
Tertiary treatment removes the load of nitrogen and phosphorus present in the water. It includes processes like filtration, ion exchange, activated carbon adsorption
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, or molecules from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the absorbate) is dissolved by or permeates a li…
What is an example of tertiary care?
Tertiary treatment is the advanced treatment process, following secondary treatment of waste water, that produces high—quality water. Tertiary treatment includes removal of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen and practically all suspended and organic matter from waste water.
What does tertiary treatment remove?
Dec 07, 2021 · Tertiary treatment is the final cleaning process that improves wastewater quality before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. The treatment removes remaining inorganic compounds, and substances, such as the nitrogen and phosphorus.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment, and how does it work?
Tertiary treatment is the next wastewater treatment process after secondary treatment. This step removes stubborn contaminants that secondary treatment was not able to clean up. Wastewater effluent becomes even cleaner in this treatment process through the use of stronger and more advanced treatment systems.
What is the definition of tertiary care?
Tertiary treatment is the final cleaning process that improves wastewater quality before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. The treatment removes remaining inorganic compounds, and substances, such as the nitrogen and phosphorus.
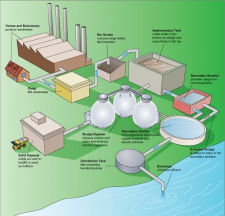
What does a tertiary treatment do?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final polishing treatment stage prior to discharge or reuse of the wastewater. Chlorination – A water treatment method that destroys harmful bacteria, parasites, and other organisms.
What elements are removed in the tertiary treatment?
As shown in Figure 3, individual treatment processes are necessary to remove nitrogen, phosphorus, additional suspended solids, refractory organics, heavy metals and dissolved solids. Because advanced treatment usually follows high-rate secondary treatment, it is sometimes referred to as tertiary treatment.
What is an advantage of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment improves the quality of wastewater before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. Industrial wastewater can contain high numbers of inorganic compounds. These are harmful to rivers and lakes as they are of mineral origin rather than biological.Apr 3, 2019
What can tertiary treated water be used for?
In California, tertiary-treated water is called “recycled water” and can be used for irrigation or industry.Apr 4, 2011
What does tertiary treatment remove from wastewater?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.Sep 11, 2018
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment?
The basic function of wastewater treatment is to speed up the natural processes by which water is purified. There are two basic stages in the treat- ment of wastes, primary and secondary, which are outlined here. In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater.
Is tertiary water treatment necessary?
Incorporating a tertiary treatment system into your operation can dramatically reduce the amount of water your facility uses, which is becoming increasingly important to regions, states, and localities that face shortages.
What is tertiary solids removal?
Total Suspended solids (TSS) removal by tertiary treatment implies the removal of those materials that have been carried over from a secondary clarification process. Pretreatment is required prior to physical chemical treatment processes.
What are 3 methods of tertiary treatment?
The tertiary treatment methods are: 1.Filtration 2.Air/Steam Stripping 3.Biological Processes 4. Adsorption 5.Membrane Separation Processes 6.Ion Exchange Process 7.Precipitation 8.Oxidation and Reduction and 9.
What is removed during primary wastewater treatment?
Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. It includes the physical processes of screening, comminution, grit removal, and sedimentation. Screens are made of long, closely spaced, narrow metal bars.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
What are the two types of chemical treatments?
There are two different types of chemical treatments, flocculation and precipitation , as they involve different types of purification mechanisms. Flo cculation, is based on an addition of ferric ions, aluminum ions, or/and long-chained polymers to the effluents.
What are the drawbacks of biological treatment?
Although chemical treatment shows good results, the treatment has associated drawbacks such as dewatering and disposal of the generated sludge.
What is suspended solid removal?
Suspended solids removal in tertiary treatment implies the removal of those materials that have been carried over from a secondary clarification process. It is also employed as a pretreatment method prior to physical chemical treatment processes. Influent suspended solids concentration must be less than about 100 mg/liter or backwashing requirements become excessive. Finely dispensed suspended solids may require the addition of coagulant prior to filtration. Several means for removal of suspended solids have been proposed and tested. These include the use of diatomaceous earth filtration, pressure filtration, chemical clarification, sand filtration with conventional units and multimedia, ultrafiltration, and the moving-bed filter. With the exception of the chemical clarification processes, these methods all involve the physical straining of the finely divided solids that are removed.
What is sand filtration?
Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance. In this system, chemical reagents are not required, resulting in lower costs in comparison with other methods.
What is chemical precipitation?
Chemical precipitation is a very common and well-known technology, especially for phosphorous removal in municipal wastewater treatment. It involves the addition of metal salts of aluminum, iron, or calcium to alter the physical state of dissolved solids and facilitate their removal by sedimentation.
What does tertiary treatment of wastewater do?
Tertiary treatment is the final cleaning process that improves wastewater quality before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. The treatment removes remaining inorganic compounds, and substances, such as the nitrogen and phosphorus.
