
Explore
Treatment for vaginal cancer typically includes surgery and radiation. Types of surgery that may be used to treat vaginal cancer include: Removal of small tumors or lesions. Cancer limited to the surface of your vagina may be cut away, along with a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all of the cancer cells have been removed.
What are the treatment options for vaginal cancer?
Key Points 1 Vaginal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the vagina. 2 Age and being exposed to the drug DES (diethylstilbestrol) before birth affect a woman’s risk of vaginal cancer. 3 Signs and symptoms of vaginal cancer include pain or abnormal vaginal bleeding. More items...
What do you need to know about vaginal cancer?
This extensive surgery may be an option if cancer has spread throughout your pelvic area or if your vaginal cancer has recurred. During pelvic exenteration, the surgeon may remove many of the organs in your pelvic area, including your bladder, ovaries, uterus, vagina, rectum and the lower portion of your colon.
What happens during pelvic exenteration surgery for vaginal cancer?
Removal of small tumors or lesions. Cancer limited to the surface of your vagina may be cut away, along with a small margin of surrounding healthy tissue to ensure that all of the cancer cells have been removed. Removal of the vagina (vaginectomy).
What can be removed from a vagina?

Does vaginal cancer have cure?
Since the cancer has spread to distant sites, it can't be cured. Radiation therapy to the vagina and pelvis might be used to ease symptoms and reduce bleeding. Chemo might also be given with the radiation. Chemo alone has not been shown to help women live longer.
What happens after cervical cancer treatment?
Most women feel fine after having treatment for abnormal cervical cells but some may feel unwell and need to go home and rest. You can go home the same day you have treatment, unless you've had a hysterectomy or a cone biopsy. But you shouldn't plan to do anything else that day.
What do you do after cancer treatment?
What Is Follow-up Care? Once you have finished your cancer treatment, you should receive a follow- up cancer care plan. Follow-up care means seeing a doctor for regular medical checkups. Your follow-up care plan depends on the type of cancer and type of treatment you had, along with your overall health.
What is the next step after being diagnosed with cervical cancer?
If you've been diagnosed with cervical cancer, your doctor will talk to you about cervical cancer treatment options. Depending on the cervical cancer stage and your plans for pregnancy, your treatment plan might include: Surgery to remove a part of your cervix, all of your cervix, or all of your reproductive organs.
How do you prevent cervical cancer from coming back?
Here, Dewdney offers five tips for reducing your risk of cervical cancer:Get routine Pap tests. Pap tests enable doctors to detect abnormalities — changes on the cells on your cervix — and take action before cervical cancer develops. ... Follow up on abnormal Pap smears. ... Get vaccinated. ... Practice safe sex. ... Quit smoking.
Can you live a normal life after cervical cancer?
This is very common if you've had cancer. For other women, the cancer may never go away completely. These women may get regular treatments with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other therapies to try to control the cancer for as long as possible.
How long after cancer treatment are you considered cancer free?
In a complete remission, all signs and symptoms of cancer have disappeared. If you remain in complete remission for 5 years or more, some doctors may say that you are cured.
How do you tell if your cancer is gone?
How Do You Know You're in Remission? Tests look for cancer cells in your blood. Scans like X-rays and MRIs show if your tumor is smaller or if it's gone after surgery and isn't growing back. To qualify as remission, your tumor either doesn't grow back or stays the same size for a month after you finish treatments.
Which cancers are most likely to recur?
Related ArticlesCancer TypeRecurrence RateMelanoma2115% to 41%, depending on stage 87%, metastatic diseaseNSCLC22,2326% after curative surgery 27% after chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced diseaseOsteosarcoma1211%-12% local recurrence 5%-45% metastasisOvarian385%15 more rows•Nov 30, 2018
Can you fully recover from cervical cancer?
If you have advanced cervical cancer, it might be very hard to treat. It may not be possible to cure the cancer. If this is the case, the aim of your treatment will be to limit the cancer and its symptoms, and help you live longer. Finding out the cancer cannot be cured can be very hard news to take in.
What foods should you avoid if you have cervical cancer?
