An EEG (electroencephalogram) should be done and often shows spike or sharp waves in the tip or front of the temporal lobe. These can be seen when a person is awake or asleep. When seizures arise in more mesial (middle) temporal lobe areas, the EEG may only show rhythmic slowing during seizures.
Full Answer
How does a sleep-deprived EEG work?
Focal and Generalized Slowing and Significance. EEG can provide evidence for underlying diffuse or focal cerebral dysfunction through demonstration of background slowing. The two main types of slowing are focal and generalized slowing. As previously discussed, generalized background slowing in the theta and delta frequency ranges is a normal finding on EEG when it represents …
What are SREMs of drowsiness on EEG?
The EEG may also be used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain (for example, to evaluate trauma, drug intoxication, or extent of brain damage in comatose patients). The EEG may also be used to monitor blood flow in the brain during surgical procedures. There may be other reasons for your healthcare provider to recommend an EEG.
What does slow wave activity on EEG indicate?
Apr 19, 2019 · An EEG is also useful in diagnosing narcolepsy and insomnia. Doctors use EEG as part of a sleep study or polysomnography. During the said test, a patient stays overnight in a medical facility. While connected to an EEG, the sleep specialist monitors the stages of sleep of a patient. This is a non-invasive test and is safe even for children.
What happens after an EEG?
however, having some pain during the treatment illustrates that shockwaves are having a positive effect. Will I be in pain after the treatment? You will normally experience a reduced level of pain or no pain at all immediately after the treatment, but a mild and diffused pain may occur a few hours later. This dull pain can last for a day or so.
Which EEG waves are indicative of REM sleep?
Which EEG brain wave patterns are found in stage 1 sleep?
What is a sleep induced EEG?
What does an EEG confirm about brain activity when we sleep?
What are the EEG patterns seen during stage 2 sleep?
What brain waves are in Stage 3 sleep?
What is a routine EEG?
Do you sleep during EEG?
What is the process of EEG?
What can EEG diagnose?
How long do you sleep during an EEG?
Can EEG cause seizures?
In rare instances, an EEG can cause seizures in a person with a seizure disorder. This is due to the flashing lights or the deep breathing that may be involved during the test. If you do get a seizure, your healthcare provider will treat it immediately.
What is an EEG?
An EEG is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain. During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp. The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells.
How does a scalp electrode work?
During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp. The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells. The charges are amplified and appear as a graph on a computer screen, or as a recording that may be printed out on paper.
How many pages does an EEG take?
Electroencephalogram (EEG) During an EEG, your healthcare provider typically evaluates about 100 pages, or computer screens, of activity. He or she pays special attention to the basic waveform, but also examines brief bursts of energy and responses to stimuli, such as flashing lights.
How many pages are evaluated in an EEG?
During an EEG, your healthcare provider typically evaluates about 100 pages, or computer screens, of activity. He or she pays special attention to the basic waveform, but also examines brief bursts of energy and responses to stimuli, such as flashing lights.
Why do we need an EEG?
The EEG may also be used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain (for example, to evaluate trauma, drug intoxication, or extent of brain damage in comatose patients). The EEG may also be used to monitor blood flow in the brain during surgical procedures. There may be other reasons for your healthcare provider to recommend an EEG.
Is it safe to do an EEG?
The EEG has been used for many years and is considered a safe procedure. The test causes no discomfort. The electrodes record activity. They do not produce any sensation. In addition, there is no risk of getting an electric shock. In rare instances, an EEG can cause seizures in a person with a seizure disorder.
What does EEG mean in sleep?
The EEG readings can give a doctor a clearer picture of a patient’s sleep patterns. Different brain activities correspond to different stages of sleep. In fact, the stages of sleep were first discovered via the use of EEG. This is why doctors also call Stage 3 of sleep as Delta Wave Sleep. Delta waves indicate the deepest levels ...
Is EEG a sleep study?
