The treatment variance is based on the deviations of treatment means from the grand mean, the result being multiplied by the number of observations in each treatment to account for the difference between the variance of observations and the variance of means
What is variance and why is it important?
Variance is important to consider before performing parametric tests. These tests require equal or similar variances, also called homogeneity of variance or homoscedasticity, when comparing different samples. Uneven variances between samples result in biased and skewed test results.
What is the analysis of variance test?
The analysis of variance test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the analysis of variance test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency.
What is a treatment variable in research?
What is a treatment variable? Treatment. In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels, i.e., different values of the factor. Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
How do you use sample variance in statistics?
Statistical tests such as variance tests or the analysis of variance (ANOVA) use sample variance to assess group differences of populations. They use the variances of the samples to assess whether the populations they come from significantly differ from each other.

What does variance test tell you?
Variance tests are a type of hypothesis test that allows you to compare group variances. Variance is a measure of the spread, or variability, within a dataset. Like all hypothesis tests, variance tests use sample data to infer the properties of an entire population.
What is the importance of the variance?
Variance in statistics is important as in a measurement it allows us to measure the dispersion of the set of the variables around their mean. These set of the variables are the variables that are being measured or analyzed.
Why variance is important in research?
Variance is most useful in determining the overall spread of a data set. Range simply takes two data points, the lowest and highest values, and measures the space between them. The interquartile range also interprets the amount of spread within a set of data by using only the middle 50% of scores.
What is treatment effect in ANOVA?
The ANOVA Model. A treatment effect is the difference between the overall, grand mean, and the mean of a cell (treatment level). Error is the difference between a score and a cell (treatment level) mean.
Is variance a risk?
Variance is a measurement of the degree of risk in an investment. Risk reflects the chance that an investment's actual return, or its gain or loss over a specific period, is higher or lower than expected.
What is a good variance?
As a rule of thumb, a CV >= 1 indicates a relatively high variation, while a CV < 1 can be considered low. This means that distributions with a coefficient of variation higher than 1 are considered to be high variance whereas those with a CV lower than 1 are considered to be low-variance.
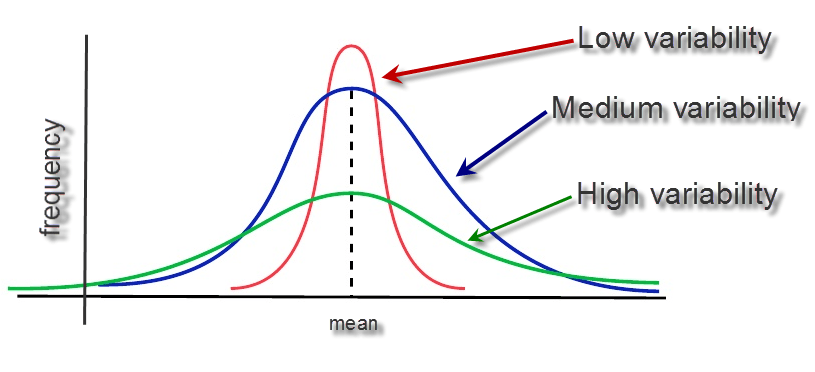
What is variance in simple terms?
Variance is a measure of how data points differ from the mean. According to Layman, a variance is a measure of how far a set of data (numbers) are spread out from their mean (average) value. Variance means to find the expected difference of deviation from actual value.
What does a high variance mean?
A high variance indicates that the data points are very spread out from the mean, and from one another. Variance is the average of the squared distances from each point to the mean. The process of finding the variance is very similar to finding the MAD, mean absolute deviation.
What is the importance of variance and standard deviation?
Variance helps to find the distribution of data in a population from a mean, and standard deviation also helps to know the distribution of data in population, but standard deviation gives more clarity about the deviation of data from a mean.
What is a treatment effect in statistics?
Treatment effects can be estimated using social experiments, regression models, matching estimators, and instrumental variables. A 'treatment effect' is the average causal effect of a binary (0–1) variable on an outcome variable of scientific or policy interest.
