gum and teeth begin to show signs of decay and the gums might even bleed at regular intervals
- You become to face problems with hearing ability
- Your mouth and the skin becomes extremely dry. ...
What can happen if diabetes is not under control?
What Can Happen if Diabetes Is Not Under Control? Out-of-control blood sugar levels can lead to short-term problems like hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, or diabetic ketoacidosis. In the long run, not controlling diabetes can also damage the vessels that supply blood to important organs, like the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
What happens when you eat too much sugar with diabetes?
What Happens When a Diabetic Has Too Much Sugar?
- Hyperglycemia. According to Diabetes Care Group, normal blood sugar levels are between 80 and 120 mg/dl. ...
- Neuropathy. Neuropathy, or nerve damage, occurs when excess sugar damages the walls of the capillaries. ...
- Ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to coma and death. ...
- Diabetic Retinopathy. ...
- Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy. ...

What can a doctor do to help with diabetes?
If a change is needed, your doctor may adjust your current medication, add new diabetes medications, or suggest starting an insulin regimen.
Why is it important to review your diabetes management plan?
There are many factors that can affect your A1C, so it’s important to review your diabetes management plan regularly so you don’t miss the opportunity to do what’s best for you.
What to do if metformin doesn't work?
If metformin no longer works for you, your doctor may add another drug to your treatment plan. “But there’s no magical second drug; the secondary options will depend on the individual,” she says. Your doctor may prescribe other oral medications or noninsulin injectables.
How to keep blood sugar stable?
Eating a healthy diet to keep your blood sugar levels stable, with the help of your diabetes educator or a registered dietitian. While there is no one-size-fits-all diet, for most people it means cutting back on calories and saturated fats; reducing carbohydrates and distributing them evenly throughout the day; and bumping up your intake of vegetables, fruits, and other high-fiber foods.
What is the best reading for diabetes?
Your results are reported with a percentage. Generally speaking, a reading of less than 7 percent is usually optimal to prevent type 2 diabetes complications.
How to lower blood sugar?
Getting more physical activity , which helps lower blood sugar. Aim for 30 to 60 minutes most days of the week — everything from walking and gardening to swimming and biking — and combine that with two days of resistance training, such as weight lifting or yoga, for the best results.
Does metformin help with diabetes?
Metformin is a typical first medication for people with type 2 diabetes, says Powers. It works by decreasing the amount of sugar the liver produces and making muscle cells more sensitive to insulin so sugar can be absorbed. If metformin no longer works for you, your doctor may add another drug to your treatment plan.
What happens if you don't treat diabetes?
In this, the nerves of the hands and feet and also other body parts get damaged severely over time. You will start feeling a tingling sensation and numbness in the lower legs, forearms and hands giving rise to a condition called ‘glove and stocking neuropathy’. Injuries such as stubbed toes and blisters begin to occur which may go unnoticed due to reduced sensation in the feet. Moreover, untreated infections, skin lesions or injuries can cause gangrene, the treatment of which may require leg amputation to prevent the infection from spreading to the rest of the body.
What is the short term complication of untreated diabetes?
A short-term complication of untreated diabetes is ketoacidosis, a condition which progresses rapidly. Sugar buildup occurs in the blood with low insulin levels. The body then breaks down fat for energy and causes a buildup of ketones which are byproducts thereby lowering the blood pH levels.
Why is erectile dysfunction irreversible?
The major cause for it is that the blood vessels or the nerves in the reproductive system either get blocked or damaged due to the high blood sugar levels. In most cases, it is irreversible.
What is the main aim of diabetes?
The main aim of treating diabetes is to prevent the complications. Let us know what happens if type 2 diabetes is untreated for long. Being a metabolic disease, diabetes cannot be treated completely but can be managed quite well if the patient takes the right medications, consumes a healthy diet and also makes necessary lifestyle changes. ...
How old do you have to be to get Type 2 diabetes?
Though the relation between the two is still unclear, studies reveal that people who have type 2 diabetes untreated run a high risk of developing this disease after 60 years of age.