Which category of impurities are removed by tertiary treatment?
phosphate levels must be reduced, tertiary treatment methods are used. Tertiary processes can remove more than 99 percent of all the impurities from sewage, producing an effluent of almost drinking-water quality.
What happens to sludge from a sewage treatment plant?
Sewage sludge is a product of wastewater treatment. Wastewater and stormwater enter the sewage system and flow into wastewater treatment facilities, where the solid wastes are separated from the liquid wastes through settling. At this point, they are processed and “digested,” or decomposed by bacteria.
Where does human waste go after a sewage treatment plant?
What happens to the treated water when it leaves the wastewater treatment plant? The treated wastewater is released into local waterways where it’s used again for any number of purposes, such as supplying drinking water, irrigating crops, and sustaining aquatic life.
What are two possible uses of sewage sludge after further treatment?
Otherwise any pathogens present in the sewage may contaminate fruit, crops and grazing animals. Sewage is therefore treated to remove any pathogens. Waste water sludge is a useful source of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matter, and after further processing can be used as a liming material.
Which is used to remove sludge?
Digested sludge is put through large centrifuges that work in the same fashion as a washing machine spin cycle. The spinning centrifuge produces a force that separates the majority of the water from the sludge solid, creating a biosolid substance.
How is sludge useful after its treatment?
When a liquid sludge is produced, further treatment may be required to make it suitable for final disposal. Sludges are typically thickened and/or dewatered to reduce the volumes transported off-site for disposal.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment of Wastewater – Methods and Process. Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
What is the final stage of tertiary wastewater treatment?
The final stage of the tertiary wastewater treatment process involves removing the chlorine that was used to disinfect the water. This step is very important because chlorine is harmful to aquatic life. Chlorine also reduces biological water quality when it is present in high concentrations. To remove the chlorine, a compound called sodium ...
What is the primary treatment of wastewater?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves filtering out large solid contaminants. Secondary treatment then purifies the wastewater through biofiltration, aeration, and oxidation. These are all processes that help to remove sediment from the water.
What is alum used for in water treatment?
When needed, it sometimes involves using alum to remove phosphorus particles from the water. Alum also causes any solids that were not removed by primary and secondary wastewater treatment to group so they can be removed by filters.
What is the purpose of chlorination in wastewater treatment?
Chlorination in wastewater treatment kills bacteria and viruses, and eliminates parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium, which can cause very serious illnesses. In summary, this process disinfects water so that it is safe to reuse or recycle.
How does chlorine affect water quality?
Chlorine also reduces biological water quality when it is present in high concentrations. To remove the chlorine, a compound called sodium bisulfite is added to the water. Chlorine ions in the water react with this chemical and are removed.
What is tertiary treatment?
What is Tertiary Sewage Treatment? After biochemical degradation of the sewage in the secondary treatment, the clarified effluent is further treated to treat it of the non-biodegradable toxic organic pollutants such as chlorophenols, polychlorinated biphenyls and other synthetic pollutants.
How is nitrogen removed from wastewater?
Nitrogen is removed by volatiIisation as ammonia. Ammoniacal nitrogen is removed by breakpoint chlorination by adding hypochlorous acid in 1:1 ratio. Disinfection. The final step of tertiary process is disinfection, which is typically carried out by adding chlorine to the wastewater.
What metals are removed from sewage?
For this purposes activated carbon filters are used. Removal of heavy metals like mercury, lead, chromium and cadmium are also done during tertiary treatment. These metal ions, which are found absorbed in the sewage water are converted into either toxic products or residues.
What is the process of filtration?
Filtration. In the filtration process, either sand, charcoal or activated carbon are used to filter the wastewater. The water is made to pass through a bed of sand or charcoal, so that the particulate matter in the water adheres to the filter medium and gets removed from the water. Lagooning.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment is the third, and final, stage in a standard wastewater management system. Once effluent has been treated in the primary and secondary stages by removing suspended solids, pH balancing and reducing its biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), it is ready to enter the tertiary stage.
Why is tertiary treatment important?
Incorporating a tertiary treatment system into your operation can dramatically reduce the amount of water your facility uses, which is becoming increasingly important to regions, states, and localities that face shortages.
How long does it take to install a tertiary treatment system?
After collecting data and making a system recommendation, we’ll begin the 2-3 week process of installing your tertiary treatment system. Once the installation is complete, we’ll compile documentation and create a custom service checklist that’s specific to the customer’s site and system.
Is gray water better than black water?
It is much easier to reuse gray water (processed wastewater) than blackwater. For high strength wastewater, it is critically important to reduce both the organic loading (BOD) as well as the suspended solids (TSS) to make final stage treatment feasible.
What is tertiary treatment?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final treatment stage to raise the effluent quality before it is discharged to the receiving environment (sea, river, lake, ground, etc.). More than one tertiary treatment process may be used at any treatment plant. It is also called “effluent polishing.”
Why do you need to clean a filter?
Cleaning filters is necessary to remove the solids collected by the media during the filtration run . As solids are accumulated in the filter media, the headloss or force required to maintain the flow increases. A point is reached where either the flow cannot be maintained or solids are driven through the filter.
