
Medication
Taking the following steps to stay healthy might help you avoid complications of sickle cell anemia: Take folic acid supplements daily and choose a healthy diet. Bone marrow needs folic acid and other vitamins to make new red blood cells. Ask your doctor about a folic acid supplement and other vitamins.
Procedures
Sickle cell anemia can lead to a host of complications, including: Stroke. Sickle cells can block blood flow to an area of your brain. Signs of stroke include seizures, weakness or numbness of your arms and legs, sudden speech difficulties, and loss of consciousness.
Therapy
When one has sickle cell anemia the red blood cells are sticky, rigid and crescent-shaped, these features make them get stuck in the blood vessels or block the small capillaries in various organs. This condition has no cure for most people.
Self-care
Sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed in infancy through newborn screening programs. If you or your child develops any of the following problems, see your doctor right away or seek emergency medical care: Fever. People with sickle cell anemia have an increased risk of serious infection, and fever can be the first sign of an infection.
Nutrition
How can I avoid complications of sickle cell anemia?
What are the complications of sickle cell anemia?
What is sickle cell anemia and how is it treated?
When should I be worried about sickle cell anemia?
What happens if sickle cell anemia is not treated?
If it's not treated quickly, damage can cause problems with getting erections later in life. Stroke: Sickle-shaped cells can block small blood vessels in the brain, causing a stroke. Signs can include headache, seizure , weakness of the arms and legs, speech problems, a facial droop, or loss of consciousness.
What will happen if sickle cell anemia is neglected?
These cells die early, leaving healthy red blood cells in short supply and intermittently blocking organ blood flow. If not diagnosed early and properly managed, the disease can lead to serious complications, including severe pain, infection and stroke, and significantly reduced life expectancy.
What is the major cause of death for patients with sickle cell anemia?
Sickle cell anaemia is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder. The leading causes of death in sickle cell diseases (SCD) are infection, pain episodes, acute chest syndrome and stroke [1, 2].
How does sickle cell anemia get worse over time?
Splenic sequestration occurs when sickled red blood cells get trapped in the spleen and block blood flow, causing it to suddenly get bigger, fill with blood, and become swollen and painful. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the abdomen (belly) that helps the body fight an infection.
What happens during a sickle cell crisis?
A sickle cell crisis is pain that can begin suddenly and last several hours to several days. It happens when sickled red blood cells block small blood vessels that carry blood to your bones. You might have pain in your back, knees, legs, arms, chest or stomach. The pain can be throbbing, sharp, dull or stabbing.
What is the life expectancy of someone with sickle cell anemia?
Results. Among children and adults with sickle cell anemia (homozygous for sickle hemoglobin), the median age at death was 42 years for males and 48 years for females. Among those with sickle cell-hemoglobin C disease, the median age at death was 60 years for males and 68 years for females.
Can a person with sickle cell disease live a normal life?
People with sickle cell disease can live full lives and enjoy most of the activities that other people do.
Is Sickle Cell Crisis fatal?
People with sickle cell anemia can develop high blood pressure in their lungs. This complication usually affects adults. Shortness of breath and fatigue are common symptoms of this condition, which can be fatal.
What is the difference between sickle cell anemia and sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a serious group of conditions which are inherited (genetic). It affects the red blood cells in the blood. Sickle cell anaemia is the name of a specific form of SCD in which there are two sickle cell genes (see below).
Does sickle cell get worse as you age?
Because SCD is a genetic disease, people must be born with it. Children begin showing symptoms around 5 months old. Symptoms and complications then tend to get worse with age. The transition from pediatric to adult care is also linked to more medical problems.
Does sickle cell affect your period?
The results of this preliminary study indicate that patients with sickle cell disease have shorter menstrual cycles than normal control subjects. Their periods last longer and are heavier, and they have a greater incidence of dysmenorrhea.
Is sickle cell painful?
Pain is a common problem for people with sickle cell disease. It happens when the sickle-shaped red blood cells that cause the condition get stuck in small blood vessels and block blood flow. That can cause a pain episode or crisis to start suddenly, usually in the lower back, arms, legs, chest, and belly.
When do sickle cell anemia symptoms appear?
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia usually show up at a young age. They may appear in babies as early as 4 months old, but generally occur around the 6-month mark. While there are multiple types of SCD, they all have similar symptoms, which vary in severity. These include:
How to help sickle cell pain?
There are things you can do at home to help your sickle cell symptoms: Use heating pads for pain relief. Take folic acid supplements, as recommended by your doctor. Eat an adequate amount of fruits, vegetables, and whole-wheat grains.
How long do sickle cells live?
This breaking apart of RBCs is called chronic hemolysis. RBCs generally live for about 120 days. Sickle cells live for a maximum of 10 to 20 days.
What is the most common type of sickle cell disease?
Hemoglobin SS disease is the most common type of sickle cell disease. It occurs when you inherit copies of the hemoglobin S gene from both parents. This forms hemoglobin known as Hb SS. As the most severe form of SCD, individuals with this form also experience the worst symptoms at a higher rate.
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell anemia, or sickle cell disease (SCD), is a genetic disease of the red blood cells (RBCs). Normally, RBCs are shaped like discs, which gives them the flexibility to travel through even the smallest blood vessels. However, with this disease, the RBCs have an abnormal crescent shape resembling a sickle.
Why do sickle cells deform?
