endocrine therapy. Listen to pronunciation. (EN-doh-krin THAYR-uh-pee) Treatment that adds, blocks, or removes hormones. For certain conditions (such as diabetes or menopause), hormones are given to adjust low hormone levels. Hormones can also cause certain cancers (such as prostate and breast cancer) to grow.
Full Answer
What are the treatment for endocrine disorders?
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
- Antithyroid Medication for Hyperthyroidism. Mercy physicians may prescribe antithyroid medication to lower thyroid levels. ...
- Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Hyperthyroidism. Depending on various factors, we may recommend radioactive iodine. ...
- Surgery for Hyperthyroidism. ...
What diseases are caused by the endocrine system?
Potential endocrine disorders according to the specific neurologic manifestations
- Headache
- Altered mentality
- Abnormal muscle strength, muscle tone and gait
- Movement disorders
- Developmental delay
What are the symptoms of endocrine disorder?
Symptoms of this condition include:
- Tiredness
- Anxiety
- Palpitations of the heart
- Skin that has become pale
- Sweating
- Irritability
- Sensation the makes a tingling around the mouth
- Pain while sleeping
What is an example of endocrine?
The following are integral parts of the endocrine system:
- Hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is located at the base of the brain, near the optic chiasm where the optic nerves behind each eye cross and meet.
- Pineal body.
- Pituitary.
- Thyroid and parathyroid.
- Thymus.
- Adrenal gland.
- Pancreas.
- Ovary.
What are examples of endocrine therapy?
Types of hormone therapyAromatase inhibitors (AIs), such as anastrozole, exemestane, and letrozole.Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), such as tamoxifen and raloxifene.Estrogen receptor antagonists, such as fulvestrant and toremifene.More items...•
What does endocrine therapy treat?
Treatment that adds, blocks, or removes hormones. For certain conditions (such as diabetes or menopause), hormones are given to adjust low hormone levels. Hormones can also cause certain cancers (such as prostate and breast cancer) to grow.
Is endocrine therapy the same as hormonal therapy?
Hormone therapy (also called hormonal therapy, hormone treatment, or endocrine therapy) slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the body's ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells.
What are the side effects of endocrine therapy?
Side effects of hormone therapy in womenTiredness. You may feel more tired when you are taking hormone therapy. ... Digestive system problems. Hormone therapy can cause a few problems with your digestive system. ... Menopausal symptoms. ... Hair thinning. ... Muscle and bone changes. ... Weight gain. ... Headaches. ... Memory problems.More items...
Which is better chemo or hormone therapy?
Contrary to the commonly held view, 2 years after diagnosis, hormone therapy, a highly effective breast cancer treatment worsens quality of life to a greater extent and for a longer time, especially in menopausal patients. The deleterious effects of chemotherapy are more transient.
What cancers are treated with hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy is used to treat prostate and breast cancers that use hormones to grow. Hormone therapy is most often used along with other cancer treatments.
What cancers are caused by hormones?
Estrogen-dependent cancers, like breast cancer, ovarian cancer and endometrial (uterine) cancer, rely on estrogen to develop and grow. Treatments can stop your body from making estrogen or prevent hormone receptors from binding to estrogen.
What are endocrine drugs?
Endocrine drugs are agents directed to a malfunctioning endocrine path. Several agents are secreted in or target the nervous system, and are thus more prone to cause neurologic adverse events (AEs).
When does a woman need hormone replacement therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy is medication that contains female hormones. You take the medication to replace the estrogen that your body stops making during menopause. Hormone therapy is most often used to treat common menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes and vaginal discomfort.
What is the success rate of hormone therapy?
Hormone replacement therapy users had a 100% survival rate at 6 years as opposed to 87% in nonusers. Both groups of tumors were detected by screening mammography, thus detected "early" by current convention. Yet, we observed a survival benefit for those women who had received HRT.
