In medicine, refraction is the bending of light rays that takes place in the eye. A refraction test, also known as a vision test, is an eye examination that is performed to determine a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses. It is commonly performed as part of a comprehensive eye examination to determine refractive errors.
Full Answer
Why is refraction not covered by insurance?
Why is refraction not covered by insurance? A refraction is a test done by your eye doctor to determine if glasses will make you see better. For example, Medicare does not cover refractions because they consider it part of a “routine” exam and Medicare doesn't cover most “routine” procedures - only health-related procedures.
What contributes to refraction in the eye?
The Human Eye as an Optical System
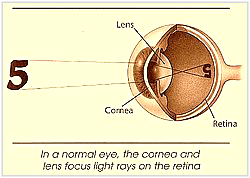
- Introduction. The eye is a compound optical system composed of a cornea and a lens shown in Figure 1. ...
- History. The nature of the ocular image has been studied since the times of the ancient Greeks. ...
- Refractive State of the Eye
- Emmetropia
- Ametropia
- Far-point
- Length of Eye in Axial Ametropia
- Correction of Myopia
- Correction of Hyperopia
- Astigmatism
Why do I have to pay for refraction?
- Astigmatism (a refractive issue based on the shape of the lens of the eye, which can cause blurry vision).
- Hyperopia ( farsightedness ).
- Myopia ( nearsightedness ).
- Presbyopia (inability of the lens of the eye to focus, related to changes in the structure of the eye due to aging).
What does refraction mean in eye exams?
This is calculated by means of a refraction test (also known as a vision test ), typically conducted as part of a standard eye examination. A refraction test gives a doctor the precise measurement for a prescription that a patient will need for their glasses or contact lenses.
What is refraction treatment?
What's the treatment for refractive errors? Eye doctors can correct refractive errors with glasses or contact lenses, or fix the refractive error with surgery. Glasses. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest way to correct refractive errors.
What is eye refraction procedure?
A refraction is an eye exam that measures a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses. Normal vision occurs when light is focused directly on the retina rather than in front or behind it.
Is eye refraction necessary?
Eye Exams are Important The sooner we can diagnose vision problems, the sooner we can begin treatments to protect your eyesight. If you have worn glasses or contacts for a while, it's important to have these refraction tests to monitor any additional refractive errors that may be developing.
What is a normal refraction for eyes?
Normal Results A value of 20/20 (1.0) is normal vision. This means you can read 3/8-inch (1 centimeter) letters at 20 feet (6 meters). A small type size is also used to determine normal near vision.
Are eyes dilated for refraction?
1 A dilated eye exam allows the doctor to measure the degree of light refraction. Another aspect of dilation is that it may help determine your true refractive error because it stops your eye from focusing, This can be helpful for your corrective lens prescription.
Why is refraction important?
This bending by refraction makes it possible for us to have lenses, magnifying glasses, prisms and rainbows. Even our eyes depend upon this bending of light. Without refraction, we wouldn't be able to focus light onto our retina.
What is a refraction fee for?
What is a refraction fee? When the doctor asks “which is better, 1 or 2”, the test is called a refraction and there is a refraction fee. A refraction determines the lens prescription you will need for glasses or contacts. It is also a necessary part of a cataract evaluation.
Does Medicare ever cover refraction?
Medicare doesn't cover eye exams (sometimes called “eye refractions”) for eyeglasses or contact lenses. You pay 100% for eye exams for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
Why is refraction not covered by Medicare?
The charges for a refraction are covered by some insurances but not all. For example, Medicare does not cover refractions because they consider it part of a “routine” exam and Medicare doesn't cover most “routine” procedures - only health-related procedures.
What is disorder of refraction?
Refractive disorders, also known as refractive errors, occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing directly on the retina. This typically results in blurred vision, the most common symptom of a refractive disorder.
Can refractive errors be corrected?
Refractive errors cannot be prevented, but they can be diagnosed by an eye examination and treated with corrective glasses, contact lenses or refractive surgery. If corrected in time and by eye-care professionals, they do not impede the full development of good visual function.
Is Cataract a refractive error?
Given the high prevalence of age related cataract, the refractive error induced by nuclear and cortical cataract is likely to be a major cause of the uncorrected refractive error in the elderly.
Where does the most refraction occur?
Most refraction in the eye occurs when light rays travel through the curved, clear front surface of the eye (cornea). The eye's natural lens also bends light rays. Even the tear film on the surface of the eye and the fluids inside the eye (aqueous humor and vitreous) have some degree of refractive ability.
How does an optician determine the degree of refractive error?
Your optician determines the type and degree of refractive error you have by performing a test called a refraction. This can be be done with a computerised instrument (automated refraction) or with a mechanical instrument called a phoropter that allows your optician to show you one lens at a time (manual refraction).
What is it called when the cornea is not spherical?
