
Medication
Sometimes an enlarged heart doesn’t cause any symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can include: an irregular heart rhythm ( arrhythmia) or heart palpitations swelling in the legs and ankles caused by fluid buildup ( edema) Symptoms that indicate a medical emergency include:
Procedures
If your enlarged heart is related to coronary artery disease, your doctor may recommend coronary artery bypass surgery. Left ventricular assist device (LVAD). If you have heart failure, you may need this implantable mechanical pump to help your weakened heart pump.
Nutrition
You can be more susceptible to blood clots and cardiac arrest. You may also have persistent heart murmurers, which are due to friction during the flow of blood and disrupt the rhythm of your heart. If it is left untreated, an enlarged heart can also lead to sudden death.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged heart?
Potential health complications from an enlarged heart can include: Blood clots, which can block blood flow and lead to a heart attack, stroke or pulmonary embolism (clot in the lung). Heart failure, if the left side of your heart is enlarged (left ventricular hypertrophy). Heart murmur, if your heart valves do not close properly.
What can I do about an enlarged heart?
What happens if an enlarged heart is left untreated?
What happens if the left side of Your Heart is enlarged?
See more

Can enlarge heart be treated?
Depending on the condition, an enlarged heart may be temporary or permanent. Treatment for an enlarged heart may include medications, medical procedures or surgery.
Is an enlarged heart a serious problem?
Depending on the cause of the enlarged heart, it may or may not be reversible. Over time, an enlarged heart can cause serious health problems. Most notably, it can increase the risk of sudden death. In addition, it can cause fluid to build up in the body and lungs, which can lead to heart failure.
Can you live with an enlarged heart?
It may not pump blood effectively, which can cause congestive heart failure. It may improve over time. But most people with an enlarged heart need lifelong treatment with medications.
How long can a person live with an enlarged heart?
The effect of an enlarged heart on life expectancy depends in part on the underlying cause. But even with treatment, many people have a downhill course. Most with severe heart disease die within a few years.
What is the symptoms of heart enlargement?
People with cardiomegaly may not have any symptoms until their condition becomes more severe....Symptomsshortness of breath.chest pain.heart palpitations (rapid, fluttering, or pounding heartbeat)arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)dizziness.fainting.rapid exhaustion with physical activity.swelling.
Can a enlarged heart go back to normal?
Some people have an enlarged heart because of temporary factors, such as pregnancy or an infection. In these cases, your heart will return to its usual size after treatment. If your enlarged heart is due to a chronic (ongoing) condition, it usually will not go away.
Can enlarged heart cause death?
Cardiac arrest and sudden death: An enlarged heart may disrupt the heart's electrical system, which can lead to a cardiac arrest. This can sometimes result in sudden death. Heart failure: If the heart is so enlarged that it loses its ability to pump blood throughout the body, we call this heart failure.
What food is good for enlarged heart?
eating a heart-healthy diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean poultry, fish, low fat dairy, and whole grains. limiting salt and saturated and trans fats. avoiding tobacco and alcohol.
What does it mean when your heart is enlarged?
An enlarged heart (cardiomegaly) means that your heart is bigger than normal. Your heart can become enlarged if the muscle works so hard that it thickens, or if the chambers widen. An enlarged heart isn’t a disease. It’s a symptom of a heart defect or condition that makes the heart work harder, such as cardiomyopathy, heart valve problems, ...
How to prevent heart enlargement?
Yet you can prevent later damage to your heart that can make it enlarge by: eating a heart-healthy diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean poultry, fish, low-fat dairy, and whole grains. limiting salt, along with saturated and trans fats.
What is the condition that causes a hole in the heart?
Congenital conditions. Congenital cardiomegaly is a heart disorder you’re born with. Congenital heart defects that cause this symptom include: atrial septal defect, a hole in the wall separating the two upper chambers of the heart. ventricular septal defect, a hole in the wall separating the two lower chambers of the heart.
Why does my heart get bigger?
Any disease that makes your heart work harder to pump blood through your body can cause an enlarged heart. Just as the muscles of your arms and legs get bigger when you work them, your heart gets bigger when you work it. The most common causes of an enlarged heart are ischemic heart disease and high blood pressure.
What is the term for a progressive heart disease?
Cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy is a progressive heart disease with several types. Diseases that damage the heart muscle can cause it to enlarge. The more damage that occurs, the weaker and less able to pump the heart becomes.
What is the first test to see if your heart is enlarged?