How many people in the US have diabetes?
Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in America and the number of people being affected by it is increasing. A recent survey revealed that more than 30 million Americans are currently suffering from diabetes and are adhering to various means of treatment for the same. The main aim of treating diabetes is to prevent the complications.
How to keep blood sugar level in check?
In some cases, all you need to do is make some minor lifestyle changes, avoid smoking and drinking, resort to physical activity and eat healthy to keep your blood sugar level in check. In other severe cases the patient might need appropriate medicines and injected insulin to control it.
How to manage diabetes?
Management of a diabetic lifestyle requires a multidisciplinary approach on your part. With a combination of diet, exercise, and knowledge , you can lead a completely normal and active life even though you've been diagnosed with diabetes. The key is to carefully manage your condition, know how your body reacts to various situations and diets and listen to what it's trying to tell you. In this article, we'll cover some ideas and suggestions for taking back control of your life and leading as normal of a lifestyle as possible. Of course, you can expect to have some ups and downs, but with practice and adapting some of your activities and habits, you'll find the diabetes doesn't have to slow you down at all. In any situation, a person with diabetes needs to monitor and maintain their blood glucose levels. After you've worked out adequate dosages and goals with your doctor, you'll better regulate how you feel on a daily basis. Be prepared to give this some time, as it may take several weeks or even a couple of months for you to adapt to your condition and the ups and downs of your blood glucose levels until you've regulated your blood sugar. At work and at school, you'll need to watch what you eat. A nutritionist, in conjunction with your doctor or a dietitian, will offer you guidelines of what you can eat, what you should eat, and the foods you should stay away from. Of course, a diabetic should stay away from high-sugar foods, but this doesn't mean you'll never be able to enjoy a piece of the chocolate cake or ice cream again. The key is to maintain self-control and self-discipline when monitoring your condition. Carefully monitor how much you eat, get adequate amounts of exercise, and make some adjustments in your lifestyle at home, at school, and at work so that you fee Continue reading >>
What happens if you take too much insulin?
If this happens, they may end up with too much insulin in their blood. This, in turn, can lead to hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar. A serious condition called insulin shock may occur if a person: ignores mild hypoglycemia takes too much insulin by mistake misses a meal completely does excessive unusual exercise without changing their carbohydrate intake Insulin shock is a diabetic emergency. It involves symptoms that, if left untreated, can lead to diabetic coma, brain damage, and even death. How insulin works When we consume food or beverages that contain carbohydrates, the body converts them into glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar that fuels the body, giving it the energy it needs to perform everyday functions. Insulin is a hormone that works like a key. It opens the door in the body’s cells so they can absorb glucose and use it as fuel. People with diabetes may lack enough insulin or have cells that aren’t able to use insulin as they should. If the cells of the body aren’t able to absorb the glucose properly, it causes excess glucose in blood. This is called high blood glucose, which is linked with a number of health issues. High blood glucose can cause eye and foot problems, heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and nerve damage. Insulin shots help people with diabetes use glucose more efficiently. Taking an insulin shot before eating helps the body absorb and use glucose from the food. The result is a more balanced and healthy blood sugar level. Usually, it works great. Sometimes, however, things go wrong. What causes insulin shock? Having too much insulin in your blood can lead to having too little gluco Continue reading >>
What organs are responsible for the release of insulin into the bloodstream?
In a normal digestive system, the arrival of food stimulates the organ called the pancreas to secrete insulin into the bloodstream to regulate glucose levels. More food, more insulin. More insulin, less glucose in the blood (and more in cells to use for energy). At its simplest, diabetes is a disorder of this process.
Why is insulin the best for dogs?
Reasons Why Insulin Is the Best Treatment for Diabetic Dogs The primary reason that insulin is the best treatment for canine diabetes is the fact that dogs with diabetes almost always suffer from insulin-dependent diabetes.
Why do people take insulin shots?
