What are the benefits of electric shock therapy?
Electric shock treatment 'improves academic performance' Stimulating the brain with tiny electric shocks can boost people’s learning and memory ability, research has found.
What should I do if I get an electric shock?
- Do not touch the person, as they may be in contact with the electrical source.
- Call 911 or have someone else call 911.
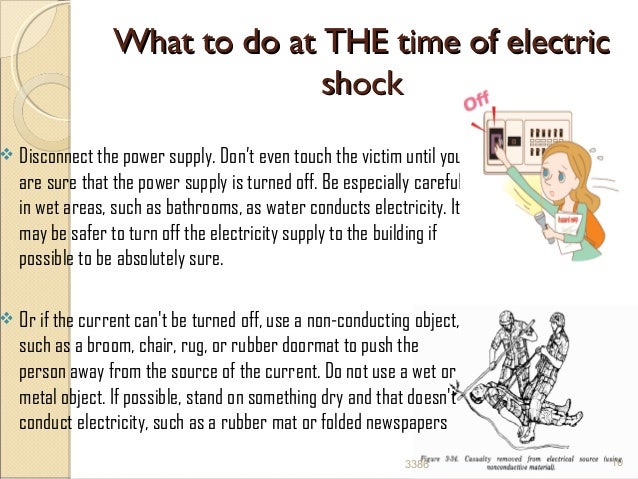
- If it is safe to do so, turn off the source of electricity. ...
- After removing the electrical source, check the person for a pulse, and determine whether they are breathing. ...
What are the after effects of electric shock therapy?
What are the three stages of shock?
- Restlessness, agitation and anxiety – the earliest signs of hypoxia.
- Pallor and clammy skin – this occurs because of microcirculation.
- Nausea and vomiting – decrease in blood flow to the GI system.
- Thirst.
- Delayed capillary refill.
What to do in the event of an electric shock?
What to do in the event of an electric shock
- Cut off the source of electricity. Electrocution is caused by the intense electric shock the victim receives. ...
- Call emergencies. After cutting off the power or clearing the victim, it is important to contact the emergency room. ...
- Attempt to resuscitate the victim. ...
- Make the first dressings. ...
How long does electric shock therapy last?
A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes).
What are the side effects of electro shock therapy?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours. These risks must be balanced with the consequences of ineffectively treated severe psychiatric disorders.
Do they still do electric shock therapy?
But electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is still being used -- more in Europe than the United States -- and it may be the most effective short-term treatment for some patients with depressive symptoms, a newly published review in the journal The Lancet suggests.
Does electric shock treatment hurt?
In a 1986 survey of 166 patients who had received ECT, psychiatrists C.P.L. Freeman and R. E. Kendell of the University of Edinburgh found that 68 percent reported that the experience was no more upsetting than a visit to the dentist. For the others, ECT was more unpleasant than dentistry, but it was not painful.
Does ECT damage the brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
Can ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
Is ECT worth the risk?
Risk Assessment of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Clinical Routine: A 3-Year Analysis of Life-Threatening Events in More Than 3,000 Treatment Sessions. Background: Extensive research has reported that electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be highly effective in approximately 80% of patients suffering from depression.
Who is a good candidate for ECT?
People who have had ECT before and responded well are good candidates for ECT. Other first-line indications for the procedure include people who are catatonic or suffering from a form of depression known as psychotic depression (depression associated with delusions and hallucinations).
Why did doctors use electric shock treatment?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat.
Does ECT lower IQ?
However, former patients have publicly testified that ECT can result in a very significant (>30 point) permanent decrement in IQ score (Food and Drug Administration, 1982; Andre, 2001; Cott, 2005: p.
How much memory do you lose with ECT?
Safety: among 7 studies that reported on memory loss, the rate of persistent or permanent memory loss after ECT ranged from 29% to 55%.
Does ECT erase memories?
One of the known side-effects of ECT is memory loss. According to the Royal College of Psychiatrists, that memory loss is normally temporary, but some patients report severe and long-lasting memory losses after ECT. This study took advantage of this side-effect to see if it was possible to target specific memories.
How to help someone with electric shock?
Electric shocks can be very serious, so it’s important to seek help as soon as possible. If the shock seems severe, call 911 or your local emergency number . Even if the shock seems minor, it’s best to follow up with a doctor to make sure there aren’t any less visible injuries.
What can cause an electric shock?
A range of things can cause an electric shock, including: power lines. lightning. electric machinery. electric weapons, such as Tasers. household appliances.
How do you know if you have electric shock?
Potential symptoms of an electric shock include: loss of consciousness. muscle spasms. numbness or tingling. breathing problems. headache. problems with vision or hearing. burns.