A chest X-ray may be the first test your doctor does because it can show whether your heart is enlarged. Tests like these can help your doctor find the cause of the enlargement: Echocardiogram (ECG or EKG) uses sound waves to look for problems with your heart’s chambers.
What is the name of the hole in the wall that separates the lower chambers of the heart?
ventricular septal defect, a hole in the wall separating the two lower chambers of the heart. coarctation of the aorta, a narrowing of the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. patent ductus arteriosus, a hole in the aorta.
What are the health risks of an enlarged heart?
The health risks of an enlarged heart depend on the cause. They also depend on which part of your heart is enlarged. Potential health complications from an enlarged heart can include: Blood clots, which can block blood flow and lead to a heart attack, stroke or pulmonary embolism (clot in the lung).
What is an enlarged heart?
What's an enlarged heart? An enlarged heart (cardiomegaly) refers to a heart that is bigger than typical. The heart may be unusually thick or dilated (stretched). An enlarged heart may be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Why does my heart get enlarged?
Some people may have an enlarged heart because of a temporary condition, such as pregnancy. Or underlying conditions , such as high blood pressure or cardiomyopathy, may lead to an enlarged heart. You can prevent cardiomegaly by living a healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors. Though an enlarged heart may not go away, ...
What are the best medications for heart disease?
Common heart medications include: Anti-arrhythmics to keep your heart beating in a normal rhythm. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors to lower your blood pressure. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) to lower your blood pressure . Anticoagulants to reduce your risk of blood clots.
Why does my heart get bigger?
Some people have an enlarged heart because of temporary factors, such as pregnancy or an infection. In these cases, your heart will return to its usual size after treatment. If your enlarged heart is due to a chronic (ongoing) condition, it usually will not go away.
What is the purpose of an echocardiogram?
Echocardiogram to evaluate and create an image of your heartbeat and blood flow. Electrocardiogram (EKG) to study your heart’s electrical activity. Exercise stress test, raising your heart rate with medicine or exercise to learn how your heart responds.
How to help your heart beat?
Implant a pacemaker to help your heart beat a steady rhythm. Place an implantable cardioverted-defibrillator (ICD), a device that can shock your heart back into rhythm. Repair or replace a damaged heart valve. Coronary artery bypass or stent placement.
What are the complications of an enlarged heart?
Complications of an enlarged heart can include: Heart failure. An enlar ged left ventricle, one of the most serious types of enlarged heart, increases the risk of heart failure.
What does it mean when your heart is enlarged?
Enlarged heart, in heart failure. As the heart weakens, as it can with heart failure, it begins to enlarge, forcing the heart to work harder to pump blood on to the rest of the body. An enlarged heart (cardiomegaly) isn't a disease, but rather a sign of another condition.
What causes the left ventricle to enlarge?
High blood pressure. Your heart may have to pump harder to deliver blood to the rest of your body, enlarging and thickening the muscle. High blood pressure can cause the left ventricle to enlarge, causing the heart muscle eventually to weaken. High blood pressure may also enlarge the upper chambers of your heart.
Why does my heart look enlarged on X-rays?
Accumulation of fluid in the sac that contains your heart may cause your heart to appear enlarged on a chest X-ray. Blocked arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease). With this condition, fatty plaque in your heart arteries obstruct blood flow through your heart vessels, which can lead to a heart attack.
What happens when your heart is in a dilated state?
In heart failure, your heart muscle weakens, and the ventricles stretch (dilate) to the point that the heart can't pump blood efficiently throughout your body. Blood clots. Having an enlarged heart may make you more susceptible to forming blood clots in the lining of your heart.
What is the condition where the heart pumps blood?
Cardiomyopathy. This disease of the heart makes it harder for your heart to pump blood throughout your body. As it progresses, your heart may enlarge to try to pump more blood. High blood pressure in the artery that connects your heart and lungs (pulmonary hypertension).
What is high blood pressure?
High blood pressure. Having a blood pressure measurement higher than 140/90 millimeters of mercury. A family history of enlarged hearts or cardiomyopathy. If an immediate family member, such as a parent or sibling, has had an enlarged heart, you may be more susceptible. Congenital heart disease.
How to reduce heart enlargement?
One of the main ways you can reduce the effects of an enlarged heart and help combat the underlying causes of the condition is through diet. You should eat foods low in saturated fats, sodium, and cholesterol. You should incorporate more fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and healthy proteins into your diet.
What is an enlarged heart?