Up to 99.7% of cervical cancer cases result from infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV)....Thus, foods to limit or avoid include:foods high in added sugar.processed meats such as deli meat.red meats.foods high in saturated and trans fats.
What's the chances of cervical cancer returning?
Recurrence was symptomatic in 64.6% of patients. Imaging identified recurrence in 97.9% of patients. The most frequent recurrence sites were locoregional and lymph node metastases.
How to diagnose vaginal cancer?
Tests to diagnose vaginal cancer. Your doctor may conduct a pelvic exam and Pap test to check for abnormalities that may indicate vaginal cancer. Based on those findings, your doctor may conduct other procedures to determine whether you have vaginal cancer, such as: Inspecting the vagina with a magnifying instrument.
What kind of radiation is used for vaginal cancer?
Most women with vaginal cancer receive external beam radiation. Internal radiation. During internal radiation (brachytherapy), radioactive devices — seeds, wires, cylinders or other materials — are placed in your vagina or the surrounding tissue. After a set amount of time, the devices may be removed.
What is pelvic exenteration surgery?
This extensive surgery may be an option if cancer has spread throughout your pelvic area or if your vaginal cancer has recurred.
How to build emotional intimacy with cancer patients?
Spending quality time together and having meaningful conversations are ways to build your emotional intimacy. When you're ready for physical intimacy, take it slowly. If sexual side effects of your cancer treatment are hurting your relationship with your partner, talk to your doctor.
How to make decisions about cancer?
Learn enough about your cancer to make decisions about your care. Write down the questions to ask at your next doctor appointment. Get a friend or family member to come to appointments with you to take notes. Ask your health care team for further sources of information. The more you know about your condition, the more comfortable you may feel when it comes time to make decisions about your treatment.
How to determine the stage of cancer?
In order to determine the stage of your cancer, your doctor may use: Imaging tests. Your doctor may order imaging tests to determine whether cancer has spread.
Does palliative care help with cancer?
When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer.
What happens after treatment?
After surgery, it is important that you not place anything in your vagina until your doctor tells you that it is OK. During the first few weeks after surgery, you may experience side effects such as discomfort or bleeding. If you receive radiation treatment, you will notice less natural lubrication from the vagina and some narrowing of the vagina.
Survivorship Toolkit
The SGO Survivorship Toolkit helps survivors organize their treatment history and future care plans. You can develop a survivorship plan along with your gynecologic oncologist and use this as an opportunity to evaluate and improve your overall health.
What is the treatment for stage 2 vaginal squamous cell cancer?
Stage II. The usual treatment is radiation, using both brachytherapy and external beam radiation. Radical surgery (radical vaginectomy or pelvic exenteration) is an option for some women with stage II vaginal squamous cell cancer if it’s small and in the upper vagina. Radiation might be given after surgery. Surgery is also used to treat women who ...
What is the treatment for a tumor in the lower third of the vagina?
If the tumor is in the lower third of the vagina, external radiation may be used to treat lymph nodes in the groin or pelvis. Chemotherapy (chemo) with radiation may also be used to treat stage II disease. Giving chemo to shrink the cancer before radical surgery may be helpful.
What type of radiation therapy is used for cancer in the vagina?
For cancers lower down in the vagina, external beam radiation therapy may be used, along with either interstitial or intracavitary radiation therapy. The lymph nodes in the groin and/or pelvis are often treated with external beam radiation therapy.
What is radiation used for after vaginal surgery?
After radical partial or complete vaginectomy, radiation (external beam) may be used to treat cancer cells that might have spread to lymph nodes in the groin and/or pelvis.
What is the best treatment for a distant recurrence?
For a distant recurrence, the goal of treatment is to help the woman feel better. Surgery, radiation, or chemo may be used. Again, a clinical trial is a good option.
What to do if cancer comes back after radiation?
Surgery is the usual choice when the cancer comes back after radiation therapy.
What is it called when cancer comes back?
If a cancer comes back after treatment it's called recurrent cancer. If it comes back in the same place it was the first time, it's called a local recurrence. If it comes back in another part of the body, like the liver or lungs, it's called a distant recurrence.