An EEG is also useful in diagnosing narcolepsy and insomnia. Doctors use EEG as part of a sleep study or polysomnography. During the said test, a patient stays overnight in a medical facility. While connected to an EEG, the sleep specialist monitors the stages of sleep of a patient. This is a non-invasive test and is safe even for children.
What is stage 3 sleep?
In fact, the stages of sleep were first discovered via the use of EEG. This is why doctors also call Stage 3 of sleep as Delta Wave Sleep.
What is EEG test?
Read our full medical disclaimer. An Electroencephalography (EEG) is a test that can detect abnormalities in the brain waves or the electrical activity of the brain. This test uses electrodes made of small metal discs that get pasted on the scalp of the patient.
What does rapid spiking waves mean on an EEG?
An EEG is useful in evaluating several types of brain disorders. For example, rapid spiking waves on an EEG may indicate the presence of epilepsy. On the other hand, a person with lesions on the ...
What is the purpose of an EEG?
The brain is an amazing organ. Through the use of an EEG, it is possible to record brain waves that indicate whether a person is sleeping well or not.
Why is EEG important?
The brain is an amazing organ. Through the use of an EEG, it is possible to record brain waves that indicate whether a person is sleeping well or not. This is why an EEG is a helpful tool not just in diagnosing a sleep disorder but in pinpointing the cause of the disorder. With the help of an EEG, a doctor can help a patient effectively deal ...
What is sleep deprived EEG?
Sleep disorders. A sleep-deprived EEG further assesses changes in brain activity that can indicate various brain disorders, like epilepsy or other seizure disorder s. A sleep-deprived EEG can be used to diagnose and differentiate various types of epilepsies. Sometimes seizure activity can manifest with psychiatric symptoms.
How long does it take to do an EEG?
A standard EEG procedure can be about one hour to an hour and a half, with time spent applying the electrode wires and a 20 to 40 minute period for recording brain activity, while the sleep-deprived EEG procedure usually takes a few hours. The recording will continue while that patient is falling asleep or dozing.
What to do if you have a seizure during sleep deprived EEG?
In case you have a seizure, which is a possibility among those who are predisposed to this condition and thus undergoing the testing, you would be treated with a fast-acting anti-seizure medication immediately.
Can an EEG detect seizures?
A standard EEG can detect seizures and diagnose epilepsy, but a sleep-deprived EEG may better detect more subtle seizures, like absence seizures or focal seizures. Learn about sleep-deprived EEGs, their purpose in diagnosing seizures, potential risks, and costs, and what to expect before, during, and after the testing is completed.
What is the relationship between sleep and epilepsy?
The relationship between sleep and epilepsy has been studied for years. Sleep deprivation is proposed as an “activation procedure” used to trigger epileptic seizures and to initiate interictal epileptiform abnormalities. The latter are abnormal electrical patterns that are characteristic of epilepsy and occur between clinical seizures.
Can an EEG be deprived?
The latter are abnormal electrical patterns that are characteristic of epilepsy and occur between clinical seizures. A board-certified neurologist may recommend a sleep-deprived EEG after a person with suspected seizures has had a standard EEG test that failed to show any unusual electrical activity.
Does sleep deprivation improve the diagnosis of epilepsy?
Sleep deprivation can improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of epilepsy and increase the probability of detecting the characteristic electrical patterns known as epileptiform discharges. Standard EEGs may detect many findings, including evidence of: Brain tumors. Brain damage from a head injury.
Do vertex waves persist in stage 2 sleep?
They can be contoured sharply and occur in repetitive runs, especially in children. They persist in stage II sleep but usually disappear in subsequent stages. Unlike K complexes, vertex waves are narrower and more focal and by themselves do not define stage II.
Is sleep a sharp wave?
The importance of normal sleep patterns is that they should not be mistaken for pathologic sharp waves. Several normal stage I patterns easily can be mistaken for epileptic sharp waves or spikes, including vertex sharp transients, POSTS, and even fragments of alpha rhythm as it drops out.
