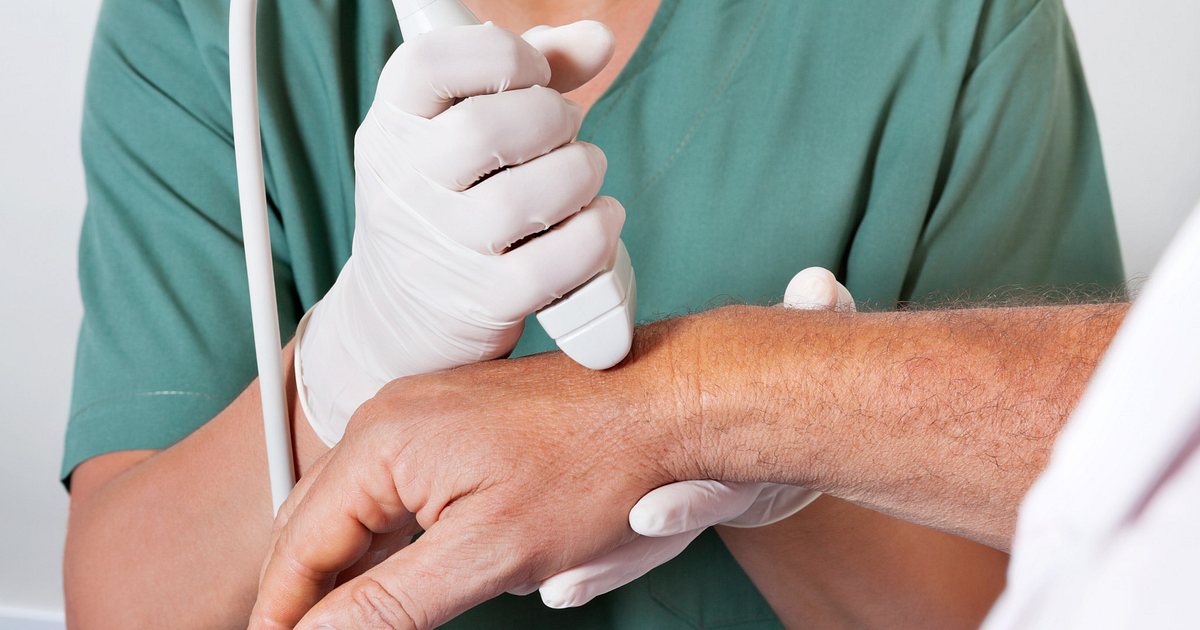
Does ultrasound therapy really work?
Unfortunately — although there are some interesting exceptions and tantalizing hopes for some conditions — ultrasound is not a promising therapy for most of the painful problems it is used for. There is a jarring, bizarre lack of quality research for such a popular, mainstream therapy. What little research is available paints a bland picture.
What are the contraindications of therapeutic ultrasound?
- The patient is supported while lying supine, prone, or on their side on a table.
- An immobilizer is an option on tissues such as breast
- Local anesthetic (1% lidocaine, 0.5% bupivacaine with epinephrine) may be used for pain control
- The tissue of interest is visualized and outlined with ultrasound or MRI
Why would an ultrasound hurt?
Your doctor may recommend this test if you have a problem in any of these body areas:
- Blood vessels in the abdomen
- Gallbladder
- Intestines
- Kidneys
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Spleen
Does ultrasound reduce joint inflammation?
Yet another study published in 2011 in the journal Orthopaedic Surgery, concluded that ultrasound significantly relieved joint symptoms and joint swelling while improving joint mobility and reducing inflammation in people with osteoarthritis. The study involved 87 people with knee osteoarthritis who received ultrasound treatment for 9 months. 3

What are some injuries commonly treated with ultrasound?
How is ultrasound used therapeutically?carpal tunnel syndrome.shoulder pain, including frozen shoulder.tendonitis.ligament injuries.joint tightness.
Does ultrasound speed healing?
Ultrasound is also thought to improve cellular function by making microscopic gas bubbles near your injury expand and contract rapidly, a process called cavitation. This expansion and contraction are thought to speed up the healing process in your injured body part.
What is the purpose of ultrasound during physical therapy?
Ultrasound physical therapy is a branch of ultrasound, alongside diagnostic ultrasound and pregnancy imaging. It's used to detect and treat various musculoskeletal issues you may have including pain, tissue injury, and muscle spasms.
