
Treatment burden refers to the workload imposed by healthcare on patients, and the effect this has on quality of life. The Treatment Burden Questionnaire (TBQ) aims to assess treatment burden in different condition and treatment contexts.
What is the difference between disease and treatment burden?
Although treatment burden is often inseparable from disease burden, it is not based on the natural history of the disease, but on the need to treat the disease in order to change its course or ameliorate its effects. Treatment burden is, therefore, an important concept that is distinct from disease burden, symptom burden and other related terms.
What are the attributes of treatment burden?
The attributes of treatment burden include burden as a dynamic process, as a multidimensional concept, and comprising of both subjective and objective elements.
Why is it important to reduce the burden of treatment?
There is a clear need to implement services that help alleviate the burden of treatment experienced by patients in order to improve their health and well‐being. Another alarming consequence of treatment burden, particularly from a public health perspective, was the ineffective use of resources.
Is there a burden of treatment for families?
This preliminary work opens the door for more studies about the burden of treatment. As of today, researchers have only considered the burden of treatment for individual patients. I strongly believe that capacities of the patients’ families play a significant role in how patients can cope with the burden of treatment.
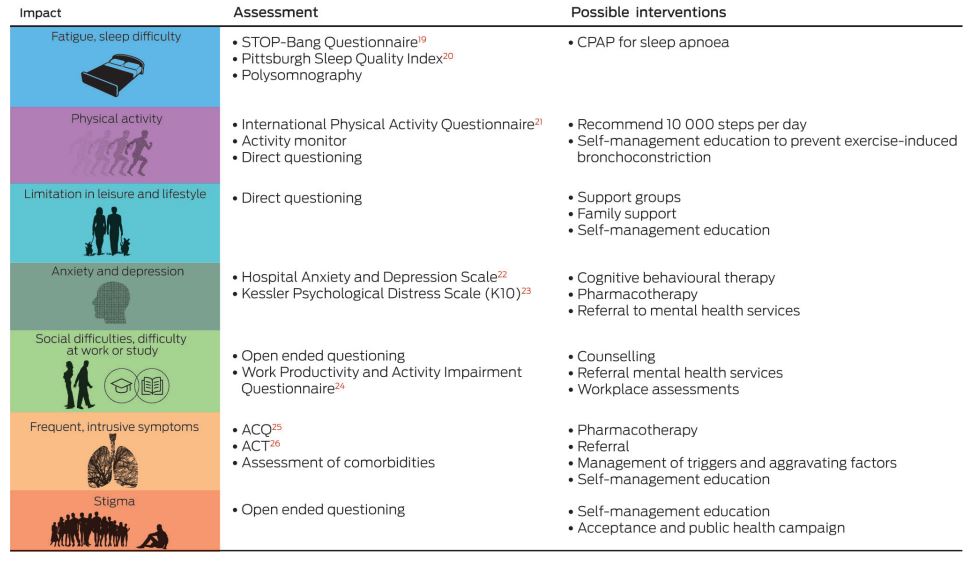
What is the burden of treatment?
Treatment burden can be defined as the impact of health care on patients' functioning and well-being, apart from specific treatment side effects. It takes into account everything patients do to take care of their health: visits to the doctor, medical tests, treatment management, and lifestyle changes.
What is patient burden?
The Patient Burden Index, or PBI, developed by Medidata is an effective tool for improving trial design, downstream operations, and patient centricity. An example illustrates the application of the PBI.
What is meant by clinical burden?
clin·i·cal bur·den a burden that differs from genetic burden mainly in the added component of morbidity; a trait that is neither a clinical or a genetic lethal may be grossly disabling.
How do you treat the patients?
No matter what the disease or condition, all evaluation and treatment of patients must involve caring, investigation of all complaints, respect for the patient's perspective, avoidance of excessive testing, and joint decision making regarding treatment, to the extent that is possible.
What is burden of infection?
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators.
How do you assess burden of disease?
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem on a given population, and can be measured using a variety of indicators such as mortality, morbidity or financial cost.
How do we measure burden of disease?
Burden of disease analysis quantifies the gap between a population's actual health and an ideal level of health—that is, every individual living without disease or injury to the theoretical maximum life span—in a given year. Burden of disease is measured using the summary measure disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
What does treatment mean in medical terms?
Definition of medical treatment. Medical treatment means the management and care of a patient to combat disease or disorder. Medical treatment includes: All treatment not otherwise excluded (below). Using prescription medications, or use of a non-prescription drug at prescription strength.
What is meant by treating the whole person?
Treating the whole person involves giving each person tailored and personalized therapies specific to their genetics, nutrition status, lifestyle, and capacity for implementing suggestions, not just a set of instructions to follow.
Why is it important to complete treatment?