What is the treatment for a burn?
burn treatment, including the application of antibiotic ointment and sterile dressings. pain medication. intravenous fluids. a tetanus shot, depending on the source of the shock and how it occurred.
What to do if someone is shocked?
If someone else receives a shock, keep several things in mind to both help them and keep yourself safe: Don’t touch someone who has been shocked if they’re still in contact with the source of electricity. Don’t move someone who has been shocked, unless they’re in danger of further shock.
How to stop someone from being shocked?
Don’t move someone who has been shocked, unless they’re in danger of further shock. Turn off the flow of electricity if possible. If you can’t, move the source of electricity away from the person using a non-conducting object. Wood and rubber are both good options.
Can electric shocks cause compartment syndrome?
Electric shocks can also cause compartment syndrome. This happens when muscle damage causes your limbs to swell. In turn, this can compress arteries, leading to serious health problems. Compartment syndrome might not be noticeable immediately after the shock, so keep an eye on your arms and legs following a shock.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
How long after ECT can you drive?
However, some people may be advised not to return to work, make important decisions, or drive until one to two weeks after the last ECT in a series, or for at least 24 hours after a single treatment during maintenance therapy.
What is the test called when you have a seizure?
Internally, activity in your brain increases dramatically. A test called an electroencephalogram (EEG) records the electrical activity in your brain. Sudden, increased activity on the EEG signals the beginning of a seizure, followed by a leveling off that shows the seizure is over.
Is it safe to take ECT?
Risks. Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: Confusion. Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer.
What is shock therapy?
"Shock therapy" was so-called, as an electric shock is used to induce a controlled seizure intended as a treatment , primarily for mood disorders, although other conditions may be treated as well. Shock therapy is now known as electroconvulsive therapy or ECT.
Where is shock therapy performed?
Shock therapy is performed in a hospital, sometimes in an area specifically set aside for this treatment. An intravenous (IV) is inserted to provide anesthetic medication. Vital signs are taken initially and continuously throughout the shock therapy treatment.
How does shock therapy feel?
How Shock Therapy Feels. When you awake from the anesthesia, you may be confused and tired. You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration ...
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat seizures?
A paralyzing agent called succinylcholine is then administered to prevent the seizure from spreading to your body. The electrodes are then applied to your head with conducting jelly and a brief shock (less than 2 seconds) is administered.
How to know if you are recovering from shock?
Your vital signs will be monitored closely after the shock treatment to ensure proper recovery. You may feel head, muscle or back pain. Such discomfort tends to be relieved by mild medications. If any post-treatment effect is concerning you, you should talk to the treating physician immediately.
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
Electroconvulsive therapy has also shown effectiveness in treating other disorders such as neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a rare, severe, adverse reaction to antipsychotic medication). Shock treatment for depression and other disorders is indicated when the patient needs rapid improvement because the patient is:
Does mania respond to shock?
Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture is not as bright for schizophrenia, which is more difficult to treat and is characterized by frequent relapses. A small number of patients are placed on maintenance shock therapy.
Causes
An electric shock occurs when someone has direct contact with a high-voltage current that travels through the body.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of electrical shock can vary based on the type and amount of voltage. Some may include: 1
Treatment
When electrical shock occurs outside, the treatment may also involve several steps to ensure the area is safe before helping the victim, such as: 2
Summary
Electrical shock occurs when a high voltage current travels through the body. This usually happens when someone accidentally comes into contact with an electrical source. The aftercare may require anything from minor first aid care to treatment for internal and external burns.
A Word From Verywell
Electrical shock is almost always accidental, as well as preventable. The resulting injuries can range from minor to severe and, in some cases, fatal. Therefore, it's essential to be aware of electrical dangers in and around your home to keep you and any small children safe.
When is ECT administered?
Promotional materials are careful in describing the procedure and present a picture that’s quite benign: “ECT treatment is generally administered in the morning, before breakfast,” reads one brochure. “Prior to the actual treatment, the patient is given general anesthesia and a muscle relaxant.
Why did terror stalk the halls of euthanasia hospitals?
According to history professor Henry Friedlander, “Terror stalked the halls of the euthanasia hospitals not only because patients feared being selected for killing at any time or because some of the staff beat and maltreated them, but also because some medical procedures imposed unusual pain.”.
Why do we use higher voltages in the brain?
Much higher voltages are employed in the modern procedure because muscle relaxants and anesthetics raise the seizure threshold, with more electricity required to produce a seizure. The greater heat and electricity themselves cause more brain cell death, he says.
Does electric current cause seizures?