High blood glucose can cause eye and foot problems, heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and nerve damage. Insulin shots help people with diabetes use glucose more efficiently. Taking an insulin shot before eating helps the body absorb and use glucose from the food.
Why do people with diabetes have high blood glucose?
People with diabetes may lack enough insulin or have cells that aren’t able to use insulin as they should. If the cells of the body aren’t able to absorb the glucose properly , it causes excess glucose in blood. This is called high blood glucose, which is linked with a number of health issues.
What is the cause of high blood sugar?
Our bodies use glucose—or sugar—for energy. Insulin allows the cells in our body to process glucose. If your body doesn’t have enough insulin, glucose can collect in your blood. This causes high blood sugar. There’s no cure for type 2 diabetes. People with this disease will need to manage it with medication, diet, and exercise for the rest of their life. The reason doctors call diabetes a “chronic” disease is because it is a long-term health problem that can’t be cured or prevented with medication. Type 2 diabetes is also called adult onset diabetes. It’s also the most common kind of diabetes. Doctors and researchers don’t know exactly causes type 2 diabetes. Some families have higher rates of the disease. But lifestyle factors like poor diet, obesity, and not exercising enough increase your chances of developing the disease. Some medications also may increase your chances of getting it. Risk Factors For Type 2 Diabetes A risk factor is anything that increases your chances of getting a certain kind of disease. There are many risk factors for type 2 diabetes. This means that if you have or do any of these things, you have a higher chance of getting type 2 diabetes. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include the following: Having a history of diabetes in your family Being overweight Age. People who are older than 45 have a higher chance of developing diabetes. Not getting enough exercise Being pregnant Race and ethnicity. Hispanic Americans, African Americans, Asian Americans, and American Indians have higher chances of developing type 2 diabetes than Continue reading >>
What happens to glucose when you don't have insulin?
Without insulin, the glucose builds up in the blood and is excreted in the urine. This Continue reading >>. Diabulimia: the little-known eating disorder that's killing women with type 1 diabetes.
How long can you live with type 1 diabetes?
The answer, perhaps, mostly lies in how long the person has had type 1 diabetes. For someone like yourself, who indicated that you have had diabetes for more than 10 years, you MIGHT be able to live for 7 to 10 or so days without insulin. But, the death would be awful and difficult and not peaceful.
Why do people with diabetes need insulin?
Your body doesn’t produce the hormone insulin, and without that, your body can’t properly get the energy and fuel it needs from glucose. Because people with type 1 diabetes rely on insulin , it was formerly called insulin-dependent diabetes. To learn about how the hormone insulin works, we have an article that explains the role of insulin. As soon as you are (or your child is) diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, you will be immersed in the world of insulin, and it may feel overwhelming at first. There are doses to calculate, different types of insulin to consider, and the pressure of needing to keep blood glucose in a normal range to prevent short- and long-term complications. Your diabetes treatment team is there to help you. They can walk you through the basics of insulin dosing, answer any questions, and help you figure out how to balance food, exercise, and insulin. You will learn to take care of your diabetes with your diabetes team. If you are a parent of a child with type 1 diabetes, we also encourage you to visit our Patients' Guide to Managing Your Child's Type 1 Diabetes. It's often comforting to hear stories about others who are also going through the same things you are. Jay Cutler, quarterback for the Chicago Bears, was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes in 2008, and he is still getting used to regular blood sugar testing and insulin injections. To learn more about his journey with type 1 diabetes, read Jay Cutler's interview with EndocrineWeb. This article will provide basic details on insulin treatment. You can also visit our Patients' Guide to Insulin for more details. Types of Insulin With type 1 diabetes, you will need to take insulin on a daily basis, and there are several types of insulin you Continue reading >>
Why does Type 1 diabetes start?
Type 1 diabetes starts because the body destroys those beta cells. Experts don't know why this happens.
Why is it important to test blood glucose?
Testing Blood Glucose Because diabetes affects the glucose in your blood, it is important to measure this with a blood glucose meter. You will get used to having your blood glucose meter with you all of the time because checking your glucose level is the only way to know if your diabetes is under control.
