How is drinking water treated and treated?
a common water treatment plant involves the following processes: (1) pretreatment to remove big objects that can be found in the pipelines that transport water from the supply to the treatment plant, (2) softening and/or coagulation for the removal of hardness and/or suspended particles, (3) filtering through sand beds to remove any fine …
What does reverse osmosis water treatment remove?
Aug 23, 2018 · Certain technologies have been found to remove PFAS from drinking water, especially Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), which are the most studied of these chemicals. Those technologies include activated carbon adsorption, ion exchange resins, and high-pressure membranes.
What are the different types of water treatment systems?
Effective water treatment removes microscopic bacteria, pesticides, and other harmful substances so that we can replenish our bodies and go about cleaning, washing, and many other daily activities, all of which would not be possible without clean water.
What is waste water treatment process?
Jan 18, 2022 · The distillation process is one of the most thorough water treatment techniques available today. It doesn’t just remove bacteria from water – it also removes iron, manganese, fluoride, chlorine (in chlorinated water), other disease-causing pathogens like viruses, chemicals like pesticides and herbicides, and much more.

What does water treatment remove?
Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
What types of things does water treatment serve to remove from the water?
A process in which water passes through a water system that may include one or more filters for the purpose of removing turbidity, taste, color, iron or odor and certain chemicals such as chlorine.
Does the water treatment process remove all chemicals from the water?
All wastewater first goes through the primary treatment process, which involves screening and settling out large particles. secondary treatment process, during which organic matter is removed by allowing bacteria to break down the pollutants.
What is removed from the water in the purification process?
water purification, process by which undesired chemical compounds, organic and inorganic materials, and biological contaminants are removed from water.
What are the three main purposes of water treatment?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water.
What are the benefits of a drinking water treatment plant?
The water treatment plants remove the chemicals, particulates, organic materials as well as other debris from the water and treat the water resulting in clean and potable water that can be used for cooking, cleaning, etc.Jul 14, 2017
Why is filtration important in water treatment?
The importance of water filtration is that it gives people access to clean water that is free of contaminants, that tastes good, and is a reliable source of hydration.Aug 6, 2020
What is water and wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is the process of converting wastewater into water that can be discharged back into the environment. According to the U.S. EPA, one of the most common forms of pollution control in the U.S. is wastewater treatment.Mar 6, 2020
What are the 5 steps of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What is filtered out of water?
There are hundreds of physical, chemical, biological, and radiological elements removed by water filters, including lead, chlorine, bacteria, calcium, minerals, salt, and carcinogens. Most drinking water purification methods look to remove the majority of those contaminants.
What is water purification process?
There are several methods used in the water purification process, which include: (1) physical processes, such as filtration, sedimentation, or distillation; (2) biological processes, such as sand filters, active carbon; (3) chemical processes, such as flocculation, chlorination, the use of ultraviolet light.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Learn More. ... Recommended Readings.
What is the second step in water treatment?
The second step involves the addition of a chemical disinfectant like chlorine that kills any remaining bacteria, parasites, and viruses. The two most common disinfectants used by a water treatment plant are chloramine or chlorine. Chloramines are a mix of ammonia and chlorine and have been used since the 1920s.
Why upgrade wastewater treatment equipment?
Upgraded equipment helps a water treatment plant process wastewater effectively and efficiently. Replacing outdated equipment may cost some money upfront, but it also saves money in terms of electricity costs and repairs in the long run. It ensures you meet the current EPA regulations.
How often does the EPA change water treatment regulations?
Water treatment regulations change regularly as the EPA reviews the current list of contaminants every five years. To ensure your system is removing viruses and other contaminants, you must make sure your system meets the current regulations.
What are the issues with water treatment plants?
One issue water treatment plants have seen with COVID-19 is the increased use of paper supplies other than toilet paper. With toilet paper shortages, people started using tissues, paper towels, baby wipes, and napkins in place. Public awareness campaigns are essential to keeping people from flushing these items into their septic systems or sewer lines. These items can cause blocked lines and put more strain on equipment. If you’re experiencing problems and need repairs, Lakeside Equipment does supply parts for necessary repairs.
How does water flow into a reservoir?
Water flows into a reservoir where it slowly trickles through activated charcoal filters to remove odors, bacteria, and some other contaminants. That’s similar to the filtration process in a water treatment plant. The same happens in a water treatment system. Wastewater comes into the plant where screens, clarification, ...
Where does charcoal sit in a water treatment tank?