While the modern procedure is generally carried out without busted teeth and the more grisly features of its early practice, the principle is still the same: Electric current blazes through the brain to provoke a seizure—the logic being that seizures occurring in the brain have some therapeutic benefit, somehow.
Does electricity shock the brain?
And Baughman says using electricity to shock the brain into a seizure—no matter how you do it—results in real and lasting harm. “You are creating a seizure which is prima facie evidence of brain damage,” he observes.
How does an electric shock occur?
A person may get an electric shock from faulty household wiring. An electric shock occurs when an electrical current passes from a live outlet to a part of the body. Electric shock can result from contact with: Flash: A flash injury typically causes superficial burns.
How long after an electric shock do you have heart problems?
One study found that people who had received an electric shock were no more likely to experience heart problems 5 years after the incident, compared to those who had not. A person may experience a variety of symptoms, including psychological, neurologic, and physical symptoms. Symptoms may include.
What is it called when an electrical current touches or flows through the body?
When an electrical current touches or flows through the body, it is known as an electric shock. It can happen wherever there is live electricity. The effects of electric shock range from none at all to severe injury and death. of burn unit admissions in the United States are due to electrical injuries.
What are the factors that affect electric shock?
Several factors can affect how serious injury from electric shock is, including: the intensity of the current. the type of current— alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) which part of the body the current reaches. how long a person has exposure to the current. resistance to the current.
What is a flash injury?
Flash: A flash injury typically causes superficial burns. They occur as a result of an arc flash, which is a type of electrical explosion. The current does not penetrate the skin. Flame: These injuries occur when an arc flash causes a person’s clothes to ignite. The current may or may not pass the skin.
Can shocks from electrical outlets cause serious injury?
True: The person becomes a part of the circuit, and the electricity enters and exits the body. Shocks from touching electrical outlets or from small appliances in the home rarely cause serious injury. However, prolonged contact may cause harm.
Do you need to see a doctor for electric shocks?
Minor electric shocks, such as those from small household appliances, do not typically need medical treatment. However, a person should see a doctor if they have experienced electrocution. If someone has received a high voltage shock, call 911 right away.
Shock Therapy: Process, Preparation, Outcomes and more
Krystina is a Technical Writer with a background in healthcare. She has spent the last 10 years working for an internationally recognized medical facility where she found her passion for making complicated topics easier to understand.
The Electroconvulsive Therapy Process
An ECT treatment regimen will typically include sessions two to three days a week for a total of six to 12 treatments. The schedule works out to about one month of treatment, although the course may continue for longer.
How to Prepare for Your Treatment
ECT sessions generally do not require much preparation, though you will need to go over the specifics with your doctor. Your doctor may give you orders to follow based on other health conditions you have or medications you take.
Potential Outcomes of Shock Therapy
Most people who undergo ECT will see a noticeable change in their symptoms. Some people will notice an immediate improvement after one session. However, it is more common to not see or feel a significant difference in symptoms for several sessions.
Summary
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be used to treat major depressive disorde r, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric conditions. It is often considered when other treatments have not helped.
A Word From Verywell
If you are wondering if shock therapy might be a treatment option for you, discuss it with your psychiatrist. While ECT can provide lasting relief from the symptoms of MDD, bipolar disorder, and similar conditions, it's not the right choice for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Even though ECT has been around for nearly 90 years, scientists still are not quite sure why or how it benefits some people with depression.
Is electroconvulsive therapy still used?
But electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is still being used -- more in Europe than the United States -- and it may be the most effective short-term treatment for some patients with depressive symptoms, a newly published review in the journal The Lancet suggests.
Is ECT a good treatment for depression?
Researchers concluded that ECT remains an important treatment option for the management of severe depression. "Despite its image, ECT is a sophisticated and complex treatment that can be especially useful in patients who are not helped by drug therapy," researcher John Geddes, MD, of the University of Oxford in England, tells WebMD.
Is ECT more effective than drug therapy?
Findings from 18 studies involving 1,144 patients suggested that ECT was significantly more effective for the short-term treatment of depression than drug therapy.
What is ECT therapy?
Bipolar Disorder and Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Electroconvulsive therapy, also known as ECT or electroshock therapy, is a short-term treatment for severe manic or depressive episodes, particularly when symptoms involve serious suicidal or psychotic symptoms, or when medicines seem to be ineffective. It can be effective in nearly 75% of ...
When to use ECT?
ECT is generally used only when medicines or other less invasive treatments prove to be unhelpful. It is also used when mood or psychotic symptoms are so severe that it may be unsafe to wait until drugs can take effect. ECT is also often thought to be the treatment of choice for severe mood episodes during pregnancy.
What is an ECT in a maniac?