If the cornea is not perfectly spherical, then the image is refracted or focused irregularly to create a condition called astigmatism. A person can be shortsighted or longsighted with or without astigmatism.
What are the primary refractive errors?
The primary refractive errors are shortsightedness, longsightedness, and astigmatism. Refractive errors usually can be "corrected" with eyeglasses or contact lenses, or they can be permanently treated with LASIK ...
What are the three features of the eye?
The eye's ability to refract or focus light sharply on the retina primarily is based on three eye anatomy features: 1) the overall length of the eye, 2) the curvature of the cornea and 3) the curvature of the lens inside the eye.
Why is my vision blurry?
But what does it really mean when we're told that our vision is blurry because we have a refractive error? We see the world around us because of the way our eyes bend (refract) light.
How does the eye see?
How the eye sees. The process of vision begins when light rays that reflect off objects and travel through the eye's optical system are refracted and focused into a point of sharp focus . For good vision, this focus point must be on the retina. The retina is the tissue that lines the inside of the back of the eye, ...
What is refraction in eye?
Refraction is a test that optometrists and ophthalmologists use to measure a person's refractive error . A refractive error is when your eye does not bend the light coming into your eye properly as it passes through the cornea, the crystalline lens, and fluid media to come to a sharp, clear focus onto your retina. 1 .
What is the primary method used by eye doctors and technicians to determine your refractive error and your prescription for corrective
Retinoscopy: Retinoscopy is the primary method used by eye doctors and technicians to determine your refractive error and your prescription for corrective lenses. 3 Retinoscopy is considered an "objective" method because the measurements are obtained without interaction or subjective information from the patient.
What is an autorefractor?
Most eye doctors use autorefractor's routinely to develop a starting point that they may then compare to retinoscopy or traditional phoropter refraction. Wavefront Refraction: Wavefront refraction uses an aberrometer to measure higher order refractive problems of the human optical system.
What is the best tool to measure refraction?
A retinoscope is a handheld device and an invaluable tool for most eye doctors. Autorefraction: A refraction can also be measured using an autorefractor. 2 An autorefractor is a tabletop instrument that uses light rays and a computer to measure how light refracts through your eye.
Why is it called a manifest refraction?
It is called manifest because it the measure of the refraction before any eye drops are instilled or anything else that could alter the measurement. It is a measurement as the patient is in real life. A manifest refraction can be performed using a traditional manual phoropter or an automatic phoropter.
What is a retinoscope?
Doctors use a retinoscope to perform retinoscopy. A retinoscope is a handheld device and an invaluable tool for most eye doctors.
What is the device used to refract vision?
The ophthalmic technician or doctor will refract your vision using a phoropter, a device that contains hundreds of combination of lenses, to determine any possible refractive error such as nearsightedness , farsightedness , astigmatism, or presbyopia. 2 .
What is refraction in eye?
In medicine, refraction is the bending of light rays that takes place in the eye. A refraction test, also known as a vision test, is an eye examination that is performed to determine a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses. It is commonly performed as part of a comprehensive eye examination to determine refractive errors.
What happens when light refracts inside the eye?
When light incorrectly refracts inside the eye, it causes refractive errors. This results in blurry vision or reduced visual acuteness. The fault may be in the eye lens, cornea, or size of the eyeball.
Why do you need eye drops for phoropter?
The doctor will quickly change the lenses in the phoropter to help determine which combination gives the sharpest vision. Children may need eye drops for paralyzing the muscles of accommodation (muscles around the eye lens that help us focus) before undergoing vision testing.
What is the opposite of myopia?
Myopia or nearsightedness: Things can be seen clearly when they are close by but not when they are far away. This occurs when light doesn’t focus close enough to the retina. Hyperopia or farsightedness: The opposite of myopia, hyperopia means objects that are far away can be clearly seen but not close by objects.
How does an eye doctor determine the degree of refractive error?
Your eye doctor determines the type and degree of refractive error you have by performing a test called a refraction. This can be be done with a computerized instrument (automated refraction) or with a mechanical instrument called a phoropter that allows your eye doctor to show you one lens at a time (manual refraction).
What are refractive errors?
Refractive errors are optical imperfections that prevent the eye from properly focusing light, causing blurred vision. The primary refractive errors are nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism. Refractive errors usually can be "corrected" with eyeglasses or contact lenses, or they can be permanently treated with LASIK ...
What are the three features of the eye?
The eye's ability to refract or focus light sharply on the retina primarily is based on three eye anatomy features: 1) the overall length of the eye, 2) the curvature of the cornea and 3) the curvature of the lens inside the eye. Eye length. If the eye is too long, light is focused before it reaches the retina, causing nearsightedness.
What happens when the eye is too short?
If the eye is too short, light is not focused by the time it reaches the retina. This causes farsightedness or hyperopia. Curvature of the cornea. If the cornea is not perfectly spherical, then the image is refracted or focused irregularly to create a condition called astigmatism.