Experts say that an enlarged heart, also known as cardiomegaly, occurs when your heart is larger than what is considered normal. This condition is not a disease itself, but rather a condition that is brought on by other various diseases and conditions. [1]
What do doctors prescribe for blood clots?
If he is worried that you may be at risk for blood clots, your doctor may prescribe you anticoagulants. These medications reduce the risk of blood clots that can lead to strokes or heart attacks. He may also prescribe anti-arrhythmics, which are medications designed to help keep your heart at a normal rhythm. [20]
How to treat scarring in heart?
These medications help lower the levels of water and sodium in the body and help decrease the thickness of your heart muscles. This medication may lower blood pressure.
What is an ICD for heart failure?
The ICD is a matchbox-sized device that helps the heart maintain its normal rhythms through electrical shocks.
What causes a heart to enlarge?
These include heart valve or heart muscle disease, arrhythmia, weakening of the heart muscle, fluid around your heart, high blood pressure, and pulmonary hypertension.
What are the risk factors for an enlarged heart?
If you have high blood pressure, blocked arteries, congenital heart disease, valvular disease, or have had a heart attack. You are also at risk if your family has a history of enlarged hearts, since they tend to run in families.
What are the symptoms of an enlarged heart?
There may, however, be warning signs, including the following: Fainting or seizure during or immediately after exercise. Unexplained shortness of breath.
What does it mean when your heart is enlarged?
An enlarged heart is usually a sign of an underlying medical issue that is causing the heart to have to grow in order to function properly. When a heart enlarges, it can follow one of two patterns: Either the walls of the heart can get thicker, or the chambers of the heart can enlarge and expand.
How to tell if you have an enlarged heart?
One of the challenging aspects of identifying people with an enlarged heart is the fact that, often, people with an enlarged heart don’t experience any symptoms. While there are many possible symptoms caused by an enlarged heart, sometimes a cardiac arrest could be the first sign, which is why heart screenings are so important. There may, however, be warning signs, including the following: 1 Fainting or seizure during or immediately after exercise. 2 Unexplained shortness of breath. 3 Dizziness 4 Extreme fatigue. 5 Racing heart (feels like it is beating out of your chest). 6 Sudden and unexplained death of a family member under the age of 50 (e.g. drowning, auto accident, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)).
What is the best way to detect sudden cardiac arrest?
A heart screening, with a physical exam, thorough medical history, and ECG is the most effective way of detecting conditions that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest and death if left untreated. Find a heart screening near you. Find a specialist near you. For more information about enlarged hearts, visit our Best Resources List.
Why does my heart get bigger?
As people get older, chronic underlying medical problems can gradually lead to enlargement of the heart. Any medical condition that increases the amount of force the heart has to generate to pump blood , or increases the amount of blood the heart has to pump, ...
Can a virus cause an enlarged heart?
It is also possible for certain viruses , drugs, and other chronic medical issues to cause an enlarged heart. Athletes can also be more susceptible to certain conditions with links to sudden cardiac arrest and death. The heart is a muscle, so just like a bicep or quadricep, the more it gets used, the bigger it can grow.
Can a clot of blood cause a heart attack?
In addition, it can cause fluid to build up in the body and lungs, which can lead to heart failure. It can also prompt blood clots to form in the heart and travel throughout the body, which – depending where the blood clots travel – can cause a stroke, heart attack, or severe damage to any other organ in the body.
What is an enlarged heart?
What is Enlarged Heart? Enlarged heart refers to enlargement of either the heart chamber size or the heart muscle size in a process known as hypertrophy.
What is the process of enlarge heart?
This redistribution of wall stress leads the heart to enlarge over time in a process called remodeling.
What is the difference between aortic regurgitation and mitral regurgitation?
In aortic regurgitation, that same valve is leaky and there is a different type of stress in addition known as volume overload. Aortic regurgitation is somewhat unique in that there is pressure and volume overload leading to both enlarged heart chambers and thick heart muscle. In mitral regurgitation the mitral valve that separates ...
Why does the heart become thick?
The heart becomes thick to compensate in a form of enlarged heart called concentric hypertrophy. The thick heart, although pumps well, does not relax well and that can lead to heart failure, and if not treated in time can lead to severely reduced heart function and weak muscle. In aortic regurgitation, that same valve is leaky ...
What is the right sided enlarged heart?
The right side of the heart is not able to cope with large pressures in the same way the left side does, so in periods of stress it may enlarge and fail immediately.
Why does the heart enlarge when you lift weights?
If you go to the gym and lift weights, your muscles get bigger as a response to the weight and enlarge, its called hypertrophy . The heart enlarges in the same way; ultimately it’s about minimizing stress.