The other way takes place in a filtration tank where the charcoal sits in the bottom of a tank and filters out contaminants and odors after rapid mix and flocculation/sedimentation. While many water treatment systems use charcoal or activated charcoal, some may use sand, coconut fibers, or other materials to capture bacteria, viruses, chemicals, ...
How does wastewater come into a plant?
Wastewater comes into the plant where screens, clarification, and filtration equipment work together to clean the water. Filters or filtration materials remove other contaminants in one of two ways. One way is to place the activated carbon filters for post-filtration cleaning after the rapid mix, flocculation/sedimentation, ...
What are the most important problems in water?
If the water originates from a surface water supply such as a river, lake, or dam, then the suspended particles are the most important problem. Different techniques to remove suspended particles include the addition of coagulants and the use of membranes.
What is membrane technology?
The development of large-scale modules with lower-energy consumption reduced costs significantly. Especially in the water industry, membrane technology has grown much more than coagulation and ozonation, since membranes require minimal addition of aggressive chemical reagents and produce no by-products.
What is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment?
zooplankton) and macro-invertebrate filter feeders also reduce pathogen numbers. Apart from pre-chlorination, storage is the most effective method of removing bacteria and viruses from raw water prior to conventional treatment.
What is biological waste water treatment?
Biological waste water treatment is the primary method of preparing food-processing waste water flows for return to the environment. Increasing waste water loads on existing plants and more stringent government discharge requirements have put considerable pressure on the food-processing industry to refine and understand better the design and management of biological waste water treatment processes. Though activated sludge and other biological treatment processes are still frequently operated by general guidelines and ‘rules of thumb,’ facility design and operation must be guided by consideration of both the physical and biological aspects of waste water treatment. Various modifications and combinations of aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment processes are commonly used in the food-processing industry.
What is MF water treatment?
MF is used to remove turbidity and larger microorganisms. Water treatment in existing installations uses immersed membrane modules that are simply placed in water tanks where a vacuum at the permeate side drives the collection of purified water.
How to improve the taste of water?
1. Understand the treatment need: For many consumers, simply improving the taste of the water is their primary treatment need. For some, there may be health contaminants that must be treated. And others may have very hard water, causing issues with lime scale around fixtures and possibly damaging appliances. 2.
What will the future of brewing water systems be like?
Brewery water treatment systems of the future will be very flexible, allowing breweries to tailor-make their water for different products. At the same time, these future water treatment systems will aim to achieve optimum efficiency in terms of operating cost and especially wastewater produced. The advances in analysis techniques will inevitably lead to further challenges, as it will be possible to detect certain components that are not an issue today but will then need to be removed. It will also continue to be vital for brewers to pay attention to their water supply to avoid surprising and unexpected quality defects in the finished product.
What is sedimentation with coagulation?
The sedimentation with coagulation is termed as clarification. It is required to increase the efficiency of sedimentation as stated above during the water treatment process. Plain sedimentation consumed too much time.
What are the two types of sedimentation tanks?
There are two types of sedimentation or settling tanks as described below: 1. Fill and Draw Type: The above mentioned tank is also known as Quiescent Tank. The water is filled in the fill and draw type first and then allowed to remain for a particular duration.
What happens to the weight of particles in a sedimentation tank?
The weights of the particles increase as they aggregate and then settle down. A sedimentation tank is so designed that the velocity of the flowing water is reduced. As the water is discharged into the sedimentation tank, the cross section area of the water flow is in the case and therefore, velocity reduces.
What is the most important step in water treatment?
Filtration. Filtration is one of the most crucial steps of the water treatment process. The flocs formed during flocculation are not removed entirely by sedimentation. Hence, to remove the finely sized particles and flocs, filtration is required.
How far apart are bar grills installed?
Bar grills are installed and water is allowed to pass through them in this process. 25 mm bars are installed at 75 to 100 mm centre to centre distance. This traps the particles of large size as the water flows through them.
What are the two types of water sources?
There are two types of sources of water. One is the surface water source like river, reservoir, etc. the other one is ground water source like bore well. The water treatment process differs for these systems considerably.
Why is water softened?
Water softening is done to make the hard water soft. Surface water usually does not contain much hardness. However, the water taken from underground sources like bore well contains hardness due to the presence of ions.
What is activated carbon?
Activated carbon treatment is the most studied treatment for PFAS removal. Activated carbon is commonly used to adsorb natural organic compounds, taste and odor compounds, and synthetic organic chemicals in drinking water treatment systems. Adsorption is both the physical and chemical process of accumulating a substance, such as PFAS, at the interface between liquid and solids phases. Activated carbon is an effective adsorbent because it is a highly porous material and provides a large surface area to which contaminants may adsorb. Activated carbon (GAC) is made from organic materials with high carbon contents such as wood, lignite, and coal; and is often used in granular form called granular activated carbon (GAC).