Why is my vision blurry?
But what does it really mean when we're told that our vision is blurry because we have a refractive error? We see the world around us because of the way our eyes bend (refract) light.
Where does the most refraction occur?
Most refraction in the eye occurs when light rays travel through the curved, clear front surface of the eye ( cornea ). The eye's natural lens also bends light rays. Even the tear film on the surface of the eye and the fluids inside the eye ( aqueous humor and vitreous) have some degree of refractive ability.
How does the eye see?
The process of vision begins when light rays that reflect off objects and travel through the eye's optical system are refracted and focused into a point of sharp focus. For good vision, this focus point must be on the retina.
What is refractive error?
What are refractive errors? Refractive errors are a type of vision problem that makes it hard to see clearly. They happen when the shape of your eye keeps light from focusing correctly on your retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye). Refractive errors are the most common type of vision problem.
What is the best way to correct refractive errors?
Glasses. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest way to correct refractive errors. Your eye doctor will prescribe the right eyeglass lenses to give you the clearest possible vision. Learn more about eyeglasses. Contacts. Contact lenses sit on the surface of your eyes and correct refractive errors.
What are the different types of refractive errors?
There are 4 common types of refractive errors: Nearsightedness (myopia) makes far-away objects look blurry . Farsightedness (hyperopia) makes nearby objects look blurry. Astigmatism can make far-away and nearby objects look blurry or distorted. Presbyopia makes it hard for middle-aged and older adults to see things up close.
How many people have refractive errors?
Refractive errors are the most common type of vision problem. More than 150 million Americans have a refractive error — but many don’t know that they could be seeing better. That’s why eye exams are so important.
Why does my eye look blurry?
The cornea and lens bend (refract) light rays to focus them on the retina. When the shape of the eye changes, it also changes the way the light rays bend and focus — and that can cause blurry vision.
How to tell if you have blurry vision?
Other symptoms include: Double vision. Hazy vision. Seeing a glare or halo around bright lights. Squinting. Headaches. Eye strain (when your eyes feel tired or sore) Trouble focusing when reading or looking at a computer.
What causes eyeball length?
Eyeball length (when the eyeball grows too long or too short) Problems with the shape of the cornea (the clear outer layer of the eye) Aging of the lens (an inner part of the eye that is normally clear and helps the eye focus)
What is refraction in eye care?
A refraction is an eye exam that measures a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
What is the purpose of a refraction test?
The purpose is to determine whether you have a refractive error (a need for glasses or contact lenses). For people over age 40 who have normal distance vision but difficulty with near vision, a refraction test can determine the right power of reading glasses. Normal Results. Expand Section.
How often should I get an eye exam for glaucoma?
After age 40 (or for people with a family history of glaucoma ), eye exams should be scheduled at least once a year to test for glaucoma. Anyone with diabetes should also have an eye exam at least once a year. People with a refractive error should have an eye exam every 1 to 2 years, or when their vision changes.
Do glasses give you good vision?
Glasses or contact lenses should give you good vision. If you have a refractive error, you have a "prescription.". Your prescription is a series of numbers that describe the powers of the lenses needed to make you see clearly.
What is a refractive error?
What Are Refractive Errors? Refractive errors are the most common type of eye disorders. They occur when the shape of the eye does not bend light correctly, which keeps the light rays from focusing properly on your retina. The result is blurred vision.
What are the symptoms of refractive errors?
The most common symptom of refractive errors is blurred vision. Other symptoms include: Double vision. Hazy vision. Halos or glares around lights. Squinting. Headaches or migraines. Eye strain (soreness or fatigue in your eyes) Difficulty focusing (especially when reading or looking at a screen)
What is the term for the condition where the eyeball is shorter than it should be?
Hyperopia (Farsightedness) Farsightedness is very common, with about 25 percent of the population being affected by it. Hyperopia causes close objects to appear blurry, but distant objects to appear clearly. It occurs when the eyeball is shorter than it should be.
What is the name of the eye disorder where the lens is behind the iris?
The other type is lenticular astigmatism, which means that the lens of the eye (located behind your colored iris) is the wrong shape. Astigmatism often occurs with myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness). Symptoms include: Glare and starburst patterns around lights.
Why is myopia blurry?
Myopia (Nearsightedness) Nearsightedness makes distant objects appear blurry. Often your near vision will be fine, but your ability to see far away is poor. It occurs when the eyeball grows too long from front to back. Extra curvature of the cornea or a lens that is too thick can also be a cause.
How do refractive errors get passed on?
Refractive errors get passed on through genetics. Research shows that environmental factors also play a role. Children and adults who read and look at screens more have higher chances of developing refractive errors.
What is the treatment for astigmatism?
Astigmatism can be treated by an optometrist using eyeglasses, contact lenses, or an ophthalmologist performing an eye surgery such as refractive lens exchange, phakic intraocular lens implant, PRK, or LASIK.