What sources contribute to between treatments variance?
What sources of variability contribute to the within-treatment variability for a repeated-measures study? Variability (differences) within treatments is caused by individual differences and random, unsystematic differences.
When comparing more than two treatment means Why should you use an analysis of variance instead of using multiple t tests?
when comparing more than two treatment means, why should you use an analysis of variance instead of using several t tests? using several t tests increases the risk of experiment-wise Type I error.
What is variance in medical treatment?
What is a variance? Simply stated, a variance is an exception to or deviation from the medical treatment guideline recommendations. The variance recognizes that people heal at different rates, that there may be extenuating circumstances or comorbidities that may delay an individual’s response to treatment, or that new evidence may become available that would support alternative treatments that either were not addressed in the original medical treatment guidelines or were not recommended.
What is variance request?
For this type of a variance request there are two documentation requirements . One, the injured worker must continue to show objective functional improvement as a result of the treatment and that it is reasonably expected that the patient will continue to improve with additional treatment.
How many procedures require preauthorization?
Currently there are 12 procedures that require preauthorization and an additional 13th exception for repeat surgery. Effective 2013, anterior acromioplasty and chondroplasty will be removed from the list of procedures requiring pre-auth.
Do you need a variance for physical therapy after surgery?
In this case, a variance would not be required for physical therapy after surgery. The therapy would be consistent with the medical treatment guidelines and therefore, a variance not needed. However, if the patient was progressing slowly, and was reaching the maximum duration of therapy and was continuing to demonstrate objective functional improvement, a variance might be needed. The variance should be requested as soon as the physician believes that recovery is proceeding at a slower pace than anticipated.
What is a variance request?
If a treating medical provider determines that medical care which varies from the Medical Treatment Guidelines (MTG) is necessary, a variance request will need to be submitted. For example, when a treatment, procedure, or test was not originally recommended by the MTG but has become appropriate for the injured worker, he or she can then have a variance submitted to the insurance carrier or Special Fund, the Workers’ Compensation Board, or order of the Chair prior to medical care which varies from the MTG can be provided.
Can a medical provider resubmit a variance request?
If a variance request is initially denied by the carrier or Special Fund, it may be resubmitted. The Treating Medical Provider can submit the date of the denial and additional documentation or justification in support of a new variance request. If the variance request is similar to any previous request, it may not be submitted until the carrier or Special Fund has denies any previous variance request.
What is the purpose of variance testing?
Statistical tests like variance tests or the analysis of variance (ANOVA) use sample variance to assess group differences. They use the variances of the samples to assess whether the populations they come from differ from each other.
What is variance in statistics?
Published on September 24, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari. Revised on October 12, 2020. The variance is a measure of variability. It is calculated by taking the average of squared deviations from the mean. Variance tells you the degree of spread in your data set.
What is the term for a test that requires equal or similar variances?
These tests require equal or similar variances, also called homogeneity of variance or homoscedasticity, when comparing different samples. Uneven variances between samples result in biased and skewed test results. If you have uneven variances across samples, non-parametric tests are more appropriate.
Why is homogeneity important in statistical analysis?
This is an important assumption of parametric statistical tests because they are sensitive to any dissimilarities. Uneven variances in samples result in biased and skewed test results.
Is standard deviation a measure of variability?
That’s why standard deviation is often preferred as a main measure of variability. However, the variance is more informative about variability than the standard deviation, and it’s used in making statistical inferences.
When is ANOVA used?
The type of ANOVA test used depends on a number of factors. It is applied when data needs to be experimental. Analysis of variance is employed if there is no access to statistical software resulting in computing ANOVA by hand. It is simple to use and best suited for small samples.
How does ANOVA work?
ANOVA groups differences by comparing the means of each group and includes spreading out the variance into diverse sources. It is employed with subjects, test groups, between groups and within groups .
What is ANOVA in statistics?
What is Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)? Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an analysis tool used in statistics that splits an observed aggregate variability found inside a data set into two parts: systematic factors and random factors.