What is the purpose of disinfection of water?
To prevent contamination with germs, water companies add a disinfectant—usually either chlorine or chloramine—that kills disease-causing germs such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, and norovirus.
What is the purpose of disinfection process?
Disinfection processes are a proven means of ridding water of disease-causing microorganisms viz bacteria, viruses, and protozoa in piped water supply.
Is it necessary to have disinfection process in wastewater treatment Why?
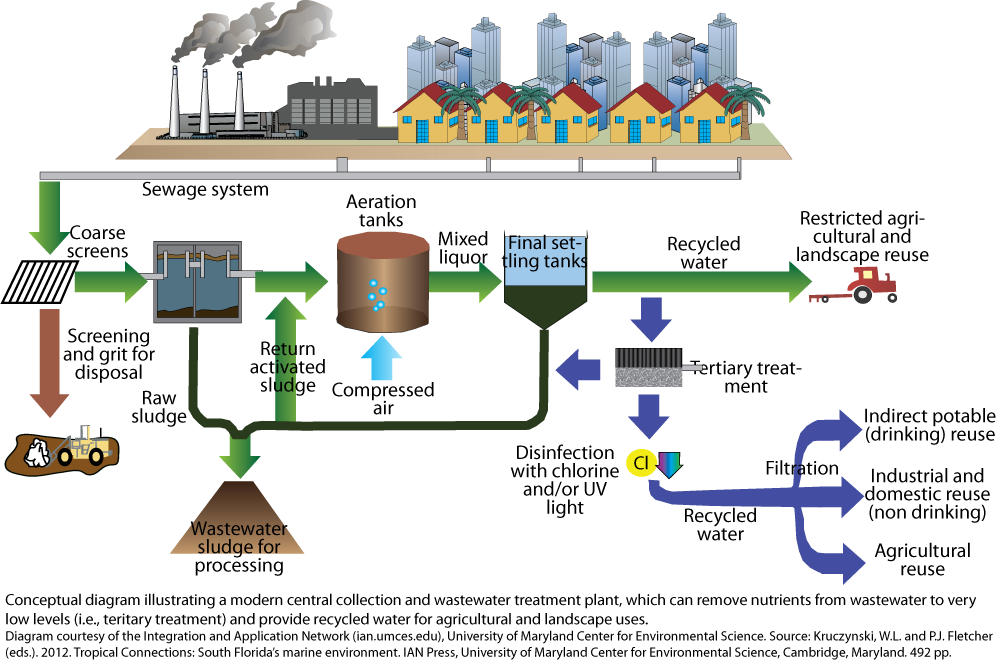
Discharges of effluent to surface waters will generally need disinfection. This reduces potentially harmful micro-organisms in wastewater to a level consistent with achieving the water quality objectives set in the SEPP (Waters of Victoria), for the protection of human health.
What is meant by disinfection in treating public water supply what is its importance?
The goal of disinfection of public water supplies is the elimination of the pathogens that are responsible for waterborne diseases.
Why is well water used?
Even when well water is used, the chemicals used to control iron, hardness and other contaminants can cause elevated chemical use and labor costs. This in turn creates more frequent blowdown and if discharged to municipal sewer systems, the surcharges again ultimately increase the cost of operation.
What is ionization used for?
When ionization is used with ozone, UV and filtration, these technologies enhance each other and provide system operators with a good alternative for disinfection, ultimately reducing costs and environmental impact of chemical use.
What is the copper level needed for algae?
Low levels of copper are all that's needed to control algae, fungus, and bacteria. A copper level below the action level established by the EPA is 1.3 ppm. Levels of 0.5 to 0.7 ppm are very effective in controlling algae and bacteria, thus reducing expensive chemical use. Conclusion.
What is copper ionization?
Copper ionization. Copper ionization (see Figure 4) is a method of reducing bacteria and also helps reduce scaling in pipes and holding tanks. This method is not very widely used and should be looked at more closely because of the synergistic effects when used in conjunction with ozone, UV and filtration.
What are the factors that affect UV light?
UV light systems are affected the same way that ozone systems are in determining successful installation. Flow rates, turbidity, demand and transmission levels, etc., are some of the factors that must be considered in UV disinfection. Total organic carbon, or TOC, remo val can be very successful when applied correctly.
Is astewater considered wastewater?
W astewater can have several meanings, depending on the industry or application. Blowdown from cooling towers is considered wastewater, leachate recovery water in greenhouses contaminated with pathogens can be considered wastewater, food processing water, and water processed in sewage plants is very definitively considered wastewater.
Is UV tubing a viable alternative to disinfectant?
Wastewater treatment plants worldwide have proven UV a viable alternative for disinfection if monitored and maintained properly. The coiled fluoropolymer tubing is a product on the horizon that brings newfound ease for installation, maintenance and safety issues.
What is the process of removing pathogenic microorganisms from water?
Water disinfection means the removal, deactivation or killing of pathogenic microorganisms. Microorganisms are destroyed or deactivated, resulting in termination of growth and reproduction. When microorganisms are not removed from drinking water, drinking water usage will cause people to fall ill. Sterilization is a process related to disinfection.
Why does disinfection occur?
Disinfection commonly takes place because of cell wall corrosion in the cells of microorganisms, or changes in cell permeability, protoplasm or enzyme activity (because of a structural change in enzymes). These disturbances in cell activity cause microorganisms to no longer be able to multiply.