What happens to your body when you take hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy side effects can include vaginal dryness, discharge, itching, or irritation. It can also cause changes to the menstrual cycle and cause vaginal bleeding that is not related to a period. Hot flashes and night sweats. Hot flashes are very common for people receiving hormone therapy.
Can hormone therapy affect your heart?
The risk of heart disease to an individual taking hormone therapy is very low. If you are in early menopause, have moderate to severe hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms, and are otherwise healthy, the benefits of hormone therapy likely outweigh any potential risks of heart disease.
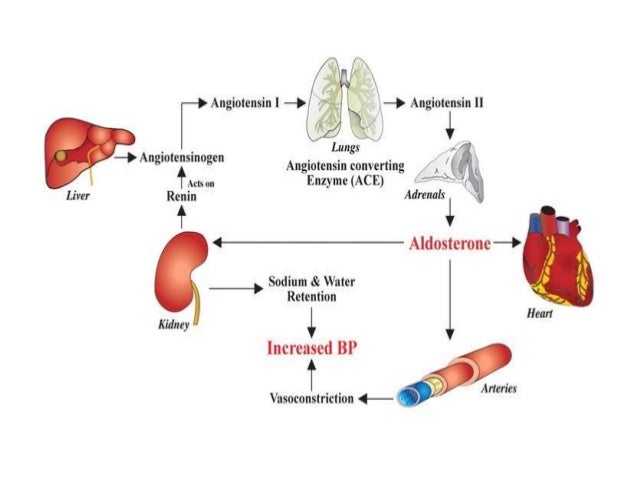
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help control many important body functions, including the body's ability to change calories into energy that powers cells and organs . The endocrine system influences how your heart beats, how your bones and tissues grow, ...
Why is endocrine disease important?
Endocrine disease due to the development of lesions (such as nodules or tumors) in the endocrine system , which may or may not affect hormone levels. The endocrine's feedback system helps control the balance of hormones in the bloodstream.
What is a problem with the endocrine feedback system?
A problem with the endocrine feedback system. Disease. Failure of a gland to stimulate another gland to release hormones (for example, a problem with the hypothalamus can disrupt hormone production in the pituitary gland) A genetic disorder, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) or congenital hypothyroidism.
Why does hormone imbalance occur?
A hormone imbalance may occur if this feedback system has trouble keeping the right level of hormones in the bloodstream, or if your body doesn't clear them out of the bloodstream properly. Increased or decreased levels of endocrine hormone may be caused by: A problem with the endocrine feedback system. Disease.
What are the different types of endocrine disorders?
Endocrine disorders are typically grouped into two categories: 1 Endocrine disease that results when a gland produces too much or too little of an endocrine hormone, called a hormone imbalance. 2 Endocrine disease due to the development of lesions (such as nodules or tumors) in the endocrine system, which may or may not affect hormone levels.
How do you know if you have an endocrine disorder?
However, most people with endocrine disease complain of fatigue and weakness. Blood and urine tests to check your hormone levels can help your doctors determine if you have an endocrine disorder.
How does the endocrine system affect the development of a baby?
The endocrine system influences how your heart beats, how your bones and tissues grow, even your ability to make a baby. It plays a vital role in whether or not you develop diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction, and a host of other hormone-related disorders.
Why do endocrine tumors need surgery?
Because hormones play such a key role in keeping the body balanced, both benign and cancerous endocrine tumors have the potential to cause serious problems . For this reason, they may require some form of treatment such as surgery or radiation therapy. Almost all endocrine tumors require at least some evaluation and monitoring, she says.
How is endocrine cancer diagnosed?
Doctors can perform a number of tests to check for a suspected endocrine tumor:
What are the types of endocrine cancer?
Tumors can occur in any of the major endocrine glands, including the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary and adrenal glands, and the pancreas. The most common sites are as follows:
What are the most common endocrine tumors?