What happens if you slack off?
Here's what can happen when you slack off. Your cholesterol and blood pressure rise. With type 1 diabetes, your body stops producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar; with type 2 diabetes, your body can't properly use the insulin you do produce. In turn, your HDL (or "good") cholesterol lowers, and your levels ...
How is type 1 diabetes different from type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is different from type 2 diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body stops making insulin. In type 2, the body doesn't make enough insulin, or the body can't use insulin the right way. There isn't a cure for type 1 diabetes. But with treatment, people can live long and healthy lives.
What happens when you don't get enough insulin?
First, let’s talk about the physical process that sets in when a person with diabetes does not get enough insulin into their body. Very quickly, severe hyperglycemia sets in. That is high blood sugar that leads to a state called DKA, short for diabetic ketoacidosis, which — untreated — leads to death. Basically what’s doing on is this: insulin ...
How long does insulin last in diabetes?
People with type 2 diabetes who take insulin “could last quite a bit of time — maybe years — depending on how their other meds might be working.
How long does it take for a diabetic to show symptoms of DKA?
Generally, the first signs of DKA show up once the blood glucose level has been north of 300 mg/dL for about four hours, but how quickly things get out of hand at that point is highly variable. Some people with diabetes feel ill immediately, while others can wander around in a daze for days.
What does insulin do to the body?
Basically what’s doing on is this: insulin helps sugar enter the cells, which use it for fuel. Without insulin, the body cannot access enough sugar to function properly, so your liver begins to turns some of the body fat into acids called ketones. These build up in the bloodstream and spill over into the urine.
What happens when you have ketones in your blood?
These build up in the bloodstream and spill over into the urine. When these excess ketones get into the blood, the blood becomes acidic, causing DKA: a combination of very high blood sugar, dehydration and shock, and exhaustion. Symptoms are vomiting and hyperventilation, and eventually passing out and going into a coma.
How long can you survive without insulin?
But their survival rate is “multiple days, to a few weeks, getting sicker and weaker as time goes on.
What to do if you missed a shot?
If you know that you have missed a shot or are running low / rationing insulin, it’s a good idea to keep very close tabs on your blood sugar readings and keep ketone test strips handy.
What happens if you have type 1 diabetes?
With type 1 diabetes, your body stops producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar; with type 2 diabetes, your body can't properly use the insulin you do produce. In turn, your HDL (or "good") cholesterol lowers, and your levels of harmful blood fats called triglycerides rise.
What happens if you don't control your sugar?
If your blood sugar is not controlled, serious problems called complications can happen to your body after many years. Learn the basic steps for managing diabetes to stay as healthy as possible. Doing so will help keep the complications of diabetes away.
How long does it take for diabetes to progress?
Swallowing pills, checking your blood sugar all the time, or sticking yourself with needles full of insulin probably doesn't sound like your idea of a good time. But taking steps to keep your diabetes under control is your best shot at preventing a slew of frightening complications. If you don't take care of yourself, "diabetes complications typically start within 5 years; within 10 to 15 years, the majority of patients will progress to have multiple health issues," says Betul Hatipoglu, MD, an endocrinologist at Cleveland Clinic. Fortunately, eating a nutritious diet, exercising, and taking your medication may not only stop complications from progressing, but can also reverse them, she says. Need motivation to stick to your treatment plan? Here's what can happen when you slack off. With type 1 diabetes, your body stops producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar; with type 2 diabetes, your body can't properly use the insulin you do produce. In turn, your HDL (or "good") cholesterol lowers, and your levels of harmful blood fats called triglycerides rise. Insulin resistance also contributes to hardened, narrow arteries, which in turn increases your blood pressure. As a result, about 70% of people with either type of diabetes also have hypertension—a risk factor for stroke, heart disease, and trouble with thinking and memory. (Add these 13 power foods to your diet to help lower blood pressure naturally.) Failing to control high blood pressure and high cholesterol, either with diet and exercise alone or by adding medications, accelerates the rate at which all your other complications progress, says Robert Gabbay, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston. More than 4 million people with diabetes have some degree of retinopathy, or dam Continue reading >>
Why is it important to test blood glucose?