How effective is GAC?
EPA researcher Thomas Speth says, “GAC can be 100 percent effective for a period of time, depending on the type of carbon used, the depth of the bed of carbon, flow rate of the water, the specific PFAS you need to remove, temperature, and the degree and type of organic matter as well as other contaminants, or constituents, in the water.”.
How effective is nanofiltration?
This also allows nanofiltration to remove particles while retaining minerals that reverse osmosis would likely remove. Research shows that these types of membranes are typically more than 90 percent effective at removing a wide range of PFAS, including shorter chain PFAS.
What is the difference between nanofiltration and reverse osmosis?
This technology depends on membrane permeability. A standard difference between the two is that a nanofiltration membrane will reject hardness to a high degree, but pass sodium chloride; whereas reverse osmosis membrane will reject all salts to a high degree. This also allows nanofiltration to remove particles while retaining minerals that reverse osmosis would likely remove.
What is PFAS in the environment?
Per- and Polyfluorinated substances (PFAS) are a group of man-made chemicals that persist in the environment. These chemicals have been used for decades in consumer products to make them non-stick and water resistant. They are also found in firefighting foams and are applied in many industrial processes. Unfortunately, the characteristics that make ...
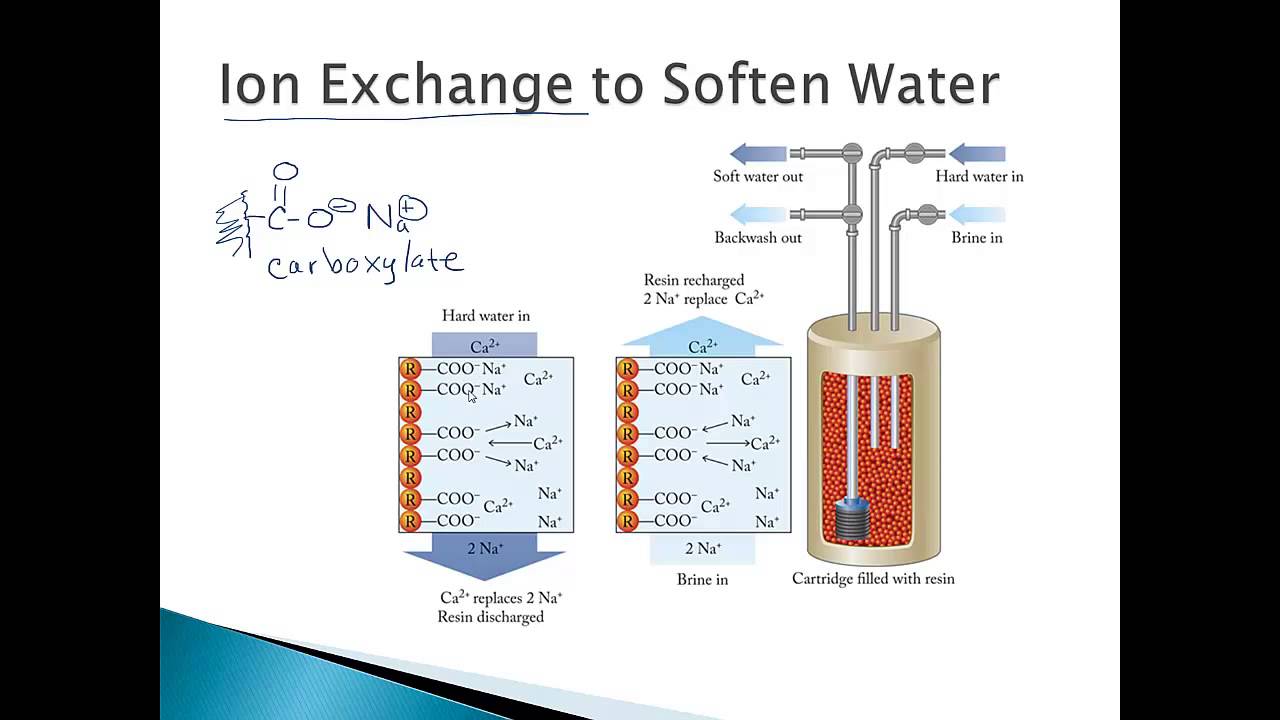
What is an ion exchange resin?