What happens when blood pressure is high?
High Blood pressure and Enlarged Heart – The heart usually pumps in to the body against the blood pressure in the body, and at a normal blood pressure level it is designed to handle this well. Now if that blood pressure is very elevated, the heart has to pump against this. This increases well stress on the wall of the heart muscle ...
What are the consequences of an enlarged heart?
Dizzy spells or fainting. Radiating pain or discomfort originating in the shoulder and going down the arms, back, neck, or stomach. The most devastating consequences of an enlarged heart are sudden cardiac arrest and heart attack.
What happens if your heart is enlarged?
Cardiac arrest and sudden death: An enlarged heart may disrupt the heart’s electrical system, which can lead to a cardiac arrest. This can sometimes result in sudden death. Heart failure: If the heart is so enlarged that it loses its ability to pump blood throughout the body, we call this heart failure.
Why are people with cardiomegaly at risk for blood clots?
Blood clots: People with cardiomegaly are at risk of blood clots because blood flow becomes stagnated. Blood clots that enter the bloodstream not only impede blood flow but may also put you at higher risk of heart attack or stroke, especially if you have a higher risk of cardiovascular complications such as a history of diabetes, ...
How to diagnose cardiomegaly?
Cardiomegaly can be diagnosed via chest X-ray, but this is far from the best way to diagnose it. The chest X-ray may alert the physician to an enlarged heart, but the confirmatory, or true diagnosis, will come from additional, more specific testing such as an echocardiogram, cardiac MRI, or cardiac CT scan. 1.
What are the complications of a damaged heart muscle?
Complications. A damaged heart muscle can lead to stagnated blood flow, arrhythmias, and even death. Complications are most often due to dilated cardiomyopathy, a thinning of the ventricle walls that leads to an enlarged heart. The ventricles generate most of the pumping force of the heart.
What is enlarged heart?
An enlarged heart, also known as cardiomegaly, is a condition that occurs when the heart has to work harder as a result of stress, infection, or heart disease.
Why does my heart enlarge?
An enlarged heart is usually the result of disease or health problems , but if the enlargement only lasts for a short while before returning to its normal size, there is likely a less ominous explanation—like pregnancy or a history of strenuous exercise.
Heart Disorders
There are a variety of heart disorders that can lead to mild cardiomegaly. Mild cardiomegaly is generally not considered to be a disease of the heart, but instead the consequence of certain heart diseases. Understanding the cause of mild cardiomegaly makes management and treatment much more effective. Causes can include:
Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders can result in the enlargement of the heart. These include:
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can impact the size of the heart temporarily. In pregnancy, your heart is responsible for pumping your blood and the blood to your baby. The extra demand makes the heart work harder and enlarge. Usually, the cardiomegaly in pregnancy is reversible, and the heart goes back to a normal size a few months after the baby is born.
Drugs and Alcohol
Consuming cocaine, methamphetamine, or large amounts of alcohol is known to cause a heart disease called cardiomyopathy. 2 Stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine place the heart under a large amount of stress. Over time, the stress causes the heart to enlarge. Alcohol can create toxins in the body that damage the heart.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mild cardiomegaly is used to describe a mildly enlarged heart. Mild cardiomegaly may be one of the first signs of another heart disorder. If you have cardiomegaly, you should consult with a physician so they can evaluate the potential causes of an enlarged heart.
A Word From Verywell
Medications and procedures to treat heart diseases can help patients live long and fulfilling lives, making issues like mild cardiomegaly manageable. Heart disease is the most common disease in the world, and many advances have been made to treat heart disease effectively.
What happens if you have left arterial enlargement?
Once diagnosed with left arterial enlargement, you may be at risk for additional cardiovascular complications if you don’t take measures to keep conditions like high blood pressure and arrhythmias in control.
How to diagnose enlarged left atrium?
Your doctor can diagnose enlargement of the left atrium using an imaging method called echocardiography. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to take pictures of the structure of your heart. During an echocardiogram, you lie on a table while the doctor places small electrodes onto your chest.
What causes left ventricle to enlarge?
Dysfunction of the left ventricle. If there’s a problem with your left ventricle, the pressure in the left atrium will increase in order to be able to fill the left ventricle properly. This increase in pressure can lead to enlargement of the left atrium. In this case, the amount of enlargement in the left atrium can reveal the level ...
What percentage of people with high blood pressure have left atrial enlargement?
A review of 15 studies over the last 12 years found that left atrial enlargement is present in 16 to 83 percent of people with either treated or untreated high blood pressure.
