
What does SRT stand for in wastewater?
retention time (SRT), a high ratio of anaerobic–aerobic hydraulic residence time, high glucose content in the waste, low phosphorus-to-carbon ratio in the feed and excessive aeration. The pH in the anaerobic zone can also affect the competition between PAOs and GAOs.
How to calculate SRT?
How do I calculate the volume of an aeration tank?
- Example #2: For an assumed aeration tank MLSS of 2100 mg/L and.
- Solution: The HRT and F:M ratio can be calculated using the last three.
- VMG = V*7.48/1,000,000 = 170,275*7.48/1,000,000 = 1.27 MG.
- HRT = 24*VMG/Qo = 24*1.27/3.5 = 8.7 hours.
- F:M = (8.34*So*Qo)/(8.34*%Vol*X*VMG) = (175*3.5)/(0.75*2100*1.27)
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
- Increasing/expanding regulations. Concerns over increasing regulations consistently ranked near the top of the list for every geographical region, pushing the topic into the No. ...
- Technology changes. Information technologies jumped to the No. ...
- Aging workforce. In the No. ...
- Water scarcity. ...
How is aeration used in wastewater treatment?
His preliminary report shows the current treatment facility and sewage system might have a few years of use left but should be replaced by an extended aeration facility as soon as possible due to potential risks of continuing to use the old system.
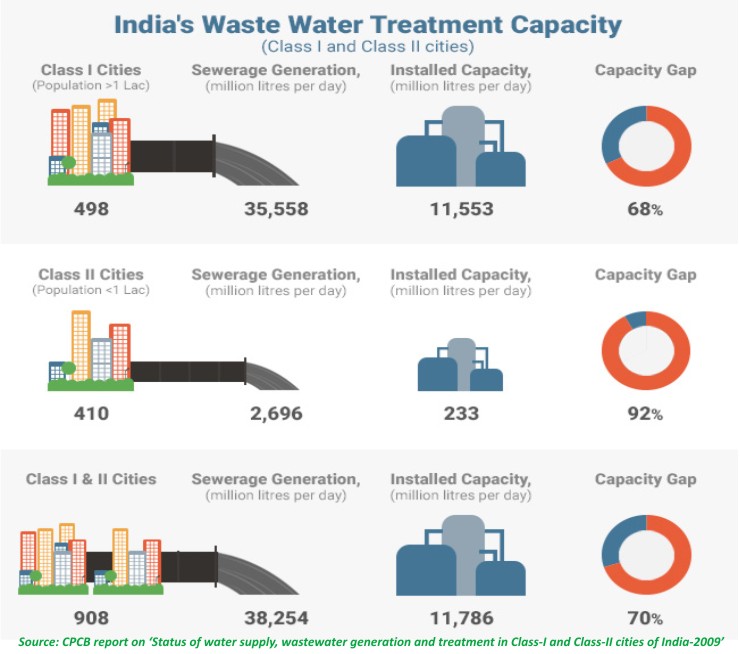
What is SRT in activated sludge process?
The Solids Retention Time (SRT) is the average time the activated-sludge solids are in the system. The SRT is an important design and operating parameter for the activated-sludge process and is usually expressed in days.
What is SRT in aeration tank?
The SRT is equal to the mass of MLSS in the aeration tank plus the mass of final clarifier solids divided by the mass of solids wasted each day.
What is SRT and HRT?
Summary. There are two significant retention times in an anaerobic digester. These are solids retention time (SRT) and hydraulic retention time (HRT). The SRT is the average time that bacteria (solids) are in the anaerobic digester. The HRT is the time that the wastewater or sludge is in the anaerobic digester.
What is the difference between MCRT and SRT?
SRT — solids retention time — is sometimes used as a synonym for MCRT. They typically mean the same thing, but they may be calculated using different pieces of data. SRT can be viewed as the total mass of the solids in the treatment system, whereas MCRT is the mass of the bacteria in the system.
Is SRT the same as sludge age?