Does ultrasound therapy reduce inflammation?
Ultrasound (US) therapy is used to reduce pain and inflammation and to accelerate healing after soft tissue injury.
How often should you ultrasound an injury?
Acute wounds should be treated as soon as possible, ideally within hours of injury. They are often treated once or twice a day to reduce pain and swelling (Young, 1996). Ultrasound accelerates the inflammatory phase, moving the wound into the proliferative phase of repair sooner (Young and Dyson, 1990a).
Does ultrasound break up scar tissue?
One of the many benefits of ultrasound therapy is breaking up scar tissue caused by injuries or surgery. Scar tissue can cause pain and restrict joint movement. Ultrasound helps by using high-frequency sound waves to break the fibres of the scar tissue down into smaller fragments.
Does ultrasound help bruising?
The primary options for treatment of hematomas include medication and invasive surgery. For certain patients, focused ultrasound could provide a noninvasive alternative to surgery with less risk of complications – such as surgical wound healing or infection – at a lower cost.
Can you see inflammation on ultrasound?
Ultrasound imaging can detect inflammation in your joints, even if you don't have noticeable symptoms. This can help your doctor form an accurate picture of your condition and provide more effective and targeted treatment.
How Does Ultrasound Work?
Inside your PT's ultrasound unit is a small crystal. When an electrical charge is applied to this crystal, it vibrates rapidly, creating piezoelect...
How Is Ultrasound applied?
Ultrasound is performed with a machine that has an ultrasound transducer (sound head). A small amount of gel is applied to the particular body part...
Contraindications to Using Ultrasound
There are some instances where you should not use ultrasound at all. These contraindications to ultrasound may include: 1. Over open wounds 2. Over...
What Does Ultrasound Feel like?
While you are receiving an ultrasound treatment, you will most likely not feel anything happening, except perhaps a slight warming sensation or tin...
Common Injuries Treated With Ultrasound
Usually, orthopedic injuries are treated with ultrasound. These may include: 1. Bursitis 2. Tendonitis 3. Muscle strains and tears 4. Frozen should...
Caution During Ultrasound
If you are going to physical therapy and are getting an ultrasound, you should know that many studies have found that ultrasound offers little bene...
Why is ultrasound therapy important?
One of the greatest proposed benefits of ultrasound therapy is that it is thought to reduce the healing time of certain soft tissue injuries. Ultrasound is thought to accelerate the normal resolution time of the inflammatory process by attracting more mast cells to the site of injury.
What is ultrasound therapy?
Ultrasound Therapy. Ultrasound therapy has been used as an electrotherapy treatment modality by therapists over the last 50 years.It involves passing high frequency sound waves into soft tissue.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasonic waves or sound waves of a high frequency that is not audible to the human ear are produced by means of mechanical vibration in the metal treatment head of the ultrasound machine. The treatment head is then moved over the surface of the skin in the region of the injury transmitting the energy into the tissues.
How does ultrasound affect collagen?
As the ultrasound waves pass from the treatment head into the skin they cause the vibration of the surrounding tissues, particularly those that contain collagen. This increased vibration leads to the production of heat within the tissue. In most cases, this cannot be felt by the patient themselves. This increase in temperature may cause an increase in the extensibility of structures such as ligaments, tendons, scar tissue, and fibrous joint capsules. In addition, heating may also help to reduce pain and muscle spasm and promote the healing process.
Why do you put ultrasound gel on your skin?
When sound waves come into contact with air it causes a dissipation of the waves, and so a special ultrasound gel is placed on the skin to ensure maximal contact between the treatment head and the surface of the skin and to provide a medium through with the sound waves can travel. Ultrasound can also be applied underwater which is also a medium ...
How long does it take for an ultrasonic to work?
This is moved continuously over the skin for approximately 3-5 mins. Treatments may be repeated 1-2 times daily in more acute injuries and less frequently in chronic cases.
Does ultrasound help with scar tissue?
Hence ultrasound may accelerate the proliferative phase of tissue healing. It is thought to improve the extensibility of mature collagen and so can have a positive effect on fibrous scar tissue which may form after an injury.
Why is ultrasound used in the body?
Ultrasound is often used to provide deep heating to soft tissue structures in the body. Deep heating tendons, muscles, or ligaments increases circulation to those tissues, which is thought to help the healing process. Increasing tissue temperature with ultrasound is also used to help decrease pain.