The red blood cells are more likely to deform and assume the sickle shape if you’re dehydration . Treating underlying or associated infections is an important part of managing the crisis, as the stress of an infection can result in a sickle cell crisis. An infection may also result as a complication of a crisis.
Why is the spleen removed?
The spleen may have to be removed due to complications of sickle cell disease in an operation known as a splenectomy. Some sickle cell patients will sustain enough damage to their spleen that it becomes shrunken and ceases to function at all. This is called autosplenectomy.
Why do doctors give sickle cell anemia?
Doctors commonly give infants and children with sickle cell anemia vaccinations and antibiotics to prevent potentially life-threatening infections, such as pneumonia. Delayed growth or puberty. Red blood cells provide your body with the oxygen and nutrients needed for growth.
What is the first sign of sickle cell anemia?
Fever. People with sickle cell anemia have an increased risk of serious infection, and fever can be the first sign of an infection.
What does sickle cell anemia look like?
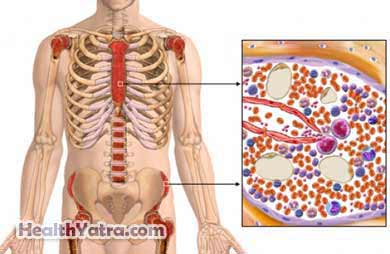
Overview. Normal red blood cells are rounded and disk-shaped. In sickle cell anemia, some red blood cells become deformed, so they look like sickles used to cut wheat. These unusually shaped cells give the disease its name. Sickle cell anemia is one of a group of disorders known as sickle cell disease.
What causes red blood cells to become sticky?
In sickle cell anemia, the abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become rigid, sticky and misshapen. Both mother and father must pass the defective form of the gene for a child to be affected. If only one parent passes the sickle cell gene to the child, that child will have the sickle cell trait.
What happens if you have sickle cells in your eyes?
Tiny blood vessels that supply your eyes can become plugged with sickle cells. This can damage the retina — the portion of the eye that processes visual images — and lead to vision problems.
How long do sickle cells last?
Red blood cells usually live for about 120 days before they need to be replaced. But sickle cells usually die in 10 to 20 days, leaving a shortage of red blood cells (anemia).
Do sickle cells have hemoglobin?
With one normal hemoglobin gene and one defective form of the gene, people with the sickle cell trait make both normal hemoglobin and sickle cell hemoglobin. Their blood might contain some sickle cells, but they generally don't have symptoms.
What medicines treat sickle cell disease?
Until recently, hydroxyurea was the only drug that treats SCD approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It reduces the number of pain crises and episodes of acute chest syndrome by increasing fetal hemoglobin levels and decreasing white blood cell count. It also reduces the need for blood transfusions and hospital visits. 1-3
What procedures are done to manage complications?
The most common procedure done to treat sickle cell disease is blood transfusion. Doctors may use single transfusions to treat complications, such as severe anemia and acute chest syndrome. They may also recommend regular blood transfusions to reduce the risk of stroke or if hydroxyurea is not working. 3,7,9
What other medicines are used to prevent or treat complications?
Preventing infections in children with sickle cell disease has greatly improved childhood survival rates. Children may take penicillin or other antibiotics once diagnosed or from 2 months old to 5 years old. Children older than 5 years old and adults may also take penicillin to prevent infections, especially if they have had their spleen removed. 4,5
Can you exchange blood with a donor?
Blood transfusions can either be simple or exchange. A simple blood transfusion adds blood from a donor without removing any of your blood. An exchange transfusion replaces some of your blood with the donor blood. Blood transfusion risks include immune reactions to the donor blood and excessive iron buildup. 4,10
What happens when you have sickle cells?
Sickle cells are destroyed rapidly in the body of people with the disease causing anemia, jaundice and the formation of gallstones.
What is the treatment for complications?
Treatment of complications often includes antibiotics, pain management, intraven ous fluids, blood transfusion and surgery all backed by psychosocial support. Like all patients with chronic disease patients are best managed in a comprehensive multi-disciplinary program of care.

Diagnosis
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Overview
- A blood test can check for the form of hemoglobin that underlies sickle cell anemia. In the United States, this blood test is part of routine newborn screening. But older children and adults can be tested, too. In adults, a blood sample is drawn from a vein in the arm. In young children and babi…
Symptoms
- Taking the following steps to stay healthy might help you avoid complications of sickle cell anemia: 1. Take folic acid supplements daily and choose a healthy diet.Bone marrow needs folic acid and other vitamins to make new red blood cells. Ask your doctor about a folic acid supplement and other vitamins. Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, as well as whole g…
Causes
- If you or someone in your family has sickle cell anemia, you might consider the following to help you cope: 1. Finding someone to talk with.Living with a chronic illness is stressful. Consider consulting a mental health professional, such as a psychologist, counselor or social worker, to help you cope. 2. Join a support group.Ask your health care provider about support groups for fa…
Risk Factors
- Sickle cell anemia is usually diagnosed through genetic screening done when a baby is born. Those test results will likely be given to your family doctor or pediatrician. He or she will likely refer you to a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist) or a pediatric hematologist. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment.
Complications
Prevention
- Signs and symptoms of sickle cell anemia usually appear around 6 months of age. They vary from person to person and may change over time. Signs and symptoms can include: 1. Anemia.Sickle cells break apart easily and die. Red blood cells usually live for about 120 days before they need to be replaced. But sickle cells typically die in 10 to 20 days, leaving a shortage of red blood cells (a…