What stage does SREM disappear?
However, they are slow (ie, typically 0.25-0.5 Hz). SREMs disappear in stage II and deeper sleep stages. Attenuation (drop out) of the alpha rhythm: Drop out of alpha activity typically occurs together with or nearby SREM. The alpha rhythm gradually becomes slower, less prominent, and fragmented. Central or frontocentral theta activity.
What is the amplitude of a vertex wave?
Their amplitude is 50-150 µV. They can be contoured sharply and occur in repetitive runs, especially in children.
What is the first sign of sleep transition?
The earliest indication of transition from wakefulness to stage I sleep (drowsiness) is shown here and usually consists of a combination of (1) drop out of alpha activity and (2) slow rolling eye movements. Slow rolling (lateral) eye movements during stage I sleep.
What is a positive occipital sharp transient of sleep?
Positive occipital sharp transients of sleep (POSTS) are seen in both occipital regions, with their typical characteristics contained in their name . They also have morphology classically described as "reverse check mark" and often occur in consecutive runs of several seconds, as shown here.
What is stage 2 hypersynchrony?
Hypnagogic hypersynchrony: Hypnagogic hypersynchrony (first described by Gibbs and Gibbs, 1950 [ 3] ) is a well-recognized normal variant of drowsiness in children aged 3 months to 13 years.
What is the phase of sleep in EEG?
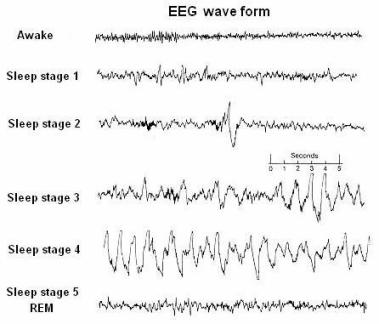
When one begins to fall asleep, the EEG begins to slow. Brain wave activity in the alpha band is common. It is easy to be aroused by external stimuli. Stage 1 Sleep follows this transition from wakefulness, and is of brief duration (5-10 minutes). Stage 1 sleep is characterized by alpha (8-12 cps) and emerging theta wave activity (4-7 cps).
What is the EEG activity during REM sleep?
Irregular breathing and heart rate are also characteristic of REM sleep. EEG activity during this stage is similar to that found during wakefulness, dominated by low-amplitude (voltage), high-frequency beta waves. Most of the dreaming we experience occurs during REM sleep.
What are the stages of sleep spindles?
During this stage, breathing and heart rate decline along with muscle tone and temperature. During Stage 2 Sleep, breathing, heart rate, muscle tone, and temperature continue to slow. Brief bursts of high-frequency brain wave activity are superimposed on an EEG of varying frequency. These bursts of high-frequency activity are called sleep spindles.
What is slow wave sleep?
The slow-wave sleep of Stage 3 Sleep and Stage 4 Sleep is characterized by ever increasing amounts of delta wave activity (less than 4 cps). One usually enters slow-wave sleep toward the end of the first hour of sleep and stays in that state for approximately 30 ...
How long does it take to go into slow wave sleep?
One usually enters slow-wave sleep toward the end of the first hour of sleep and stays in that state for approximately 30 minutes. After stage 4 of the slow-wave period, the cycle reverses itself and slowly moves backward into lighter stages of sleep. This is when REM sleep, or the 5th stage of sleep occurs.
How long is REM sleep?
Shortly before we awaken, the typical REM period will last approximately one hour. As the duration of REM sleep increases throughout the night, the duration of NREM sleep decreases.
Is sleep a regulated process?
As demonstrated by the experiments that address the effects of sleep deprivation, sleep is a regulated process. The amount of sleep we experience is monitored by a physiological mechanism that then exerts control to ensure our survival and optimal functioning .
Does REM sleep cause zaps?