What is therapeutic ultrasound?
Therapeutic ultrasound is a treatment modality commonly used in physical therapy. It is used to provide deep heating to soft tissues in the body. These tissues include muscles, tendons, joints, and ligaments.
How Does Ultrasound Work?
Inside your physical therapist's ultrasound unit is a small crystal. When an electrical charge is applied to this crystal, it vibrates rapidly, creating piezoelectric waves. These waves are emitted from the ultra sound sound head as ultra sound waves.
How Is Ultrasound Applied?
Ultrasound is performed with a machine that has an ultrasound transducer (sound head). A small amount of gel is applied to the particular body part; then your physical therapist slowly moves the sound head in a small circular direction on your body.
What are the contraindications for ultrasound?
There are some instances where you should not use ultrasound at all. These contraindications to ultrasound may include: 1 Over open wounds 2 Over metastatic lesions or any active area of cancer 3 Over areas of decreased sensation 4 Over parts of the body with metal implants, like in a total knee replacement of lumbar fusion 5 Near or over a pacemaker 6 Pregnancy 7 Around the eyes, breasts, or sexual organs 8 Over fractured bones 9 Near or over an implanted electrical stimulation device 10 Over active epiphyses in children 11 Over an area of acute infection
Can ultrasound be used for rotator cuff tears?
Generally speaking, any soft-tissue injury in the body may be a candidate for ultrasound therapy. Your physical therapist may use ultrasound for low back pain, neck pain, rota tor cuff te ars, knee meniscus tears, or ankle sprains.
Can a physical therapist use ultrasound?
Your physical therapist may use ultrasound to help improve your condition. If so, be sure to ask about the need for ultrasound and possible risks. Also, be sure that you are also performing an active self-care exercise program in the PT clinic and at home. If you are actively engaged in your rehabilitation, you can ensure that you have a safe and rapid recovery back to normal function.
What injuries can ultrasound therapy help treat?
Ultrasound therapy can be effective in the early stages of treating an acute injury or chronic pain. Some injuries best treated by ultrasound therapy include:
What are the best injuries to treat with ultrasound?
Some injuries best treated by ultrasound therapy include: Arthritis. Back pain. Bursitis. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Fractures. Frozen shoulder. Joint pain and tightness.
What is ultrasound therapy?
Ultrasound therapy, also referred to as therapeutic ultrasound, is a treatment used in physiotherapy to help reduce inflammation in an injured area, increase blood flow, reduce muscle and connective tissue stiffness, and help to break down scar tissue.
What are the risks, limitations, or side effects associated with ultrasound therapy?
That being said, ultrasound therapy may not work for some, but it can result in decreased pain, help improve the healing process, scar tissue reduction, and increased joint mobility.
How does ultrasound help with healing?
A five-minute treatment of ultrasound in the affected area increases the temperature of the tissue being treated and increases blood flow, making the injured area more responsive to manual therapy. This increase in circulation helps with healing since all the properties that are vital to healing such as oxygen, specialized cells, proteins, and nutrients, are all located within the blood.
Why is ultrasound therapy beneficial?
If you are experiencing chronic pain from a slow-healing injury or your injury is not responding to other treatments , ultrasound therapy may also be beneficial. Ultrasound generates heat deep into the tissues, increases circulation and metabolism.
Why is rotator cuff inflammation important?
Inflammation is an important part of the initial healing process as it boosts the body’s immune response and promotes tissue regeneration. However, it can lead to excessive swelling, which restricts blood flow and causes the joints to stiffen.
What is ultrasound used for?
It can also be used to inject drugs into tissues ( phonophoresis ), or to violently vibrate the tip of an invasive probe ( lithotripsy, usually used for gall stones).
Why is therapeutic ultrasound out of favor?
Therapeutic ultrasound … has fallen out of favor as research has shown a lack of efficacy and a lack of scientific basis for proposed biophysical effects.
What is ESWT ultrasound?
Many concerns about the widespread usage of therapeutic ultrasound, especially extracorporeal shockwave therapy ( ESWT) Ultrasound therapy ( US) is the use of sound waves above the range of human hearing 1 2 to treat injuries like muscle strains or runner’s knee.
How long after ultrasound to treat trigger point?