Testing Blood Glucose Because diabetes affects the glucose in your blood, it is important to measure this with a blood glucose meter. You will get used to having your blood glucose meter with you all of the time because checking your glucose level is the only way to know if your diabetes is under control.
How to know if you have diabetes?
If your blood sugar is not controlled, serious problems called complications can happen to your body after many years. Learn the basic steps for managing diabetes to stay as healthy as possible. Doing so will help keep the complications of diabetes away. Steps include: Also, be sure to take any medicine or insulin as instructed. Your provider will also help you by ordering blood tests and other tests. These help make sure your blood sugar and cholesterol levels are each in a healthy range. Also, follow your provider's instructions about keeping your blood pressure in a healthy range. Your doctor will likely ask you to visit other providers to help you control your diabetes. These providers include a: Dietitian Diabetes pharmacist Diabetes educator Foods with sugar and carbohydrates can raise your blood sugar too high. Alcohol and other drinks with sugar can also raise your blood sugar. A nurse or dietitian can teach you about good food choices. Make sure you know how to have a balanced meal with protein and fiber. Eat healthy, fresh foods as much as possible. Don't eat too much food at one sitting. This helps keep your blood sugar in a good range. Managing your weight and keeping a well-balanced diet are important. Some people with type 2 diabetes can stop taking medicines after losing weight (even though they still have diabetes). Your provider can let you know a good weight range for you. Weight-loss surgery may be an option if you a Continue reading >>
What is the best medication for diabetes?
The most common medication worldwide for treating diabetes is metformin (Glumetza, Riomet, Glucophage, Fortamet). It can help control high blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. It’s available in tablet form or a clear liquid you take by mouth before meals.
What happens when you slack off?
Here's what can happen when you slack off. Your cholesterol and blood pressure rise. With type 1 diabetes, your body stops producing insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar; with type 2 diabetes, your body can't properly use the insulin you do produce.
What happens if you have type 2 diabetes?
If type 2 diabetes goes untreated, the high blood sugar can affect various cells and organs in the body. Complications include kidney damage, often leading to dialysis, eye damage, which could result in blindness, or an increased risk for heart disease or stroke.
What is it called when a diabetic doesn't produce enough insulin?
(Not being judgemental: these are simply the facts.) As a result, they may not produce enough insulin, and their body cells don’t respond to insulin as non-diabetics’ cells would: this is called insulin resistance.
What type of diabetic has fatty cells?
A Type 2 diabetic normally has fatty cells, fatty pancreas and/or fatty liver issues. (Not being judgemental: these are simply the facts.) As a result, they may not produce enough insulin, and their body cells don’t respond to insulin as non-diabetics’ cells would: this is called insulin resistance.
How to reverse Type 2 diabetes?
If you learn to eat properly, exercise, and test often you can reverse Type 2 diabetes. Don’t stop the insulin until you have controlled the lifestyle factors that are causing your insulin resistance. Having high insulin (from insulin resistance) and using pig or synthetic insulin in addition will shorten your lifespan.
Is insulin a type 1 or type 2?
Insulin is for Type 1 diabetics (who do not make insulin) not Type 2s who have excessive insulin but are not usin. There is no reason why a Type 2 diabetic (insulin resistant) should be taking insulin! The person needs to stop eating garbage and trying to control it with insulin.
When is insulin therapy used in type 2 diabetes?
Insulin therapy in type 2 is used after other methods of managing blood sugar have failed.
Does insulin shorten your lifespan?
Having high insulin (from insulin resistance) and using pig or synthetic insulin in addition will shorten your lifespan. Insulin is for Type 1 diabetics (who do not make insulin) not Type 2s who have excessive insulin but are not using it properly. I wound up in the hospital twice as a result of taking insulin.