What happens during sterilization?
However, during the sterilization process all present microorganisms are killed, both harmful and harmless microorganisms. Media. Disinfection can be attained by means of physical or chemical disinfectants. The agents also remove organic contaminantsfrom water, which serve as nutrients or shelters for microorganisms.
What happens when you oxidize disinfectant?
This will cause the microorganisms to die out. Oxidizing disinfectants also demolish organic matter in the water, causing a lack of nutrients. More information about the effects of detergent pollution in freshwaterecosystems.
What is the final step to reduce pathogenic microorganisms in drinking water?
Chemical inactivation of microbiological contamination in natural or untreated water is usually one of the final stepsto reduce pathogenic microorganisms in drinking water. Combinations of water purification steps (oxidation, coagulation, settling, disinfection, filtration) cause (drinking) water to be safe after production.
Do disinfectants kill bacteria?
Disinfectants should not only kill microorganisms. Disinfectants must also have a residual effect, which means that they remain active in the water after disinfection. A disinfectant should prevent pathogenic microorganisms from growing in the plumbing after disinfection, causing the water te be recontaminated.
Can bacteria be in water?
Bacteria can remain in the water after the first disinfection step or can end up in the water during backflushing of contaminated water (which can contain groundwater bacteria as a result of cracks in the plumbing). Disinfection mechanism.
How much does a chlorine tablet cost?
These units can range from $325-$700, depending on the flow to be chlorinated. Tablets
What is UV disinfection?
UV disinfection system consists of mercury arclamps, a contact vessel, and ballasts. The source ofUV radiation is either a low- or a medium-pressuremercury arc lamp with low or high intensity.Medium- pressure lamps are generally used forlarge facilities. The optimum wavelength toeffectively inactivate microorganisms is in therange of 250 to 270 nm. The intensity of theradiation emitted by the lamp dissipates as thedistance from the lamp increases. Low-pressurelamps emit essentially monochromatic light at awavelength of 253.7 nm. Standard lengths of thelow-pressure lamps are 0.75 and 1.5 m (2.5 and 5.0ft), with diameters of 15 to 20 mm (0.6-0.8 inches).The ideal lamp wall temperature is between 35 and50EC (95-122EF). The United States Public HealthService requires that UV disinfection equipmenthave a minimum UV dosage of 16,000 FW@s/cm².There are two types of UV disinfection reactorconfigurations: contact and noncontact. In bothtypes, wastewater can flow either perpendicular orparallel to the lamps. In the contact reactor, a seriesof mercury lamps are enclosed in quartz sleeves tominimize the cooling effects of the wastewater.Flap gates or weirs are used to control the level ofthe wastewater. In the noncontact reactor, UVlamps are suspended outside a transparent conduitwhich carries the wastewater to be disinfected. Inboth types of reactors, a ballast—or controlbox—provides a starting voltage for the lamps andmaintains a continuous current.
What is Oculus in Florida?
OCULUS (Electronic Document Management) All Domestic Wastewater Program Content. The vast majority of domestic wastewater treatment facilities in Florida use chlorination for disinfection. However, there are some rather significant concerns associated with chlorination including the production of potentially hazardous byproducts ...
What is the Florida Administrative Code?
Rule 62-600.440 (1), Florida Administrative Code (F.A.C.), states that: "The Department (of Environmental Protection) is aware of the possible harmful effects of chlorine used in conjunction with wastewater treatment and encourages the use of alternative disinfection methods.".
Why is filtration required in Florida?
Florida's high-level disinfection criteria were designed to ensure that the reclaimed water would be essentially virus-free.
Is UV irradiation a disinfectant?
Many utilities are beginning to evaluate and implement alternative disinfection methods, with UV irradiation among the most popular. UV has long been recognized as an effective disinfectant. However, unlike chlorine, UV does not pose disinfection byproducts, toxicity or hazardous materials concerns.
What is UV disinfection?
UV disinfection systems provide municipalities with a safe, effective and environmentally friendly method of disinfecting wastewater. Thousands of municipalities have converted from chemical-based wastewater disinfection (such as chlorine gas) to UV. This is due to the significant safety advantages for their communities, ...
Why is it important to inspect UV sleeves?
For UV equipment with cleaning systems, it’s important to visually inspect sleeves to ensure they are being evenly and effectively cleaned. The O&M manual will also outline consumable parts.
What are the primary considerations for effective UV disinfection?
Primary considerations for effective UV disinfection are total suspended solids and UVT. There are numerous organic and inorganic UV absorbing compounds. Take ferric (iron), for example. It is a chemical that is sometimes used at wastewater treatment plants. When used at high concentration, it can have a detrimental effect on UV efficacy.
Can UV SCC be connected to SCADA?
In many cases, the UV SCC will be connected to a plant SCADA system, so system status and any alarms will be available remotely. However, we still recommend a local visual inspection for UV dose, lamp status and any alarms.
Is UV effluent effective?
When properly designed and sized, UV has been proven effective on virtually all treated effluent, including primary, secondary and tertiary. However, it’s critical to consider the correlation between upstream effluent quality and the desired microbiologic inactivation and to size the UV system accordingly. Generally, UV is more amenable ...