Trigger points treated with ultrasound were more tolerant of pressure than those that were not treated, at 1, 3 and 5 minutes after treatment. 34 The improvement was no longer significant just 10 and 15 minutes later, however — so the effect in this case was brief. The authors concluded:
How long is an ultrasound useless?
In most cases I consider ultrasound less than useless — that's 8-10 minutes wasted that could be used doing something that might actually help.
Does ultrasound close the gate?
It’s just a mechanism for transient, minor pain relief. It can be achieved just as easily by rubbing the area yourself! It certainly doesn’t “fix” anything, which is what ultrasound is supposed to be doing. So bringing it up is just a bit of bafflegab, a scientific-sounding rationalization for an expensive therapy. There is no reason to think that any kind of ultrasound closes the gate better or longer than any other stimulus.
Is ultrasound quackery?
Ultrasound is pseudo-quackery. The disconnect between the popularity of US and the more or less total lack of informative research is troubling. A handful of good studies is a joke for a therapy that is worth literally billions of dollars in the marketplace.
What Injuries Do We Use Ultrasound For?
Ultrasound is most effective when used for soft tissue injuries including:
When was ultrasound therapy used?
Ultrasound therapy has been used by physiotherapists since the 1950s and remains a popular and evidenced intervention for a variety of injuries.
What happens when scar tissue is damaged?
When a tissue such as muscle or ligament is damaged, local blood flow and swelling brings an inflammatory soup of chemicals that begins the healing process. New tissue known as scar tissue is formed and laid down. As the scar tissue is generated, the fibres that make up the scar tissue are often laid down in an unorganised fashion. If the fibres of a tissue are unorganised or not correctly aligned they are not as strong or as flexible as the original tissue. Sometimes if this scar tissue remains unorganised it can leave us with tight and/or weak muscle or ligament even once healing is complete.
Why do we use ultrasound?
But, it's most commonly used to solve problems in muscle tissue. The heating effect of the ultrasound helps to heal muscle pain and reduces chronic inflammation. . Ultrasound also helps tissue fluids flow better — which means that more lymph passes through the tissues.
How does ultrasound work?
How Ultrasound Physical Therapy Works. The ultrasound machine works by sending an electric current through crystals found in the ultrasound probe — also known as the ultrasound wand. The probe vibrates, causing waves to travel through the skin to the body underneath. The waves transfer energy to the tissues to cause the desired effects.
What is mechanical ultrasound?
In mechanical ultrasound — also known as cavitation ultrasound therapy — the waves created by the ultrasound create pressure differences in tissue fluids, which lead to the forming of bubbles.
What is ultrasound in 2021?
Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on June 23, 2021. Ultrasound — or ultrasonography — is an imaging technique used not just during pregnancy but also for many medical procedures. Ultrasound physical therapy is a branch of ultrasound, alongside diagnostic ultrasound and pregnancy imaging. It's used to detect and treat various musculoskeletal ...
What determines how ultrasound physical therapy is done?
The frequency and intensity of the ultrasound, the duration of the procedure, and the area of its application all determine how ultrasound physical therapy is done.
Why is ultrasound not used in pregnancy?
Therapeutic ultrasound is not used for problems near a pregnant woman’s womb because it could put the pregnancy at risk. It's also generally not used over the spine, eyes, pacemakers, other implants, and areas with active infections. The procedure is generally painless and easy to do.
What are the two types of ultrasound?
There are two types of therapeutic ultrasound: thermal and mechanical.
Why do people use ultrasound?
For the last 80 years, ultrasound therapy has been used as a non-invasive procedure to treat a wide variety of ailments. It is often used to treat swelling, particularly when the swelling is spread over a larger area than usual.
What are the benefits of ultrasound?
As well as heating and relaxing the muscles, ultrasound therapy breaks down scar tissue and increases local blood flow.
How long does ultrasound last?
In general, ultrasound therapy sessions will last no longer than 5 minutes.
Is ultrasound therapy safe for pregnant women?
Despite its similarity to ultrasound machines, ultrasound therapy is not suitable for issues located near the womb of a pregnant woman. The wavelengths used in this therapy are different to those used in a prenatal ultrasound, and could put the pregnancy at risk.
Can ultrasound help with swollen muscles?
Since the benefits of ultrasound are so broad, it can be used for a huge range of issues. However, it is usually reserved for problems with swollen muscles, particularly when time is a factor in the recovery.