Ion exchange resins are made up of highly porous, polymeric material that is acid, base, and water insoluble. The tiny beads that make up the resin are made from hydrocarbons. There are two broad categories of ion exchange resins: cationic and anionic.
Is PAC as efficient as GAC?
Used in this way, PAC is not as efficient or economical as GAC at removing PFAS . Speth says, “Even at very high PAC doses with the very best carbon, it is unlikely to remove a high percentage PFAS; however, it can be used for modest percent removals.
How much does a reverse osmosis system cost?
Most units go for around $200 or more , depending on the make, model and features that are offered. Another option is purchasing a reverse osmosis water purification system. Reverse osmosis works by moving tap water through a semipermeable membrane.
What is distillate condensing?
Distillate condensing helps to maintain water purity. Stainless steel condensers are used to provide more consistently pure water quality. 6. Post-treatment. In this step, an organic carbon filter is used to aerate and distill any remaining volatile organic compounds in the water.
What is the purpose of sediment filter?
Sediment filters are also used to trap dirt and other heavier particles. 3. Distillation. Steam distillation occurs next. In this process, the water is heated to 100 degrees Celsius. This is done to eliminate giardia, cryptosporidium and any other biologic impurities that may have been in the raw water.
How does steam distillation work?
Steam distillation works to either remove or significantly eliminate a great number of biological and non-organic compounds that could be found in drinking water. Because steam rises, the inorganic elements are left behind in the boiler tanks.
What is the purpose of filtration?
Filtration also works to greatly reduce any particles that may be suspended in the water as well as any volatile organic compounds that could cause harm to people or animals.
Why boil water?
This process boils the water gently to allow any volatile organic chemicals to be burned off. This process prevents substances including chlorine, pesticides, herbicides, and other dangerous chemical compounds from being left in the raw water.
What is the final step in the process of water purification?
The final step in the process collects the water that has been purified and considered safe for drinking, bathing, and other general uses. This water is contained in a stainless steel reservoir. From there, the water is ready to be used in wells or from city reservoirs for the general public in their homes and office buildings.
Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium can contaminate both well and city water, and can spread quickly in a water source. When consumed, it can cause severe stomach cramps and diarrhea in a disease known as cryptosporidiosis. It’s essential that water is properly treated to kill this parasite.
E. coli
Escherichia Coli, or E, Coli for short, is one of the most common types of bacteria found in water. When consumed, this bacteria can cause vomiting, nausea, diarrhea and abdominal pain. You will usually experience symptoms between one and eight days after drinking contaminated water.
Coliform
Coliform is most commonly found in well water. While most coliform is not harmful, someone that has been exposed may experience vomiting, fever, diarrhea or upset stomach and elderly or children are more at risk.
Giardia
Giardia Lamblia, otherwise referred to as giardia, causes a type of infection known as giardiasis. You may experience nausea, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and gas with this infection, which can last for up to two weeks.
Legionella
Legionella is another bacteria that can be found naturally in the environment. You’re especially likely to find legionella in warm waters, and it poses a particularly high health risk when inhaled (such as while showering or through an air conditioning unit), causing a lung condition called Legionnaires disease.
Shigella
Shigella causes shigellosis, one of the most contagious bacterial diseases. This bacteria can get into water in numerous ways, including in polluted stormwater runoff and sewage overflows, and after flooding. Shallow wells are especially at risk of shigella contamination.
After a Natural Disaster
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, storms or major flooding events, can contaminate both well water and public drinking water supplies.
What are the processes used to control trihalomethane precursors?
For trihalomethane precursor control, effective processes are: (1) oxidation by ozone or chlorine dioxide; (2) clarification by coagulation, settling and filtration, precipitative softening, or direct filtration; or (3) adsorption by powdered activated carbon or granular activated carbon.
When were trihalomethanes discovered?
In 1974 trihalomethanes (chloroform, bromodichloromethane, dibromochloromethane, and bromoform) were discovered to be formed during the disinfection step of drinking water if free chlorine was the disinfectant. This, coupled with the perceived hazard to the consumer's health, led the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to amend ...
What is the maximum contaminant level in drinking water?
Environmental Protection Agency to amend the National Interim Primary Drinking Water Regulations to include a maximum contaminant level of 0.10 mg/L tor total trihalomethanes.
How much manganese can be removed from a Berkey filtration system?
According to the laboratory test, the Berkey products can remove greater than 99.9% of the manganese. The innovative products of the Berkey filtration systems are available in 7 various models and sizes. The systems are all identical, apart from their maximum filtration rate plus storage capacity.
