Can you skip a day of taking TB medicine?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What happens if only one TB drug is taken?
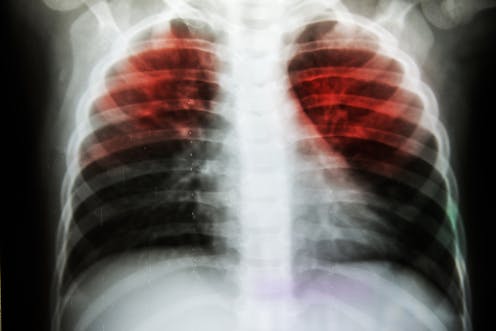
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). The bacteria, or germ, usually attack the lungs. TB germs can attack any part of the body, such as the kidney, spine, or brain. There is good news. People with TB can be …
How long does it take for TB to go away?
Archbishop Desmond Tutu received TB treatment as a child. TB is caused by bacteria which are in a person's body. TB drugs can kill all the TB bacteria in a person's body. This means that the person is then cured of TB. But TB bacteria die very slowly, and so the drugs have to be taken for several months.
What happens when a TB patient fails treatment?
The most common medications used to treat TB disease are isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Be sure to take your medicine exactly as prescribed, for …
What happens if I skip 2 days of TB treatment?
IF YOU FORGET TO TAKE YOUR MEDICINE: If it is still the same day, take the dose as soon as you remember. If the day has passed, skip the missed dose and take your next scheduled dose — do not take 2 doses at the same time.
How long does tuberculosis last without treatment?
Left untreated,TB can kill approximately one half of patients within five years and produce significant morbidity (illness) in others. Inadequate therapy for TB can lead to drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis that are even more difficult to treat.Feb 1, 2013
Is it necessary to take TB medicine on time?
You will need to stay on medicine so you don't get TB disease. You will need to stay on the TB medicine for 3, 6, or 9 months, depending on what your doctor thinks is best for you. With TB disease: You will need to take TB medicine for at least 2 to 3 weeks before you can no longer spread TB germs to other people.
What happens if I miss a day of rifampin?
Missed Dose If you miss a dose of this medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. If rifampin is taken on an irregular schedule, side effects may occur more often and may be more serious than usual.
Can you survive tuberculosis without treatment?
Without treatment, tuberculosis can be fatal. Untreated active disease typically affects your lungs, but it can affect other parts of your body, as well. Tuberculosis complications include: Spinal pain.Apr 3, 2021
What happens if you don't treat TB?
Without treatment, latent TB infection (LTBI) can progress to TB disease. If you have LTBI, you should be treated to prevent TB disease even if you do not feel sick. Treatment of LTBI is essential to preventing TB because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
Can TB be cured in 3 months?
ATLANTA - Health officials on Monday celebrated a faster treatment for people who have tuberculosis but aren't infectious, after investigators found a new combination of pills knocks out the disease in three months instead of nine.May 16, 2011
How do you know if TB treatment is not working?
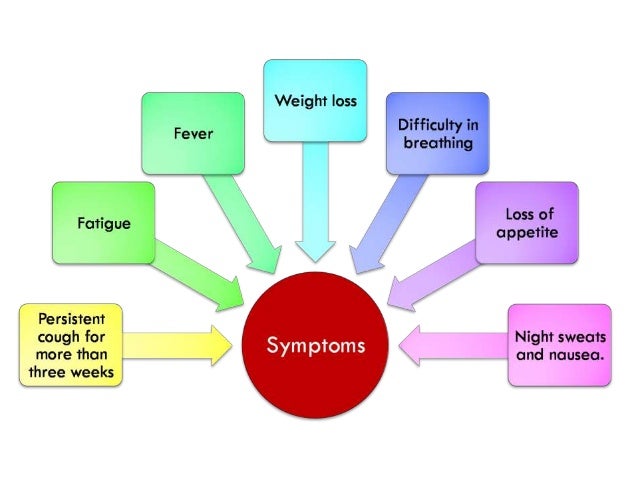
A reduction in symptoms, such as less coughing. Overall improvement in the way one feels. Weight gain. Increased appetite....These could include:Permanent damage to the lungs.Spread to other organs and organ damage.Development of strains of TB bacteria that are resistant to typical drugs.Death.Dec 16, 2009
Can lungs heal after TB?
Researchers have found that more than one-third of patients who are successfully cured of TB with antibiotics developed permanent lung damage which, in the worst cases, results in large holes in the lungs called cavities and widening of the airways called bronchiectasis.Aug 11, 2019
What is one exception to temporarily suspending TB drugs?
Exceptions are disseminated tuberculosis and tuberculous meningitis, for which there are inadequate data to support 6-month therapy; thus 9--12 months of treatment is recommended.Jun 20, 2003
What happens if I stop taking rifampin?
If you don't take Rifampin, miss too many days, or stop taking the medicine before your doctor or nurse tells you to, you may become sick with active TB disease. It is important to kill TB germs so you and your family stay healthy.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol. You may begin to feel better only a few weeks after starting to take the drugs but treating TB takes much longer than other bacterial infections.Apr 8, 2020
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
How long does pyrazinamide last?
pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment). Drug Susceptible TB Disease Treatment Regimens. Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, ...