Many operators refer to the mean cell residence time (MCRT), the solids retention time (SRT), and the sludge age as being one and the same and they'll use these three terms interchangeably.
How do you maintain SRT?
The traditional method to maintain optimal SRT is to manually adjust the waste activated sludge (WAS) wasting rate based on mainly judgment or by removing a calculated amount of biomass that is not based on real time calculation.
How is SRT calculated in wastewater treatment?
The solids retention time (SRT) is the time the solid fraction of the wastewater spends in a treatment unit. It is the quantity of solids maintained in the reactor divided by the quantity of solids coming out of the reactor each day: SRT = V *Cd / Qout* Cout.
Why is SRT higher than HRT?
SRT is generally kept higher than HRT to take full use of adaptability of bacteria for biodegradation process. If you do not retain the bacteria longer than the water they cannot develop a effective degrader culture for the pollutants in the wastewater.
What is HRT of sludge?
The hydraulic retention time or HRT is the amount of time in hours for wastewater to pass through a tank, such as an aeration tank. Changes in the HRT of an activated sludge process can affect bio- logical activity.
What does MCRT mean in wastewater?
Mean Cell Residence TimeMean Cell Residence Time (MCRT) is an expression of the average time (days) that a microorganism will spend in the activated sludge process.
What is SVI in wastewater treatment?
Sludge Volume Index (SVI) is used to describe the settling characteristics of sludge in the aeration tank in Activated Sludge Process. It is a process control parameter to determine the recycle rate of sludge.
How do I stop sludge bulking?
To avoid sludge bulking some of the flow that enters the reactor can be bypassed, recycle ratio can be increased, lime or soda can be added to the reactor or the re-aeration rate increased.
GSA, MCRT, SRT, and Sludge Age Defined
I think there is confusion, sometimes, in how operators (which includes me) define the terms mean cell residence time (MCRT), solids retention time (SRT), sludge age, and, though seldom used these days (was it ever used?), Gould sludge age (GSA).
Gould Sludge Age (GSA)
The Gould sludge age represents the average number of days total suspended solids (TSS) entering the bioreactor remain under aeration. The GSA is calculated by dividing the pounds (or kg) of MLSS in the aeration tank by the pounds (or kg) of total suspended solids entering the aeration tank as shown schematically in Figure No. 1.
MCRT and SRT
Many operators refer to the mean cell residence time (MCRT), the solids retention time (SRT), and the sludge age as being one and the same and they'll use these three terms interchangeably.
MCRT & SRT Equations
The formula for calculating the mean cell residence time (MCRT) is shown in Equation No. 2. Actually, one final time, I'm showing both versions of the MCRT equation, the first with the constants removed, the second with the constants included. The solids in the clarifier are included in the calculation.
Difference Between MCRT and SRT
In Table No. 1 I shown an Excel spreadsheet using data from an industrial wastewater system where I have calculated both the MCRT and the SRT. As you can see, the SRT value is almost 32 percent lower than the MCRT value, the difference being the additional solids in the clarifier are increasing the MCRT value.
Why I Prefer SRT Over MCRT
Calculation of the SRT is easy because it uses data that is readily available and reliably produced. For the SRT the total suspended solids values you need are the MLSS, clarifier underflow TSS (the concentration in the return activated sludge or RAS) if you are wasting from the return sludge line, and the effluent TSS.
What is DSRT in wastewater?
DSRT, an alternate method of sludge age calculation that has been discussed in the wastewater process engineering community, is a more accurate method of accounting for the total biomass produced and removed from the system each day. The DSRT sludge age calculation includes the amount of solids wasted from the system, but also includes the solids entering the system and possibly the amount of new solids produced in the facility on a daily basis. DSRT could include information such as influent BOD, TSS and VSS in the calculation.
What is the difference between MCRT and SRT?
They typically mean the same thing, but they may be calculated using different pieces of data. SRT can be viewed as the total mass of the solids in the treatment system, whereas MCRT is the mass of the bacteria in the system. SRT is also expressed in days.
What does M stand for in MCRT?