A theory is that REM sleep (rapid-eye movement) may influence serotonergic processes in the brain, and the “zaps” are a byproduct of the rapid-eye movement. Whether this has any credibility is debatable. Those who have felt the zaps while sleeping may be able to provide more insight into this experience.
What does it mean when you feel electrical zapping?
A person experiencing these zaps may get dizzy, feel minor pain, and high levels of discomfort.
What causes brain zaps?
The zaps may also be caused via discontinuation of other psychotropic medications including: antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, MAOIs, SNRIs, and tricyclic antidepressants. Antidepressant withdrawal: During withdrawal from antidepressant medications, “brain zaps” are considered common symptoms to experience. It is believed that the severity and ...
Can looking to the side trigger a brain zap?
While this is purely speculation, there are online accounts of individuals that found things like “looking to the side” can trigger them. Medication side effects: Some individuals have reported experiencing “brain zaps” as side effects from certain medications. These may be experienced when a person initially begins taking a psychotropic medication.
Can antidepressants cause brain zaps?
Other medications: It should be mentioned that medications other than antidepressants can cause brain zaps. While they are most commonly experienced as a result of taking serotonergic antidepressants, benzodiazepines and antipsychotics have also been suggested as potential causes.
What are the factors that influence the severity of brain zaps?
These factors include things like: individual physiology, level of anxiety, the drug that was taken, how quickly a person discontinued, and whether they are currently taking other medications.
What is brain zap?
A couple of British psychiatrists described brain zaps as, “sensory symptoms or symptoms of disequilibrium in brief bursts” when a person moves their head or eyes. Analogy: Scuba diver surfacing too quickly. They emphasized that this generally occurs during discontinuation from a psychiatric medication.
Purpose of Test
Risks and Contraindications
- A sleep-deprived EEG is safe, painless, and poses no significant risk. Most people experience little or no discomfort during an EEG. Remember, the electrodes do not transmit electrical charges, they only pick up electrical activity from the brain itself. Like in alternative activation procedures involving photic stimulation(fast, flashing lights or patterns) or hyperventilation (ver…
Before The Test
- Timing
A standard EEG procedure can be about one hour to an hour and a half, with time spent applying the electrode wires and a 20 to 40 minute period for recording brain activity, while the sleep-deprived EEG procedure usually takes a few hours. The recording will continue while that patien… - Location
A sleep-deprived EEG is typically an outpatient procedure, meaning that it occurs without the need for hospitalization. It can be performed in a healthcare provider’s office, hospital, lab, or clinic. In some cases, a sleep-deprived EEG may occur as part of longer video EEG monitoring on an epile…
During The Test
- When you arrive, you will likely be checked in and asked to sign a form of consent. The EEG technician will be responsible for running your test and monitoring you during its duration. She will escort you to the testing room, or if you are in a hospital, the epileptic monitoring unit, which is usually in the neurology or epilepsy department. The room you will be tested in will probably be …
After The Test
- Once the test is over, the EEG technician will remove the electrodes, and will probably use the help of some warm water or acetone to wash off or remove the adhesive paste. After the test, you should be able to return to your normal activities, although you will likely be much more tired than normal. Again, having someone drive you or arranging a pick up would be in your best interest t…
Interpreting Results
- The EEG recordings are interpreted by a board-certified neurologist with expertise in epilepsy diagnosis. These results will be relayed via a report to your provider. The time it takes to get your results back may depend on how soon the neurologist can finish interpreting the data and share this information with your healthcare provider. You could get your results as soon as a day later, …
A Word from Verywell
- Having symptoms of seizures or having to undergo an EEG can be scary. Sleep deprivation can help optimize conditions during the EEG that can aid in the detection of more subtle epileptiform abnormalities that may not have been seen in a standard EEG. Enduring a sleep-deprived EEG and waiting for the final interpretation of the test result can be anxiety-provoking, but try to focus on …