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.
How long does it take for TB to kill?
For TB disease, it takes even longer and at least 6 months for the medicines to kill all the TB germs.
How to get rid of TB in the air?
Put a fan in your window to blow out (exhaust) air that may be filled with TB germs. If you open other windows in the room, the fan also will pull in fresh air. This will reduce the chances that TB germs will stay in the room and infect someone who breathes the air. Remember, TB is spread through the air.
How many people with LTBI will develop TB?
While not everyone with LTBI will develop TB disease, about 5–10% will develop TB disease over their lifetimes if not treated. Progression from untreated LTBI to TB disease is estimated to account for approximately 80% of U.S. TB cases. Some people who have LTBI are more likely to develop TB disease than others.
What does a negative TB test mean?
A negative TB blood test means that your blood did not react to the test and that you likely do not have TB infection. TB blood tests are the recommended TB test for: People who have received the bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG) TB vaccine.
How does TB spread?
The TB germs are spread into the air when a person with infectious TB disease of the lungs or throat coughs, speaks, or sings. People nearby may breathe in these TB germs and become infected. When a person breathes in TB germs, the TB germs can settle in the lungs and begin to grow.
What is the cause of TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). The bacteria, or germ, usually attack the lungs. TB germs can attack any part of the body, such as the kidney, spine, or brain. There is good news. People with TB can be treated if they seek medical help.
How long does it take to get a second skin test for TB?
You may need a second skin test 8 to 10 weeks after the last time you spent time with the person with TB disease. This is because it can take several weeks after infection for your immune system to react to the TB skin test. If your reaction to the second test is negative, you probably do not have TB infection.
Why does TB treatment fail?
It is often suggested that TB treatment fails because a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs correctly. However there can be a number of different reasons for TB treatment failure. It is certainly true that if a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs properly that this can lead to the development of drug resistant TB.
How long does TB treatment last?
For new patients with presumed drug susceptible pulmonary TB, the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that they should have six months of treatment. This consists of a two month intensive phase followed by a four month continuation phase.
What are the best drugs for TB?
The drugs that a patient should take depends on whether the patient has ever had TB treatment before. If the patient has never had treatment before then it can be assumed that the bacteria in the patient's body will respond, and be sensitive to all the TB drugs. So the patient can then be given the following drugs: 1 Isoniazid 2 Rifampicin 3 Pyyrazinamide 4 & Ethambutol.
What is the second exception to isoniazid?
The second exception is if the patient has been known to be in contact with a patient who is known to have drug resistant TB.
What is the responsibility of a doctor for TB?
A patient must take their drugs properly. But it is also the responsibility of the doctor to make sure that the patient has the correct drugs. The doctor must also explain to the patient how to take the drugs correctly. In many countries there are "alternative" medicines available.
How many drugs are there for TB?
There are more than twenty drugs available for TB treatment. Which ones have to be taken depends on the circumstances of the patient. If you are having TB treatment (sometimes known as antitubercular treatment or ATT), then this should always be supervised by an experienced doctor or other health person.
What happens if you take only one or two TB drugs?
If only one or two TB drugs are taken then only some of the bacteria may be killed. They may then become resistant to the TB drugs which then don't work. If the person becomes sick again then different TB drugs called second line drugs may be needed.
What to do if you think you have TB?
You may have the disease. If you don’t have a doctor, call your local health department. They’ll give you a TB skin test or special blood test to find out whether you have it. If the results show that you do have TB, you’ll have to get treatment.
What to do if you have LTBI?
If you have LTBI, you have TB germs in your body, but they’re not active. So, your doctor might prescribe preventive therapy. This involves medications that’ll keep the germs from “waking up” and spreading. If you have active TB disease, your doctor will prescribe several different medicines, which are needed to kill all of the TB bacteria.
How long do you have to take pyrazinamide?
You’ll take these drugs for at least 6 to 9 months. That’s because it takes at least 6 months for all of the bacteria to die. The most common medications used to treat TB disease are isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Be sure to take your medicine exactly as prescribed, for as long as it’s prescribed.
Why do you need to air out your room?
Air out your room whenever possible, because it’s easier for the bacteria to breed in small, enclosed spaces that lack fresh air. A few weeks into your treatment, you should start to feel better, and your doctor may let you know that you’re no longer infectious.
How to take meds every day?
Here are a few ways you might do that: Pick a daily activity and take your medicines when you do that activity -- like before or after brushing your teeth, putting in your contact lenses, or eating breakfast. Write an “X” on a calendar each day after you take your meds. Use a weekly pill dispenser.
Why do you take your medication in front of them?
There, you’ll take your medication in front of them. This ensures that you’re not missing doses. It also helps the health care worker to keep an eye out for side effects and answer any questions you might have. If DOT isn’t an option for you, it’s important to create a routine around taking your medicines.
How to stay home after taking meds?
Write an “X” on a calendar each day after you take your meds. Use a weekly pill dispenser. Ask a friend or family member to remind you. In the beginning, while you’re being treated, you’ll need to stay home – no work, no school, no visiting friends.