Tumors can occur in any of the major endocrine glands, including the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary and adrenal glands, and the pancreas. The most common sites are as follows: 1 Thyroid gland: Most endocrine cancers develop in the thyroid gland (a butterfly-shaped organ in the lower neck). Thyroid cancer is far more common in women than men. Statistics show that the annual rate of thyroid cancer is on the rise, both in the United States and worldwide. The good news is, most tumors (referred to as nodules) of the thyroid are not cancerous. 2 Pituitary gland: A pea-sized organ attached to the brain, the pituitary gland produces hormones that influence growth and fertility. Pituitary tumors are almost always benign but can result in too much or too little of one or more hormones, which in turn can upset the balance of other glands. 3 Adrenal gland: The two adrenal glands, which reside just above the kidneys, produce hormones that regulate metabolism (cortisol), the stress response (adrenaline), blood pressure (aldosterone) and certain sexual characteristics (androgens). 4 Pancreas: Though the pancreas plays an active role in the digestive system, it’s also the source of important hormones, including insulin. Rare tumors can produce too much insulin or other related hormones, which can impact blood sugar levels.
Which organ is most likely to develop endocrine cancer?
Thyroid gland: Most endocrine cancers develop in the thyroid gland (a butterfly-shaped organ in the lower neck). Thyroid cancer is far more common in women than men. Statistics show that the annual rate of thyroid cancer is on the rise, both in the United States and worldwide.
What tests are used to check for abnormal hormone levels in the blood?
Lab tests to check for abnormal hormone levels in the blood or urine. Imaging studies (CT scan, MRI or ultrasound) to look for evidence of abnormal tissue in the gland. A biopsy to obtain a sample of abnormal tissue and analyze it for cancer cells.
Which glands regulate metabolism?
Adrenal gland: The two adrenal glands, which reside just above the kidneys, produce hormones that regulate metabolism (cortisol), the stress response (adrenaline), blood pressure (aldosterone) and certain sexual characteristics (androgens).
What is the function of the endocrine system?
The human endocrine system consists of a number of glands, which release hormones to control many different functions. When the hormones leave the glands, they enter the bloodstream and are transported to organs and tissues in every part of the body.
Why do endocrinologists ask about symptoms that do not seem to be related, or that seem unnecessary?
This is because hormone levels affect so many different systems in the body that just small changes in one gland can impact parts of the body far from the site of the glands themselves.
Why is the master gland called the main endocrine gland?
It is sometimes called the main endocrine master gland because it secretes hormones that regulate the functions of other glands, as well as growth and several other bodily functions.
What is the field of hormone related diseases?
Endocrinology is the field of hormone-related diseases. An endocrinologist can diagnose and treat hormone problems and the complications that arise from them. Hormones regulate metabolism, respiration, growth, reproduction, sensory perception, and movement. Hormone imbalances are the underlying reason for a wide range of medical conditions.
What hormones are secreted by the adrenal glands?
The adrenal glands secrete: corticosteroids, the steroids involved in stress responses, the immune system, inflammation, and more. catecholamines, such as norepinephrine and epinephrine, in response to stress. aldosterone, which affects kidney function. androgens, or male sex hormones, including testosterone.
What doctor can diagnose hormones?
If your physician suspects that the underlying cause of a medical condition is related to hormone production, they may refer you to an endocrinologist, a doctor who specializes in endocrinology. These doctors are trained to diagnose and manage diseases that affect the glands and the hormones.
Which hormones affect kidney function?
aldosterone, which affects kidney function. androgens, or male sex hormones, including testosterone. Both men and women have some androgen, but men have higher levels. Androgens control the development of characteristics associated with males, like facial hair and a deeper voice.
What are the conditions that endocrinologists treat?
Some of the most common conditions that endocrinologists treat include: Diabetes (types 1 and 2) Hypoglycemia. Adrenal disorders, including Conn’s syndrome (primary hyperaldosteronism) and Cushing syndrome. Cholesterol disorders.
What does an endocrinologist do?
