Can monoclonal antibodies kill you?
For people at high risk of getting very sick from COVID-19, monoclonal antibody or antiviral therapy, given early, can greatly reduce the chance of getting COVID-19 and prevent the disease from becoming severe. It also reduces the chance of needing to be in the hospital. The treatment can also shorten how long COVID-19 symptoms last. .
When to give monoclonal antibody treatment?
Nov 10, 2021 · Antibodies are proteins that your immune system makes to help fight infection and protect you from getting sick in the future. When you are infected with a virus or bacteria, your immune system makes antibodies specifically to fight it. Your immune system can also safely learn to make antibodies through vaccination.
Are monoclonal antibodies bad for You?
This treatment involves an infusion of monoclonal antibodies (specifically bamlanivimab, or casirivimab and imdevimab) to treat COVID-19. Health care providers can only give the infusions in certain settings. Things to know Medicare also covers COVID-19 diagnostic tests , COVID-19 antibody tests, and COVID-19 vaccines.
Which monoclonal antibody is best?
Jan 06, 2022 · Given that COVID-19 vaccination provides strong protection against severe disease and need for hospitalization, monoclonal antibody therapy is an option for certain high-risk patients with COVID-19. THE FDA expanded EUA of two monoclonal antibody treatments to include patients as young as newborns. Criteria for younger pediatric patients includes a …

How do monoclonal antibodies work against COVID-19?
Monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from attaching to human cells, making it more difficult for the virus to reproduce and cause harm. Monoclonal antibodies may also neutralize a virus.Mar 31, 2022
Who could benefit from monoclonal antibody therapy to prevent COVID-19?
See full answerVaccines are the best way to protect against COVID-19. But some people with weakened immune systems do not produce enough antibodies after vaccination, and others are severely allergic to the vaccine. The FDA recently authorized Evusheld, a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) monoclonal antibody therapy developed by AstraZeneca, which should help prevent COVID-19 in these populations.To be eligible for Evusheld, individuals must be 12 years or older and have a moderately to severely weakened immune system, or have a history of severe adverse reactions to the COVID-19 vaccine or its components. In addition, the therapy cannot be given to someone with a current SARS-CoV-2 infection, or who has been recently exposed to someone who is infected. Evusheld is given as two consecutive shots, and evidence suggests it can help prevent symptomatic infection for at least six months.Apr 1, 2022
Are antibodies beneficial during the COVID-19 pandemic?
When reinfections or breakthrough infections happen, having antibodies plays an important role in helping prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. For many diseases, including COVID-19, antibodies are expected to decrease or “wane” over time.Nov 10, 2021
Can I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I was treated with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma?
If you were treated for COVID-19 symptoms with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, you should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
Is there a monoclonal antibody therapy for post COVID-19 exposure?
FDA authorizes bamlanivimab and etesevimab monoclonal antibody therapy for post-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) for COVID-19 | FDA.Sep 16, 2021
Who might benefit from dexamethasone if they have COVID-19?
Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid used in a wide range of conditions for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant effects.It was tested in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the United Kingdom’s national clinical trial RECOVERY and was found to have benefits for critically ill patients.Oct 16, 2020
Do I need the COVID-19 vaccine if I still have antibodies?
Yes, the COVID-19 vaccines are recommended, even if you had COVID-19.Nov 23, 2021
How long do COVID-19 antibodies last?
At this time, it is unknown for how long antibodies persist following infection and if the presence of antibodies confers protective immunity.Jan 31, 2022
Can you get COVID-19 if you already had it and have antibodies?
It is important to remember that some people with antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 may become infected after vaccination (vaccine breakthrough infection) or after recovering from a past infection (reinfected).Nov 10, 2021
Can you get the Covid vaccine if you were treated with convalescent plasma?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, you should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine. Talk to your doctor if you are unsure what treatments you received or if you have more questions about getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
What medication is not recommended before vaccinations for COVID-19?
It is not recommended you take over-the-counter medicine – such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen – before vaccination for the purpose of trying to prevent vaccine-related side effects. It is not known how these medications might affect how well the vaccine works.
Who should not take the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine?
If you have had a severe allergic reaction to any ingredient in the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (such as polyethylene glycol), you should not get this vaccine. If you had a severe allergic reaction after getting a dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, you should not get another dose of an mRNA vaccine.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies to fight COVID-19 are artificially manufactured antibodies designed to mimic your body’s natural antibodies.
Who is eligible for monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibody treatments are only available to certain patients.