In MCRT, the M is for “mean,” which is a substitute for “average.” The remaining letters, CRT, represent cell residence time — how long a particular bacterial cell, or a pound of bacteria, remains in the activated sludge secondary treatment train. MCRT is normally expressed in days.
What do bacteria do in the treatment system?
What to include. Bacteria in the treatment system do the work of capturing suspended and dissolved solids and organic material and converting them into new cell mass that will settle in the clarifiers. They exit the treatment system by one of three methods:
What is waste flow?
The waste flow is usually a small fraction of the influent flow; however, minimal variations of waste flow over time may have a profound effect on the performance of an activated sludge system. Inadequate wasting may cause clarifier overloading, low F/M bulking and foaming, and increased air demand for biomass endogenous respiration.
How does wasting affect sludge thickening?
Click here to enlarge image. Wasting also affects sludge thickening processes not only because excessive wasting increases loads on the thickening facility , but, more importantly, because an increased daily variation in wasting biomass increases polymer consumption and reduces efficiency of all types of thickeners.
What is MCRT in chemistry?
The MCRT is also referred to as sludge age or solids retention time (SRT). This is the "complete" or full version of the MCRT equation that includes the mass of solids in the secondary clarifiers. This form of the MCRT equation does not include the mass of solids in the secondary clarifiers.
What is the COD/BOD ratio?
If you don't have BOD data, you can use your COD data and a COD/BOD ratio of 2.1 as a starting point. Use the 2.1 ratio value with caution though as it is highly variable from one wastewater system to another.
What are visible solids in wastewater?
Visible solids present in wastewater that can be filtered out through traditional physical treatment technologies. In the metal finishing industry, for example, FOG (fats, oils and grease) and dirt particles might make up part of the total suspended solids.
What is an indirect reading of the organic content present in wastewater?
Specifically, it refers to the amount of oxygen consumed to biologically degrade the organic material. It’s very expensive to treat, typically requiring a biological treatment technology like activated sludge.
What is PSI in wastewater treatment?
A measurement of pressure. It’s often used when discussing physical wastewater treatment technologies involving filtration, but is also used with pumps. Filtration system PSI can indicate when it’s time to backwash or change a filter.
What is wastewater permit?
These terms refer to the amount of wastewater flow over a given time period. Most wastewater permits include daily flow limits, so facilities track the flow of treatment systems to stay within overall permit parameters.
Why is UV light used in wastewater treatment?
In some industries, ultraviolet light is used to sterilize water treated wastewater prior to reuse or recycling. UV light keeps algae and other bacteria from growing in the recycled wastewater.
What is biological water treatment?
A biological water treatment technology commonly used in municipal wastewater treatment systems. Sometimes private industry will harness this technique to reduce certain pollutants, such as BOD and COD (see definitions below), but usually only due to compliance concerns.
What is RO in filtration?
RO: Reverse Osmosis. A physical treatment technology based around the use of a membrane for filtration. It provides the greatest degree of filtration available and is very effective for filtering out small or even dissolved pollutants. It is subsequently the most expensive type of filtration.
How long does it take for a SBR to settle?
For example, an SBR has a settle time of 45 minutes; the operator takes his final settleability reading at 45 minutes instead of 30 minutes.
What is the SVI of activated sludge?
Most activated sludge plants seem to produce a clear , high-quality effluent with an SVI in the range of 100 to 200. The sludge typically settles slower and traps more particulate matter as it forms a uniform blanket before settling.
What is SVI in sludge bulking?
SVI is a very useful tool when using chlorine or other oxidizers to control sludge bulking conditions . Combining SVI with microscopic exam results can give the operator a great way to monitor the effect of oxidizers on overall sludge characteristics. For instance, at certain SVI values, the operator knows the plant experiences sludge bulking and solids washout of the secondary clarifiers. Using an oxidizer, such as chlorine feed into the RAS flow, can prevent the SVI from climbing too high, then shut the chlorine off when SVI numbers return to normal.
What happens when sludge settles?