In electroconvulsive therapy, an electric current is passed through the scalp to cause a brief seizure in the brain. ECT is one of the fastest ways to relieve symptoms in people who suffer from mania or severe depression. ECT is generally used only when medicines or other less invasive treatments prove to be unhelpful.
How often is ECT given?
ECT is usually given up to three times a week, typically for two to four weeks. After that, maintenance treatment can continue weekly or monthly, depending on the person's needs. ECT is among the safest treatments for severe mood disorders, with most risks being related to the anesthesia.
How long does ECT last?
Other possible side effects of ECT include: These side effects may last from several hours to several days. About a third of people who have ECT report some memory loss, but this is usually limited to the time surrounding the treatment.

Overview
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsucce...
Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications o…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…
Terminology
Mechanism
- The brain is still not well understood, nor is the reason for the treatment effects ECT (shock) therapy has on some individuals. It is known that ECT affects hormones, neuropeptides, neurotrophic factors, and neurotransmitters in the brain. All of this may come together to explain how ECT works in treatment.
Preparation
- A full physical is generally needed before shock therapy. Because general anesthesia will be administered, one should not eat or drink 8-12 hours before the shock treatment. This helps to prevent any vomiting during the procedure. Other exams like an electrocardiogram (ECG) may also be given before ECT to ensure the procedure is safe and appropriate.
Treatment
- Shock therapy is performed in a hospital, sometimes in an area specifically set aside for this treatment. An intravenous (IV) is inserted to provide anesthetic medication. Vital signs are taken initially and continuously throughout the shock therapy treatment. An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia and after you are asleep, places a tube in your throat to help you breathe…
Results
- When you awake from the anesthesia, you may be confused and tired. You will likely experience short-term memory loss around the time of the procedure. With multiple treatments, this may increase. Adverse cognitive effects tend to be the most concerning factors around ECT and tend to affect the frequency and duration of treatments and whether ECT is offered at all. Your vital si…
Uses
- It is most common to see shock therapy used in severe cases of depression. Shock therapy is also performed to improve the condition of the following disorders:1
Risks
- The complications associated with ECT / shock therapy are often related to electrode placement with bilateral placement (an electrode by each temple) typically showing greater unwanted cognitive effects than unilateral placement (one electrode at the temple and the other on the forehead). Risks of shock therapy include slow heart beat (bradycardia) and rapid heartbeat (tac…
Prognosis
- Shock treatment for depression often produces a dramatic improvement in symptoms, especially in elderly individuals, sometimes during the first week of treatment. While it is estimated many of these patients will experience a future return of depression symptoms, the prognosis for each episode of depression is good. Mania also often responds well to shock treatment. The picture i…
Causes
- An electric shock occurs when someone has direct contact with a high-voltage current that travels through the body. Several things can cause an electric shock, including: 1. Being struck by lightening 2. Contact with downed power lines 3. Putting fingers or objects into an electrical socket 4. Touching faulty or frayed electrical cords or appliances 5. Touching overloaded electri…
Signs and Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of electrical shock can vary based on the type and amount of voltage. Some may include:1 1. Numbness and tingling 2. Burns 3. Seizures 4. Irregular heartbeat 5. Breathing irregularities or difficulty 6. Vision or hearing issues 7. Muscle spasms 8. Headaches 9. Loss of consciousness 10. Cardiac arrest Symptoms caused by touching a frayed kitchen appliance cor…
Treatment
- When electrical shock occurs outside, the treatment may also involve several steps to ensure the area is safe before helping the victim, such as:2 1. Examine the person visually but do not touch them. They can pass the electrical current on to you if still connected to the electrical source. 2. Call 911 or have someone else call 911 3. Check for a ...
Prevention
- Best practices to prevent electrical shock in the home include:3 1. Cover all outlets. 2. Ensure that wires are properly insulated and covered. 3. Keep wires away from children's reach. 4. Supervise children in areas with possible electrical hazards, such as electrical appliances near a bathtub or pool. 5. Turn off the circuit breaker when working with electricity in the home. 6. Don't use electri…
Summary
- Electrical shock occurs when a high voltage current travels through the body. This usually happens when someone accidentally comes into contact with an electrical source. The aftercare may require anything from minor first aid care to treatment for internal and external burns. It's essential to be aware of potential electrical hazards to best prevent them from occurring. If you …
A Word from Verywell
- Electrical shock is almost always accidental, as well as preventable. The resulting injuries can range from minor to severe and, in some cases, fatal. Therefore, it's essential to be aware of electrical dangers in and around your home to keep you and any small children safe. If you have any cause for concern, consider having a certified electrician visit your house or call your electri…