What factors affect the size of the left atrium?
The following factors can influence the size of the left atrium: Age. It’s important to note that normal aging itself isn’t a cause. Instead, changes that occur to your body as you age can influence the size of the left atrium. Gender. Men typically have a larger left atrium than women.
Can atrial fibrillation be permanent?
In this condition, the two upper chambers of your heart, or atria, beat out of sync with the two lower chambers, or ventricles. Atrial fibrillation can happen occasionally, or it can be permanent. It’s unclear if atrial fibrillation is a cause ...
How to treat high blood pressure?
High blood pressure can be treated in the following ways: taking medications, such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, alpha-beta-blockers, and diuretics. eating a heart-healthy diet. limiting salt. being physically active and maintaining a healthy weight.
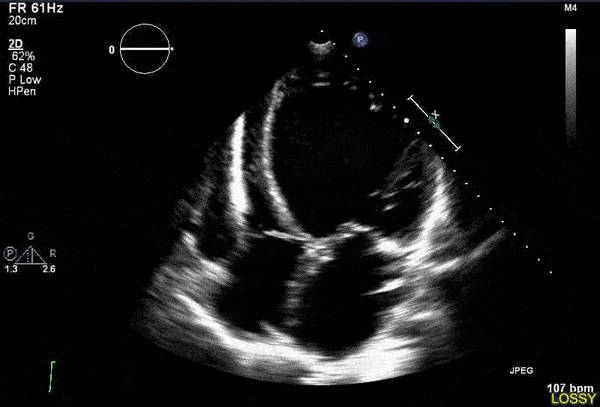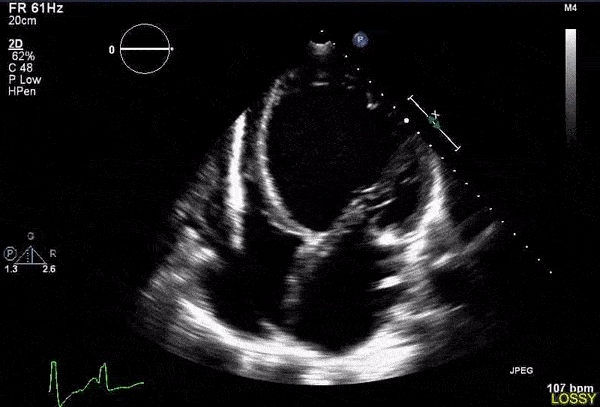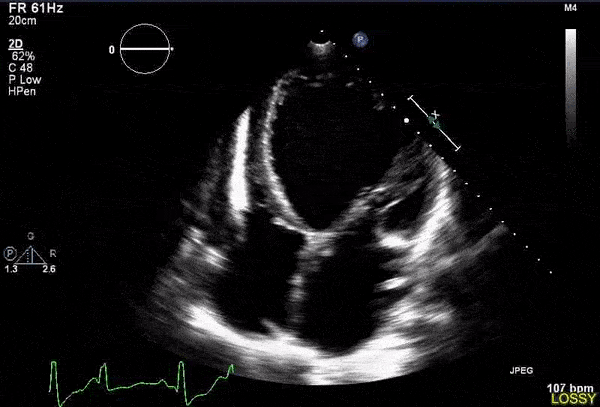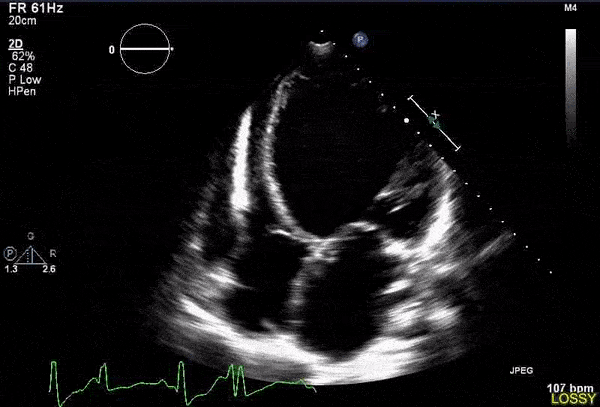
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Complications
Prevention
- If you have an enlarged heart or any type of heart disease, your health care provider will likely recommend following a heart-healthy lifestyle. Such a lifestyle typically includes: 1. Reducing or avoiding salt 2. Limiting saturated and trans fats 3. Eating plenty of vegetables, fruits and whole grain foods 4. Avoiding or limiting alcohol and caffe...