Can ultrasound be used on other parts of the body?
However, the therapy can still be used on other parts of the body, regardless of whether or not a woman is pregnant. Ultrasound therapy may also be unsuitable for people with malignant growths, or cardiovascular issues. But again, this can depend on where the therapy is to take place on the body. Ultrasound therapy is completely unsuitable anywhere ...
What is therapeutic ultrasound?
Therapeutic ultrasound has been studied and used for the past seven decades to treat musculoskeletal injuries. Recently, a significant body of animal and human research has focused on the biomechanical effects of daily-applied, low intensity therapeutic ultrasound (LITUS) on soft tissue recovery. We performed a systematic review ...
What is the treatment for acute injury?
Many use the regimen of rest, ice, compression, elevation and stabilization (RICES) to treat acute injury, but are unsure what to do if the injury becomes chronic.1Whereas, many of these current treatment options address inflammation and pain management, therapeutic ultrasound can both manage pain and facilitate healing.
How does litus help with tendon healing?
For tendon-bone junction healing, LITUS treatment significantly improved healing and osteogenesis. Application of LITUS resulted in significantly more newly formed bone and improved tissue integration compared to controls.36-40In one study,39reported the amount of new bone formed was 2.6 and 3.0 times greater in the treatment group compared to controls at weeks 8 and 16, respectively. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the tendon-bone interface was also significantly increased with LITUS treatment, particularly after 4 weeks.37,41Type I and II collagen were increased with LITUS treatment,42,43and collagen fibers demonstrated higher organization.43Similarly, there was up-regulation of type I collagen gene expression with LITUS treatment compared to controls.44Additionally, in procedures replacing ligaments with tendons (i.e., anterior cruciate ligament surgery; ACL), LITUS treated tendons showed greater stiffness and peak load compared to controls.36,40,45
What is the purpose of Exogen Bone Healing System?
The Exogen Bone Healing System is used in clinical practice to accelerate the healing of established non-unions (excluding skull and vertebra), in addition to accelerating fracture healing time in fresh, closed, posteriorly displaced distal radius fractures and fresh, closed, or Grade I open tibial diaphysis fractures. The SAM device is used to reduce inflammation and pain, and accelerate the healing of soft tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Both Exogen and SAM are non-invasive prescription-use devices that are administered and monitored by a licensed medical professional. Typically, patients prescribed wearable LITUS therapy self-apply the therapy daily in the home-setting, and have regularly scheduled follow up appointments with their healthcare provider who oversees use of the device. Overall, the use of these LITUS delivery systems has the clinical potential to accelerate healing and alleviate pain from a variety of disorders impacting soft tissues as well as bone.
How does Litus help ligaments?
Ligament healing benefitted from the application of LITUS. LITUS treated ligaments exhibited superior mechanical properties including ultimate load, stiffness, and energy absorption.33-35LITUS-treated ligaments from one study were 34.2% stronger, 27.0% stiffer, and could absorb 54.4% more energy compared to sham-treated ligaments after 2 weeks of treatment. 35Another study demonstrated that after six weeks of LITUS treatment, ligaments were 39.5% stronger, 24.5% stiffer, could absorb 69.1% more energy, and were 10.6% larger than sham-treated ligaments.33Collagen fibril diameter was larger in a group treated with LITUS compared to controls,34and there was a greater relative proportion of type II collagen in LITUS-treated ligaments compared to controls at both 3 and 6 weeks.33
Can Litus be used for soft tissue?
Collectively, these studies are encouraging for the use of LITUS to treat soft tissue injuries in human; however, the delivery of therapeutic ultrasound has been traditionally applied in the inpatient setting, which limits both the duration of treatment and frequency of application.

Overview
Availability
- Garden-variety therapeutic US is cheap and available everywhere. The machines are small, even portable: you can buy small handheld ones. Treatment is brief and painless, and applied (indiscriminately?) to almost any common musculoskeletal problem.