These specialists diagnose, evaluate and treat diseases that affect hormones and the glands that create them.
Do endocrinologists work with primary care?
Many of these disorders require highly specialized and lifelong care. Endocrinologists often work hand-in-hand with primary care physicians and other specialists as necessary to help patients effectively manage their conditions and achieve the best quality of life.
Do I Need to See an Endocrinologist?
Endocrine disorders can produce a wide array of symptoms depending on the glands they impact. Symptoms can range from subtle to debilitating and can affect virtually every system in the body. The following are just a few symptoms are that are associated with endocrine disorders:
How does hormone therapy work?
Hormone therapy (also called hormonal therapy, hormone treatment, or endocrine therapy) slows or stops the growth of hormone-sensitive tumors by blocking the body’s ability to produce hormones or by interfering with effects of hormones on breast cancer cells. Tumors that are hormone insensitive do not have hormone receptors ...
What type of cancer is adjuvant hormone therapy?
Decisions about the type and duration of adjuvant hormone therapy are complicated and must be made on an individual basis in consultation with an oncologist. Treatment of advanced or metastatic breast cancer: Several types of hormone therapy are approved to treat metastatic or recurrent hormone-sensitive breast cancer.
How long does tamoxifen last?
A common switching strategy used for adjuvant therapy, in which patients take tamoxifen for 2 or 3 years, followed by an aromatase inhibitor for 2 or 3 years, may yield the best balance of benefits and harms of these two types of hormone therapy ( 30 ).
What is a breast tumor that has estrogen and/or progesterone receptors called?
Breast tumors that contain estrogen and/or progesterone receptors are sometimes called hormone receptor positive (HR positive). Most ER-positive breast cancers are also PR positive. Breast cancers that lack ERs are called ER negative, and if they lack both ER and PR they may be called HR negative. Approximately 67%–80% of breast cancers in women ...
What is the best treatment for ER positive breast cancer?
Hormone therapy is also a treatment option for ER-positive breast cancer that has come back in the breast, chest wall, or nearby lymph nodes after treatment (also called a locoregional recurrence). Two SERMs, tamoxifen and toremifene, are approved to treat metastatic breast cancer.
How to treat hormone sensitive breast cancer?
Several strategies are used to treat hormone-sensitive breast cancer: Blocking ovarian function: Because the ovaries are the main source of estrogen in premenopausal women, estrogen levels in these women can be reduced by eliminating or suppressing ovarian function. Blocking ovarian function is called ovarian ablation.
Which hormone is released by the hypothalamus during premenopausal women?
The hypothalamus releases LHRH, which then causes the pituitary gland to make and secrete LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
What are the main endocrine gland disorders?
For purely genetic reasons it is possible that the endocrine glands produce too much of a specific hormone or not produce enough. As we will see below, depending on the affected gland, the disorder will have some consequences or others for our health.
What is it called when hormones are too low?
Situations in which the levels of hormones are too low or too high are disorders that are called endocrine diseases, as they are caused by the aforementioned endocrine glands not working as they should.
What is it called when the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone in the adult phase?
Acromegaly is an endocrine disease that occurs when the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone in the adult phase. Unlike the gigantism that we will see next, this appears in people of middle age.
Why do hormones not work?
However, these hormonal problems do not only arise because the endocrine glands are not working properly. They can also be due to the fact that the body does not recognize hormones properly and they cannot perform their function.
What is the hormone that allows glucose to enter the body?
Diabetes is an endocrine disease characterized by a lack of insulin in the blood, a hormone produced by the pancreas that is responsible for allowing glucose (from food) to enter cells and provide them with energy.
Where are hormones produced?
Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced in the endocrine glands and that travel through the blood to reach each of the organs and tissues where they perform their function.
Which organ system produces hormones?
Broadly speaking, the endocrine system is the set of organs responsible for producing hormones. These organs are the endocrine glands, which are located in different parts of our body: head, neck and trunk.