As sludge settles, it also compacts, squeezing clear water out of its blanket. These channels of water can be seen from the side of a settleometer and give the compacting sludge a ‘cottage cheese-like’ appearance. As the sludge thickens and compacts, water rises above it to form the supernatant.
What would happen if bacteria were present in sludge?
If filamentous bacteria are present in the sludge, that 1 gram of sludge would be light, fluffy and spread out, much like a cotton ball soaked in water. Now imagine a gram of dense, somewhat granular sludge, like mud. The same gram of sludge would take up less space than the same gram of fluffy, filamentous sludge.
Where to collect liquor sample for aeration?
A fresh sample of mixed liquor should be used for the test, and is normally collected from the effluent end of the aeration system just before entering the secondary clarifier. It is important to allow the sludge to settle in a quiet area where it won’t get bumped or disturbed and kept out of direct sunlight.
What happens when water rises above a sludge?
As the sludge thickens and compacts, water rises above it to form the supernatant. If a skinny cylinder is used for the settling test, the rising water velocity interferes with the sludge’s downward velocity, slowing the settling.
What is a tank in wastewater treatment?
Usually in municipal wastewater treatment, a chamber or tank in which primary influent is slowed down so heavy typically inorganic solids can drop out, such as metals and plastics.
What is TSS in water?
As the name implies, the total solid particles that are suspended (as opposed to dissolved) in the wastewater. TSS must be filtered out, flocculated, digested and so on for removal in the treatment of wastewater. Though not necessarily pollutants TSS is considered to be a measure of pollutants in water by the EPA in the US.
What is the pulse of surface water?
The pulse of surface water following a rainstorm. The water carries sediment, gas, oil, animal feces, glass and other waste from the watershed to receiving waters creating a difficult urban/suburban wastewater problem.
What is the process of adding a substance to wastewater?
The process whereby a chemical or other substance is added to wastewater to trap or attract the particulate suspended solids into clusters or clumps of floc or flocculent, wooly looking masses.
What is floc in wastewater?
Particulate and or bacterial clumps forming wooly looking clusters in wastewater. In biological processes such as extended aeration or activated sludge and others the floc contains aerobic or anaerobic microorganisms. For industrial applications flocculants are used.
Is wastewater treated industrial or municipal?
Paper and pulp mills' treatment of wastewater is an example of industrial wastewater treatment. Municipal wastewater treatment would be an example not considered to be industrial.

Variations on A Theme
- In MCRT, the M is for “mean,” which is a substitute for “average.” The remaining letters, CRT, represent cell residence time — how long a particular bacterial cell, or a pound of bacteria, remains in the activated sludge secondary treatment train. MCRT is normally expressed in days. SRT — solids retention time — is sometimes used as a synonym for M...
Taking The Measure
- Various reference manuals explain methods of calculating MCRT and SRT. One alternative for calculation is to include the solids in the secondary clarifiers. If a treatment facility has multiple clarifiers and carries a high sludge blanket (greater than 3 feet) in each, then accounting for the solids in the clarifiers can become important for accurate mass balance process control approa…
What to Include
- Bacteria in the treatment system do the work of capturing suspended and dissolved solids and organic material and converting them into new cell mass that will settle in the clarifiers. They exit the treatment system by one of three methods: By way of waste activated sludge flowing out of the secondary process to digesters or other treatment units. By “jumping over the weirs” of the fi…
A Look at Dsrt
- DSRT, an alternate method of sludge age calculation that has been discussed in the wastewater process engineering community, is a more accurate method of accounting for the total biomass produced and removed from the system each day. The DSRT sludge age calculation includes the amount of solids wasted from the system, but also includes the solids entering the system and …
References
- Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR) Operation in Wastewater Treatment Plants, WEF Manual of Practice (MOP #29), Water Environment Federation, 2005. Paper: Do You Know Your Sludge Age? Presented at WEFTEC 2008; Water Environment Federation. Operation of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants, Fifth Edition, WEF Manual of Practice (MOP #11), Volume II, Water Environme…