What is the hardness of water softener?
In general, water softeners are recommended when the pH level of the water is more than 6.7, the hardness is around 3 to 20 grains per gallon (50-350 mg/L), and the dissolved iron concentration is less than five mg/L. The oxidized manganese and iron forms will produce a foul smell to the softener resin.
How much manganese is in food?
Food is the most important source of manganese exposure in the general population. Experts suggest a daily intake of 3.5 to 7 mg of manganese per day for adults.
What is manganese used for?
Manganese has many industrial uses. They are present in making iron and steel alloys, manganese compounds, and They are also an ingredient in various products. Manganese with other compounds is present in batteries, glass, varnish, various cleaning supplies, fertilizers, fungicides, cosmetics, and livestock feeding supplements.
What is the most abundant metal on Earth?
Manganese makes up 0.1% of the earth’s crust, making it one of the most abundant metals on the earth’s surface. There is no manganese in pure (elemental) form but a component of over 100 minerals.
How many people can a Crown Berkey water system serve?
The Crown Berkey model is the largest type of unit from the company. It can provide clean drinking water to a large number of people, up to 150.
What is the responsibility of a well owner?
Large public water suppliers or well owners are responsible for testing for potential contaminants. They monitor for contaminants, including manganese. Your water supplier will know if manganese levels are too high for humans to drink and tell you if this is the case. You can test your drinking water for manganese.
What is RO treatment?
As well as tannins, an RO treatment system removes bacteria, chemicals, and fluoride. The membrane also removes heavy metals like lead, and other contaminants that could turn water brown, such as iron. Something to keep in mind with RO membranes, however, is that excessive levels of tannins in your water may result in tannin resin depositing in ...
How often does an anion resin regenerate?
Typical anion exchange water treatment resins are made to undergo regeneration once every two days to prevent organic fouling of the softening resin.
What are the contaminants in well water?
In the case of tannins being present in your water, it’s probable that additional common well water contaminants, such as iron, hardness minerals, and sulfates are also present. You can arrange for a laboratory to test for these three contaminants at the same time as testing for tannins. It’s required to test for iron, ...
Why is my well water amber?
By the time it reaches your well’s aquifer, it will have taken on an amber tone because of its tannins content. You’re particularly likely to have tannins in your well water if you live in a low-lying, marshy or swampy area, or you live near to the sea or another large source of water.
What color is a tannin?
They’re usually found in earth, leaves, and the bark of trees, and have a browny-yellow color. Drinking water tannins can stain, so if you’re washing your laundry and porcelain in tannins-laced water, your white items may actually end up looking yellow. Tannins are also known as humic or fulvic acid.
What is iron exchange?
Iron exchange is most commonly known as a softening water treatment option for removing hardness minerals, using salt, or sodium. But a cation/ion exchange absorption process can also be used in water softeners to treat and remove a high concentration of various other “difficult” contaminants, including drinking water tannins.
How to test for tannins?
The most simple means of testing for tannins, before parting with your money on expensive equipment , is to fill a glass with water and let it sit for several hours ( preferably overnight). Your water may be orange in color, but that’s not a definitive sign of tannins.

Community Water Treatment
Water Fluoridation
- Community water fluoridation prevents tooth decay safely and effectively. Water fluoridation has been named one of 10 great public health achievements of the 20th century 1. For more information on the fluoridation process and to find details on your water system’s fluoridation, visit CDC’s Community Water Fluoridationpage. Top of Page
Consumer Confidence Reports
- Every community water supplier must provide an annual report, sometimes called a Consumer Confidence Report, or “CCR,” to its customers. The report provides information on your local drinking water quality, including the water’s source, contaminants found in the water, and how consumers can get involved in protecting drinking water. 1. View the CDC’s guide to Understandi…
Protections Set by The Safe Drinking Water Act
What Does This Mean For A Water Treatment Plant?
- Every step a water treatment plant takes to rid wastewater of other viruses is taking care of the less common coronaviruses like COVID-19, MERS, and SARS. If you look at the steps that most water treatments plant use, there are different stages starting with the moment the wastewater arrives until it returns to a body of water or public water suppl...
Avoid Frequent Repairs Or Equipment Failures Through Plant Upgrades
- One issue water treatment plants have seen with COVID-19 is the increased use of paper supplies other than toilet paper. With toilet paper shortages, people started using tissues, paper towels, baby wipes, and napkins in place. Public awareness campaigns are essential to keeping people from flushing these items into their septic systems or sewer lines. These items can cause block…