What are the risk factors for vaginal cancer?
Risk factors for vaginal cancer include the following: Being 60 years or older. Having a human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the vagina is linked to HPV infection and has many of the same risk factors as SCC of the cervix. Being exposed to DES while in the mother's womb .
What is the procedure called when the cervix is cut?
If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a large incision (cut) in the abdomen, the operation is called a total abdominal hysterectomy.
What is the disease of the vagina?
Vaginal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the vagina. Older age and having an HPV infection are risk factors for vaginal cancer. Signs and symptoms of vaginal cancer include pain or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
What is the procedure called to collect cells from the surface of the cervix and vagina?
The cells are viewed under a microscope to find out if they are abnormal. This procedure is also called a Pap smear.
Why was DES given to pregnant women?
In the 1950s, the drug DES was given to some pregnant women to prevent miscarriage (premature birth of a fetus that cannot survive). This is linked to a rare form of vaginal cancer called clear cell adenocarcinoma. The rates of this disease were highest in the mid-1970s, and it is extremely rare now.
What are the organs of the female reproductive system?
Enlarge. Anatomy of the female reproductive system. The organs in the female reproductive system include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina. The uterus has a muscular outer layer called the myometrium and an inner lining called the endometrium. Vaginal cancer is not common.
What is the procedure to remove cells from the vagina?
Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues from the vagina and cervix so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. If a Pap test shows abnormal cells in the vagina, a biopsy may be done during a colposcopy.
Tubes
The tubes can be a little frightening but it helps to know what they are for. You might have:
Drains
You might have one or more drains coming out of any wounds. These include a tube connected to a suction bottle. They stop blood and fluid collecting around the operation site. This helps your wound to heal and helps to reduce the risk of infection.
Painkillers
If you have had a big operation, you will almost certainly have pain for the first week or so. There are many different painkillers you can have.
Eating and drinking
You may not be able to eat or drink for a while when you wake up. This depends on the type of operation you have had.
Your wound
Your surgeon might remove just the area containing the cancer cells if you have an early stage vaginal cancer. With this type of surgery, your wound will be inside your vagina.
Getting up
Getting up and walking is likely to be very difficult at first. Moving about helps you to get better, but you need to start gradually. Your nurses will encourage you to get out of bed and sit in a chair as soon as possible, usually a day or two after surgery. They will help you with any drips and drains.
Making progress
After a few days, you are up and about more. Gradually you will start to feel better.
How long after vaginal surgery can you put anything in?
Do not put anything into your vagina after surgery until your doctor says the area is healed (usually 6–8 weeks). This includes using tampons and having sex.
How long does it take for a vaginal bleeding to stop?
Vaginal bleeding. You can expect some light vaginal bleeding, which should stop within two weeks. Use a pad instead of tampons. Infection is a risk – report any fever, redness, pain, swelling, heavy bleeding, wound discharge or unusual smell to your surgeon or nurse.
How to get rid of a gynaecological infection?
Exercise. Check with your gynaecological oncologist or nurse about when you can start doing your regular activities. You may not be able to lift anything heavy, but gentle exercise such as walking can help speed up recovery. Because of the risk of infection, avoid swimming until your doctor says you can.
What does it feel like to lose a part of your genitals?
If you have lost part of your genital area, you may feel a sense of loss and grief. It may help to talk about how you are feeling with someone you trust. For more on this, see Effect on your emotions.
How long does it take for a lymph node to heal?
Your recovery time will depend on your age, the type of surgery you had and your general health. If only a small amount of tissue is removed, the wound will heal quickly and you can go home in a day or two. If your lymph nodes are removed or the surgery is more extensive, recovery will take longer. You may spend up to a week in hospital.
Can you take pain medication after an operation?
You will be given pain medicine as a tablet, through a drip into a vein (intravenously), through a drip into a space around the spinal cord (epidural), or through a button you press to give yourself a measured dose of pain relief (patient-controlled analgesia or PCA). After you go home, you can continue taking pain-relieving tablets as needed.
Can you sit up after vaginal surgery?
