Azithromycin and erythromycin were the most effective antibiotics in preventing COPD exacerbations.
Full Answer
What is the best oral medication for COPD?
These include both inhaled and oral (taken by mouth) medications:
- Bronchodilators to relieve shortness of breath
- Combination bronchodilators and antiinflammatories to relieve shortness of breath and to prevent flare-ups
- Antibiotics to fight infections
- Supplemental oxygen (oxygen tank) to help with low oxygen and energy levels
- Vaccines for flu and pneumonia to help prevent infections
What are the best treatments for COPD?
Treatment options that your doctor may consider include:
- Quitting smoking. ...
- Avoiding tobacco smoke and other air pollutants at home and at work.
- Medication. ...
- Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life. ...
- Avoiding lung infections. ...
- Supplemental oxygen from a portable oxygen tank may be needed if blood oxygen levels are low.
What herbs and spices are helpful for COPD?
Other common supplements recommended to people with COPD include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids. This supplement may have beneficial anti-inflammatory effects.
- Essential amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. ...
- Antioxidant vitamins. Supplementation with antioxidant vitamins A, C, and E have been shown in studies to improve lung function in people with COPD, especially when combined with omega-3s.
What inhalers are available for the treatment of COPD?
Trelegy Ellipta is the only FDA approved COPD inhaler in the United States that contains three separate, long-acting medications in one inhaler: fluticasone, an ICS, umeclidinium, a LAMA and vilanterol, a LABA. Working together, these medications reduce bronchoconstriction, open your airways, reduce inflammation and improve lung function.

What is prophylactic antibiotic therapy?
Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Use of continuous and intermittent prophylactic antibiotics results in a clinically significant benefit in reducing exacerbations in COPD patients.
What are the adverse events that led to drug discontinuation?
Some adverse events that led to drug discontinuation, such as development of long QTc or tinnitus , were not significantly more frequent in the treatment group than the placebo group but pose important considerations in clinical practice.The development of antibiotic resistance in the community is of major concern.
How many studies were there on macrolide antibiotics?
Nine studies were of continuous macrolide antibiotics, two studies were of intermittent antibiotic prophylaxis (three times per week) and two were of pulsed antibiotic regimens (e.g. five days every eight weeks). The final study included one continuous, one intermittent and one pulsed arm.
What are the treatments for COPD?
COPD treatments include both medicines and other important therapies such as pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking/vaping cessation support and immunizations. If you were asked about COPD medicines you would probably think about your inhalers and you’d probably say, "they open up my lungs".
What are the two ways that medicines open up the airways in your lungs?
There are two basic ways that medicines open up the airways in your lungs: They act as Maintenance (controllers or preventers) or Relievers (rescue or quick relief). Here we’ll refer to them as either controllers or rescue relievers.
How often should I take a medicine for lung inflammation?
Medicines only work if you take them as you and your doctor or other clinician agree; that usually means at least once a day.
What is a nebulizer?
A nebulizer is a device that changes liquid medicine into a fine mist that can be inhaled into the lungs. This mist can be breathed in through a mouthpiece or face mask. There are different types of nebulizers: jet, vibrating mesh and ultrasonic nebulizers. Sometimes the vibrating mesh and ultrasonic types are lumped together under "electronic" nebulizers.
How long does a long acting beta agonist last?
Like the LAMAs, the long-acting beta agonists (also called LABAs) can last for 12 to 24 hours and so need to be taken only once or twice a day.
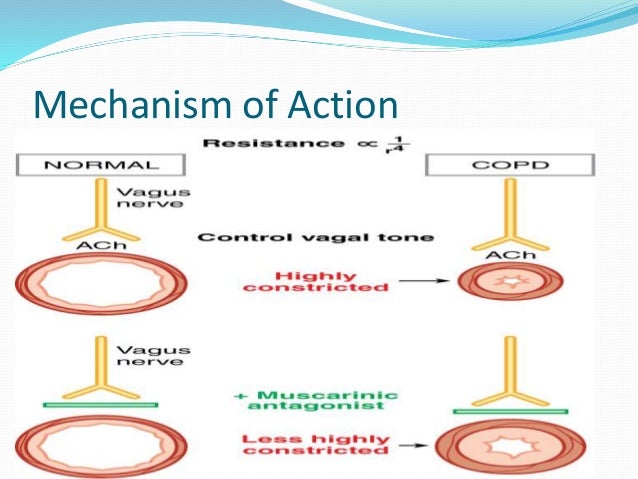
What is a long acting anticholinergic?
Long-acting Anticholinergic (an-tee-coe-luh-nur jick) Bronchodilators also called Long-acting Anti-Muscarinic (an tee mus car in ic) Bronchodilators (Maintenance or Controller) plus. Inside our bodies, there is a constant stream of messages being sent to keep us safe and well.
Can COPD be treated?
COPD can be treated. Some treatments can decrease breathlessness, increase your ability to do activities while others may reduce your risk of exacerbations (x-saa-cer-bay-shun) (flare-ups). These treatments can make it easier for you to breathe, feel better, do more and stay out of the emergency department and hospital.
How does antibiotic treatment help COPD?
In this context, the use of long-term or intermittent antibiotic treatment has shown to prevent COPD exacerbations and hospitalizations. These effects may be achieved by reducing bacterial load in the airways in stable state and/or bronchial inflammation. The drugs more extensively studied are macrolides, followed by quinolones.
What is the first line of treatment for COPD?
One of the main goals of treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the prevention of exacerbations. Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatories are the first line therapy for treatment of COPD; however, these drugs are not effective in suppressing all infective exacerbations.
What is the long term use of antibiotics?
The long-term use of antibiotics is associated with an increased risk of potentially serious adverse events and development of bacterial resistance.
Drugs used to treat COPD
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best antibiotic for COPD?
Azithromycin and erythromycin were the most effective antibiotics in preventing COPD exacerbations. In patients with stable moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), treatment with prophylactic antibiotics was effective in preventing exacerbations and improving quality of life, according to a study published in the Journal ...
Which antibiotics are most effective in the prevention of exacerbations?
Two antibiotics — azithromycin and erythromycin — were most effective in the prevention of exacerbations. The number of antibiotics needed to treat patients ranged from approximately 4 to 7.
What antibiotics were included in the analysis?
Antibiotics included in the analysis were azithromycin, erythromycin, moxifloxacin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin, and doxycycline. Exacerbations of COPD as well as overall quality of life were the primary outcome measures.