For example, treatments for chronic illnesses focus on reducing symptoms and preventing or delaying complications. If you stop treatment, these may occur more quickly, which could have a major impact not only on your quality of life, but also on your life expectancy.
What is the burden of treatment?
In addition to the burden of illness, patients are affected by the burden of treatment, defined as the impact of the “work of being a patient” on functioning and well-being. This work includes medication management, self-monitoring, visits to the doctor, laboratory tests, lifestyle changes, etc.
Why are annual reviews so difficult?
Annual reviews are difficult because there are multiple investigations required and these take place over multiple different appointments and sometimes at different hospitals in the same group .” (55-year-old woman with diabetes and a cardiac condition from the United Kingdom). Finally, patients reported consequences of the burden of treatment, ...
Should treatment objectives be based solely on attaining specific goals in specific diseases?
Treatment objectives should not be based solely on attaining specific goals in specific diseases but also on mitigating the impact of conditions and treatments on patients’ professional, family and social lives, for minimally disruptive medicine.
What is the treatment burden?
Treatment burden is, therefore, an important concept that is distinct from disease burden, symptom burden and other related terms. Treatment of chronic illness comes in many forms including surgery, physical therapy, psychological therapy and radiotherapy.
What are the health consequences of treatment burden?
The health consequences of treatment burden are particularly concerning given that treatment burden has been associated with specific symptoms, recurrence of disease, decline in health, reduced survival, decreased treatment satisfaction and reduced quality of life.
What are the aspects of treatment burden that should be considered by healthcare professionals (HCPs) when prescribing new
These include having a common understanding of the (realistic) goals of treatment, the risk of side-effects and the potential impact on lifestyle.
What is a treatment trial?
A treatment “trial” can be carried out with agreement to stop the medication if clinical goals are not achieved and/or benefit is not felt by the patient within a specific timeframe. Realistic treatment goals of a new medication must be clearly defined for both the patient and the HCP, recognising that the patient's perception of benefit may differ from a clinical definition of effectiveness. A patient, for example, may want to improve day-to-day function or to prioritise extended life, while the HCP may judge effectiveness as a change in physiological parameters. More generally, all medicines should be reviewed regularly (annually as a minimum) to check that they are still appropriate and to ensure their usage remains meaningful for the patient.
Why is treatment burden important?
The concept of treatment burden is useful when considering end-of-life care for those with heart failure . Important components of treatment burden – coherence and appraisal work, relational work, and the work of enacting and operationalizing treatments – are as readily identifiable in those with end-stage heart failure as they are in those in the earlier phases of the disease [6▪]. The research literature reviewed in this article illustrates how patients in the final phases of their disease still struggled to develop a coherent understanding of their condition and its appropriate management and were burdened by problems of discontinuity and uncoordinated care. Problems of uncertainty were pervasive in patient and carer accounts of their experiences and encounters with healthcare systems and health professionals. The notion of treatment burden is important because it can serve as a real barometer of quality of care from the patient perspective. It is also an entity with clearly identifiable components which suggests that it should be measurable. Considering treatment burden would force us to begin to move away from the prevalent disease centred care to more person centred models of care. In practical terms, this means that those providing palliative care for individuals with advanced heart failure, need to focus on supporting patients and carers to undertake all the forms of work identified so as to reduce the demands placed on patients and carers. There is a need to ensure care provision that prioritizes the goals of patients and caregivers, taking into account their personal context and prognosis.
What is fragmented and continuity of care?
Health service delivery was generally described as fragmented and continuity of care a rarity rather than the norm. This was described as a major burden for those with end-stage heart failure. Having a long-term relationship with a particular health professional, who took an interest in them and had good communication skills was highly valued but apparently uncommon. More frequently, end-stage heart failure patients described far less positive experiences, describing ‘professionally-led models of care’ rather than ‘a partnership approach’ [28]. Worryingly, it was clear that some actually ‘feared that professionals would take sanctions against them if they complained or were perceived as difficult’ [28].
What does it mean when you feel like a burden?
Feeling like a burden can greatly impact your self-perception and mental health. However, these feelings are rarely justified or true. If you are feeling like a burden to those around you, therapy can help understand just how worthy and loved you truly are.
Can anxiety make you feel like a burden?
Just as anxiety or depression may contribute to feeling like a burden, so may other mental disorders—for example, bipolar disorder or an eating disorder. And you do not have to have a mental disorder to feel like a burden: dealing with a health issue that makes you rely on others can lead to the same feeling.
What is the burden of treatment?
Burden of treatment is the workload of healthcare and its effect on patient functioning and wellbeing. 1 The cumulative treatment workload for patients with chronic conditions ...
What is a guideline recommendation?
Guideline recommendations, however, are traditionally made from a perspective that places the highest value on achieving certain clinical outcomes (such as reducing shortness of breath or increasing survival).