Treatment
- ESWT uses much stronger sound waves shock waves!7 (Radial shock wave therapy is a bit different.8) Treatment is painfully intense and painfully pricey.9
Advantages
- On the one hand, ESWT is just a more is better version of standard US, because it is often used with the same imprecise clinical intention to stimulate/provoke tissues. On the other hand, because it was originally developed for smashing gall stones, ESWT is strong enough to actually disrupt tissue, such as calcifications in tendons which is a nice precise clinical goal and a whole …
Research
- When I started studying for this article way back in the mid-2000s, I was quite surprised by how little there was to study. Back then, every scientific paper about US pointed out there is not enough research on this topic, or at least not enough good research and not much has changed. A 2015 review of ultrasound for rotator cuff tendinopathy (cited below) found only six trials, all po…
Criticism
- The disconnect between the popularity of US and the more or less total lack of informative research is troubling. A handful of good studies is a joke for a therapy that is worth literally billions of dollars in the marketplace. How can that much therapy be sold without a satisfactory body of evidence that it works? Bizarre! This is the ultimate example of pseudo-quackery: popular treatm…
Quotes
- This does not mean that US never works for anyone. It does mean that it has been prescribed and sold to patients for decades with unjustified confidence. And that is not cool. And so few patients are singing the virtues of standard US. It not only fails to generate testimonials, but actually generates many annoyed antimonials. Meanwhile, there is still just no basis for thinking that ultr…
Results
- Ultrasound is an unusually easy treatment to test scientifically.10 If it works reasonably well, then the results should be pretty clear. Just compare results in patients who received real ultrasound to patients who get a fake instead! And yet there are just a few dozen such experiments in the scientific literature, and most of them are seriously flawed. Conclusions from evidence reviews l…
Prognosis
- Standard therapeutic ultrasound probably does little or nothing for most people. A sliver of hope remains that some specific conditions will respond to ultrasound with just the right settings.
Marketing
- Not only that, but ultrasound has found new life in the marketplace as shockwave therapy faster, stronger waves, with a bigger price tag! Consider this marketing language from a Canadian company, Shockwave Institute, specializing in ESWT:
Status
- Things seem to have changed for the better, though 80-85% effective would still be a hard claim to defend.
Uses
- Bizarrely, ESWT is being used to treat conditions as unexpected as erectile dysfunction, stroke, and venous leg ulcers. Theres even some preliminary evidence for such uses though not all. But there are now multiple positive reviews of ESWT for its more common uses, like stubborn cases of plantar fasciitis, a painful irritation of the arch of the foot. A good 2016 example is Lou et al, w…
Symptoms
- Patients often express irritation with a common physical therapy business model: working with several patients at once, rotating between rooms or beds, often leaving patients with passive therapies (like a moist hot pack from a hydrocollator nice enough, but worth a steep fee?) Many patients often go a step further and complain specifically about ultrasound and TENS, skeptical …
Purpose
- The big idea is this will blow your mind! that cells and tissues respond well to being shaken (not stirred). In theory, ultrasound works by vibrating tissues back to health, which sounds like something youd hear on an infomercial, or the Dr. Oz Show. What, exactly, does vibration do to tissues? Does anyone actually understand it?
Future
- There is lots of interesting ultrasound biology to consider, and scientists may eventually nail down effects that might be the basis for new evidence-based therapies. For instance, a decade later, Tsai et al declared that There is strong supporting evidence from animal studies about the positive effects of ultrasound on tendon healing31 but animal studies are notoriously misleadin…
Example
- Another great example: the persistent hope that rattling cells with sonic vibrations might speed the healing of bone fractures, particularly low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS). Such an effect, if proven, would certainly be a delightful bit of weird good news about biology. Unfortunately, it is probably dis-proven. In 2017, the British Medical Journal published an excellent review with a ver…
Society and culture
- Physical therapists often cite the gate control mechanism as a justification for US and ESWT (and some other popular treatments, especially TENS). This is nonsense and a great example of why patients should be cautious, especially with the expense of ESWT.
Applications
- The gate control mechanism is an important idea in pain science, proposed in 1965 by Dr. Ronald Melzack and Dr. Patrick Wall, and still accepted today as an explanation for a familiar phenomenon: the way we rub injured body parts for a little pain relief. The idea is that pain signals pass through a gate in the spinal column. The state of the gate is controlled by many factors. Ho…
Reviews
- Although it may be surprising in contrast to the generally unimpressive evidence of the effectiveness about therapeutic ultrasound, it nevertheless reinforces that ultrasound does indeed do some interesting things to tissues: its just not clear exactly what. An important caveat is that there is significant scientific debate about what trigger points really are.34 Some would say its h…