What happens when you have diabetes?
When you have diabetes, your body either isn’t making enough insulin anymore, or your body is resistant to the insulin that you are creating.
What happens if your blood glucose isn't right?
If your blood glucose level isn't right, your body will react by showing certain symptoms. People with diabetes may experience hypoglycemia if they don't eat enough or if they take too much insulin — the medicine most commonly used to treat diabetes.
How long can a diabetic go without food?
A diabetic cannot go without food for long. If a diabetic doesn't eat regularly, her blood glucose level can plummet. Diabetics should eat snacks and meals on a schedule because a delay of as little as half an hour can lower blood sugar, which can have catastrophic results. Diabetics are especially prone to a condition known as hypoglycemia, a reaction caused by too much insulin in the bloodstream. Once a diabetic takes insulin, it is important to eat something within 30 minutes before blood sugar begins dropping. The dose of insulin you take must also match the amount of carbohydrates you consume in order to keep blood sugar levels under control. When a diabetic does not eat enough food, but still administers insulin, blood glucose levels can drop dangerously low, inducing hypoglycemia. Early signs of hypoglycemia include dizziness, weakness, headache, hunger or shakiness. If blood glucose drops too low, a person can become confused or even lose consciousness. In some cases, insulin shock can lead to coma. Although all diabetics suffer hypoglycemia at times, according to the American Diabetes Association, you should talk to your doctor about what your blood glucose levels should be. If your blood sugar falls below what your doctor recommends, you are likely hypoglycemic. When hypoglycemia occurs, you need to get some sugar into your body quickly. Fruit juice, milk, a few pieces of hard candy, or a tablespoon of sugar or honey can help raise glucose levels in the blood temporarily. Diabetics often need to adjust the doses of insulin they take depending on how many grams of carbohydrates they eat for a meal or snack. While this balance can be different for one person than for another, counting the carbohydrates you consume allows you to maintain a healthful blood glucose Continue reading >>
How does blood sugar work?
Part 1 of 8 What is blood sugar? Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, comes from the food you eat. Your body creates blood sugar by digesting some food into a sugar that circulates in your bloodstream. Blood sugar is used for energy. The sugar that isn’t needed to fuel your body right away gets stored in cells for later use. Too much sugar in your blood can be harmful. Type 2 diabetes is a disease that is characterized by having higher levels of blood sugar than what is considered within normal limits. Unmanaged diabetes can lead to problems with your heart, kidneys, eyes, and blood vessels. The more you know about how eating affects blood sugar, the better you can protect yourself against diabetes. If you already have diabetes, it’s important to know how eating affects blood sugar. Part 2 of 8 Your body breaks down everything you eat and absorbs the food in its different parts. These parts include: carbohydrates proteins fats vitamins and other nutrients The carbohydrates you consume turn into blood sugar. The more carbohydrates you eat, the higher the levels of sugar you will have released as you digest and absorb your food. Carbohydrates in liquid form consumed by themselves are absorbed more quickly than those in solid food. So having a soda will cause a faster rise in your blood sugar levels than eating a slice of pizza. Fiber is one component of carbohydrates that isn’t converted into sugar. This is because it can’t be digested. Fiber is important for health, though. Protein, fat, water, vitamins, and minerals don’t contain carbohydrates. These components won’t affect your blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, your carbohydrate intake is the most important part of your diet to consider when it comes to managing your blood sugar levels. Part 3 Continue reading >>
Why is skipping meals bad for diabetes?
1 / 7 Why Skipping Meals Is Harmful to Diabetes Skipping meals isn’t the best diet plan for anyone, but for people with diabetes, skipping a meal can lead to immediately dangerous blood sugar swings, as well as potential complications down the road. “An eating approach that involves consuming a consistent amount of carbohydrates — which break down into glucose or blood sugar at regular intervals throughout the day — can help prevent blood glucose spikes and improve the effectiveness of prescribed medication in people with diabetes,” says Andrea Goergen, RD, a health coach at Cultivate Healthy, a nutrition consultancy practice in Washington, DC. To better manage your blood sugar and help avoid complications, be sure to eat regularly. If you don’t, one of the following six issues may arise. Continue reading >>
What is diabetes control?