Your doctor will tell you how soon you can sit up and walk after surgery. With vaginal surgery, the stitches are all on the inside and will dissolve on their own. You need to avoid straining with bowel movements or lifting heavy objects.
What is the term for the muscle tissue in the lower abdomen?
muscle tissue from your lower abdomen (called a TRAM flap or transverse rectus abdominus muscle flap) a piece of your bowel. This operation is not suitable for all women and some may decide they don't want to have this extra surgery. A vaginal reconstruction adds to the length of the surgery and has possible side effects.
What does it feel like to have a vaginal reconstruction?
If you have a vaginal reconstruction using skin and muscle taken from your thigh, you may feel a strange sensation in your inner thighs when you have sexual intercourse. Some people have described this sensation as feeling as if your inner thighs are being stroked.
What is a dilator for vagina?
Your doctor or specialist nurse will give you a set of dilators if you need them. Dilators are smooth cone shaped objects that you put into your vagina to stretch it. They come in sets of different sizes. Your doctor or nurse will explain how long the dilator should stay in place each time you use it.
Can you contract the muscles around the vagina?
Over time, most people get used to it and it can even become sexually stimulating. Women have also said that they do not feel that they can contract the muscles around the entrance to the vagina as easily as before their surgery. You and your partner may need to experiment a bit and try different sexual positions.
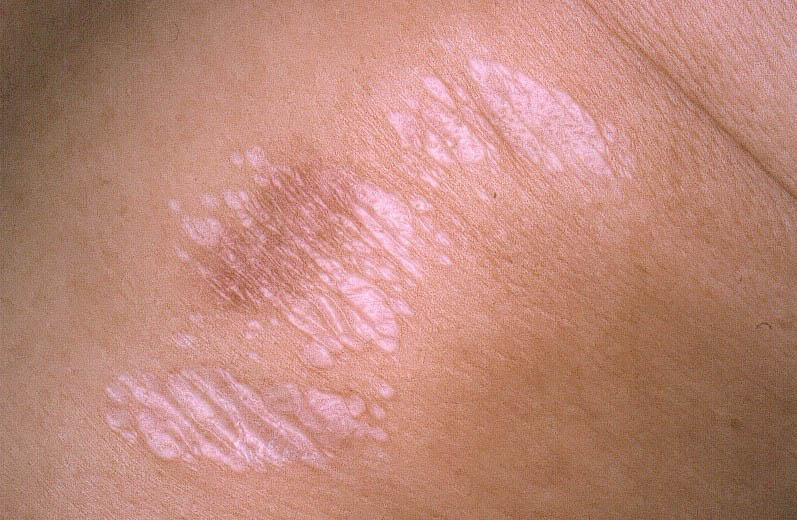
Diagnosis
- Screening for vaginal cancer
Vaginal cancer is sometimes found during a routine pelvic exam before signs and symptoms become evident. During a pelvic exam, your doctor carefully inspects the outer genitals, and then inserts two fingers of one hand into your vagina and simultaneously presses the other hand on y… - Tests to diagnose vaginal cancer
Your doctor may conduct a pelvic exam and Pap test to check for abnormalities that may indicate vaginal cancer. Based on those findings, your doctor may conduct other procedures to determine whether you have vaginal cancer, such as: 1. Inspecting the vagina with a magnifying instrument…
Treatment
- Your treatment options for vaginal cancer depend on several factors, including the type of vaginal cancer you have and its stage. You and your doctor work together to determine what treatments are best for you based on your goals of treatment and the side effects you're willing to endure. Treatment for vaginal cancer typically includes surgery and radiation.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- How you respond to your cancer diagnosis is unique. You might want to surround yourself with friends and family, or you may ask for time alone to sort through your feelings. The shock and confusion of your diagnosis may leave you feeling lost and unsure of yourself. To help you cope, try to: 1. Learn enough about your cancer to make decisions about your care.Write down the que…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Start by making an appointment with your family doctor or a gynecologist if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If it's determined that you have vaginal cancer, you'll likely be referred to a doctor who specializes in cancers of the female reproductive system (gynecologic oncologist). Because appointments can be brief and there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to …