How monoclonal antibodies are administered
Monoclonal antibodies are only given intravenously (through an IV) or as a subcutaneous injection (as a shot). That means that in order to receive them, you need to be seen in a medical setting — which limits the overall availability of the treatment.
How monoclonal antibodies compare to vaccination
If you’re not yet fully vaccinated when you receive monoclonal antibodies, you’ll have to wait 90 days to get the vaccine. Otherwise, the antibodies may impact the vaccine’s effectiveness.
Why are monoclonal antibodies used in immunotherapy?
Some monoclonal antibodies are also immunotherapy because they help turn the immune system against cancer. For example, some monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells so that the immune system will better recognize and destroy them.
What is monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune system recognize germs that cause disease, such as bacteria and viruses, and mark them for destruction.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause side effects?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend on many factors, such as how healthy you are before treatment, your type of cancer, how advanced it is, the type of monoclonal antibody you are receiving, and the dose.
What antibodies kill cancer cells?
Other monoclonal antibodies bring T cells close to cancer cells, helping the immune cells kill the cancer cells. An example is blinatumomab (Blincyto®), which binds to both CD19, a protein found on the surface of leukemia cells, and CD3, a protein on the surface of T cells. This process helps the T cells get close enough to ...
Why do we make antibodies?
The body wants to fight antigens off, so it recognizes these substances and starts making antibodies. Antibodies are able to latch onto the antigens using a unique binding site, which then disables the invaders. Put simply, the body makes antibodies to fend off germs and other harmful substances.
What is the difference between antibodies and antigens?
Antibodies vs. antigens. Antibodies are special protein molecules that the immune system produces in response to antigens. And antigens are substances that can stimulate the body’s production of antibodies. Now, there are different types of antigens, but, for our purposes here, let’s zoom in on foreign, disease-causing antigens.
What are the different types of immunoglobulins?
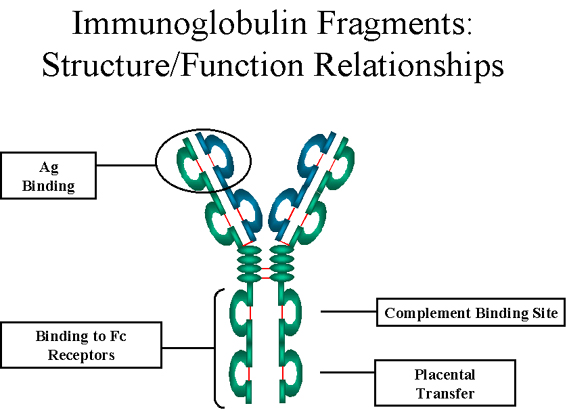
There are five classes of immunoglobulins, which can be described by where they are found and what their function is: 1 IgA ( immunoglobulin A ): found in breathing and digestive passages as well as in saliva, tears, and blood, among other places; helps protect surfaces that are exposed to foreign substances from outside the body 2 IgD ( immunoglobulin D ): found in cells in tissues in the chest and belly; function as receptors; least understood of the immunoglobulins 3 IgE ( immunoglobulin E ): found in lung, skin, and mucous membranes; help expel parasites in the intestines and are involved in allergic reactions 4 IgG ( immunoglobulin G ): found in all body fluids; critical to fighting infections from viruses and bacteria; only antibodies that can pass over the placenta from mother to fetus; most common but smallest antibody 5 IgM ( immunoglobulin M ): found in blood and lymph fluid; first antibody to respond to an infection; largest antibody
What is serological test?
It also includes serological tests to determine if a person has antibodies that can signal immunity to COVID-19. But what does serological mean, and what are antibodies, for that matter? As the coronavirus pandemic evolves, we know that vocabulary and concepts evolve with it.
Where are antibodies made?
Antibodies are produced by B cells, also called B lymphocytes, which are made in bone marrow and found in the blood and lymph. Antibodies have a distinctive Y shape, which is key to how they work. At the tips of antibodies are the unique sites where they bind with a matching site on antigens—and destroy them.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is an incredibly complex network of cells that identify and defend against foreign substances in your body. It includes the thymus, spleen, lymph nodes and lymph tissue, stem cells, white blood cells, antibodies, and lymphokines. One major type of foreign substances the immune system fends off are pathogens: infectious agents, ...
Where is IgM found?
IgM ( immunoglobulin M ): found in blood and lymph fluid; first antibody to respond to an infection; largest antibody. IgG and IgM are two of the key players in your body when it comes to warding off infectious diseases.