But what is diabetes control and why is it so important? When you hear your doctors or health care providers talk about "diabetes control," they're usually referring to how close your blood sugar, or , is kept to the desired range. Having too much or too little sugar in your blood can make you feel sick now and cause health problems later. Managing diabetes is like a three-way balancing act: The medicines you take (insulin or pills), the food you eat, and the amount of exercise you getall need to be in sync. don't take diabetes medicines as directed don't follow the meal plan (like eating too much or not enough food without adjusting diabetes medicines) don't get regular exercise or exercise more or less than usual without making changes to the diabetes plan What Can Happen if Diabetes Is Not Under Control? Out-of-control blood sugar levels can lead to short-term problems like hypoglycemia , hyperglycemia , or diabetic ketoacidosis . In the long run, not controlling diabetes can damage important organs, like the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. This means that heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems can happen to people with diabetes. These problems don't usually show up in kids or teens who have had the disease for only a few years, but they can happen to adults with diabetes. Kids and teens with diabetes who don't control their blood sugar levels can be late going into puberty and might not end up as tall as they would have otherwise. The good news is that keeping blood sugar levels under control can help keep you healthy and prevent health problems from happening later. How Do I Know When My Diabetes Is Under Control? If you have diab Continue reading >>
Why do people skip meals?
Skipping meals, however, may actually increase your blood sugar and cause you to gain weight. Here are seven rewards of eating regularly scheduled meals when you live with diabetes. Reward 1: Improve fasting blood glucose numbers. During sleep, when you're not eating, the liver sends more glucose into the blood to fuel the body. For many people during the early years of having type 2 diabetes, the liver doesn't realize there is already more than enough glucose present. "Your morning (fasting) blood sugars have much more to do with your liver and hormonal functions than what you ate for dinner last night," says Kathaleen Briggs Early, Ph.D., RD, CDE, assistant professor of biochemistry and nutrition at Pacific Northwest University of Health Sciences in Yakima, Washington Get more information about why your morning blood sugar is high and tips to help control fasting blood sugar. Real-life example: Until recently, if Cheryl Simpson's blood glucose meter flashed a high reading before breakfast, she might delay eating until midafternoon in an attempt to lower that number. Now Cheryl, PWD type 2, won't leave home without eating breakfast. Her blood glucose numbers have improved. "Plus, eating breakfast makes it a whole lot easier to make good food choices later on," she says. Tip: Pack a grab-and-go breakfast with these 13 quick-fix ideas! Reward 2: Stay off the blood sugar roller coaster. Irregular eating can have you "bouncing back and forth between normal blood sugars and high blood sugars," Early says. A meager meal can give you a meager rise in blood sugar. If you take one or more blood glucose-lowering medications tha Continue reading >>
What happens if you don't remove gangrene?
They usually die: Usual result is septic shock and death if the damaged tissues are not removed ahead of the gangrene process.
How long does it take to get answers from a doctor?
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free! Doctors typically provide answers within 24 hours. Educational text answers on HealthTap are not intended for individual diagnosis, treatment or prescription. For these, please consult a doctor (virtually or in person).
Can diabetics get gangrene?
No!: Gangrene is a major complication of diabetes when poor blood flow to a limb with damaged nerves causes damage to the tissue. This is a medical emergency where the goal is preserving as much healthy tissue as possible while keeping away infections. While not clear what " natural " means in this setting, this generally requires traditional medical care from a vascular surgeon or wound care team.
Is HealthTap a doctor-patient relationship?
Disclaimer: Content on HealthTap (including answers) should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment, and interactions on HealthTap do not create a doctor-patient relationship. Never disregard or delay professional medical advice in person because of anything on HealthTap.