
Pus is a common and normal byproduct of your body’s natural response to infections. Minor infections, especially on the surface of your skin, usually heal on their own without treatment. More serious infections usually need medical treatment, such as a drainage tube or antibiotics.
Full Answer
What are pus-causing infections and how are they treated?
Pus-causing infections can happen when bacteria or fungi enter your body through: When the body detects an infection, it sends neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, to destroy the fungi or bacteria. During this process, some of the neutrophils and tissue surrounding the infected area will die.
What is the medical term for pus?
The medical term for pus is purulent exudate. It is also sometimes called purulent drainage. The fluid is sometimes referred to as liquor puris. Pus is a sign that your body has started to fight infection. It does this by sending infection-fighting cells to the area.
What causes pus in the body?
Many types of infection can cause pus. Infections involving the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes are especially prone to pus. Both of these bacteria release toxins that damage tissue, creating pus. Where does it form? Pus generally forms in an abscess.
What is the purpose of pus?
Pus is a thick fluid containing dead tissue, cells, and bacteria. Your body often produces it when it’s fighting off an infection, especially infections caused by bacteria.

What is responsible for pus formation?
Pus is the result of the body's natural immune system automatically responding to an infection, usually caused by bacteria or fungi. Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are produced in the marrow of bones. They attack the organisms that cause infection.
What doctor treats pus?
It is a bacterial infection. Even other areas of your body will have to be examined. So kindly consult a dermatologist for further evaluation and treatment.
What condition means a collection of pus in the skin '?
An abscess is a painful collection of pus, usually caused by a bacterial infection. Abscesses can develop anywhere in the body. This article focuses on 2 types of abscess: skin abscesses – which develop under the skin.
What is pus an indication of?
Pus is a sign that a wound is infected but it is also a sign that your body is trying to fight the infection and heal the injury. Once an infection has started, your immune system begins trying to fight it off. It sends white blood cells to the area to destroy the bacteria.
What is sepsis disease?
Sepsis is the body's extreme response to an infection. It is a life-threatening medical emergency. Sepsis happens when an infection you already have triggers a chain reaction throughout your body. Infections that lead to sepsis most often start in the lung, urinary tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract.
Which antibiotic is best for pus?
When bacteria infect and inflame a hair follicle, a painful pus-filled bump can form under your skin....To fight this infection, your doctor might prescribe oral, topical, or intravenous antibiotics, such as:levofloxacin (Levaquin)mupirocin (Centany)sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (Bactrim, Septra)tetracycline.More items...
What does pus mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of pus : a thick, opaque, usually yellowish-white, fluid matter that is formed as part of an inflammatory response typically associated with an infection and is composed of exudate chiefly containing dead white blood cells (as neutrophils), tissue debris, and pathogenic microorganisms (as bacteria)
Why do infections have pus?
Your body produces pus as a response to infection. It is made up of degenerating white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Openings in the skin, such as cuts and wounds, allow bacteria to enter. When the bacteria enters, it can cause an infection.
Does pus indicate healing?
After the initial discharge of a bit of pus and blood, your wound should be clear. If the discharge continues through the wound healing process and begins to smell bad or have discoloration, it's probably a sign of infection.
Why does pus keep coming back?
Recurring boils may point to MRSA infection or an increase in other types of staph bacteria in the body. If you have several boils in the same place, you may be developing a carbuncle. See your doctor for a carbuncle. It may be a sign of a larger infection in the body.
What is the treatment for pus?
Treatments for infections with pus may include antibiotic medications, drainage procedures, or surgical removal of infected tissues. Pus is a thick, white substance that's typically a sign of infection. The medical term for pus is purulent exudate.
What is the function of pus?
Function. Pus is an indication your body has started to combat infection by sending infection-fighting cells to the area. Pus is often part of an abscess, a collection of pus in a cavity formed from the breakdown of infected tissues.
What is purulent drainage?
It is also sometimes called purulent drainage, and the fluid is sometimes referred to as liquor puris. A small amount of pus, such as from pimples, typically isn't a cause for alarm, but pus at the site of a wound, surgical incision, or deep interior location may require medical intervention.
How to get rid of boils and pimples?
Wash your hands thoroughly and regularly 4 . Don't squeeze pus out of pimples or boils. Instead, gently apply a warm compress several times a day. Don't share towels or razors. Eat a healthy, balanced diet. Be vigilant about controlling your blood sugar control if you have diabetes.
How to prevent pus infection?
Prevention. There are simple things you can do to reduce your risk of developing an infection with pus: Wash cuts and other wounds gently with soap and water. Follow your physician's care instructions after surgery or hospitalization for injuries. Wash your hands thoroughly and regularly 4 .
What happens if you ignore an infection?
Ignoring an infection can lead to serious problems, a longer recovery, and more scarring. Calling your physician or surgeon should be a priority. If you have a wound or surgical incision and experience any flu-like symptoms, even without pus, seek urgent medical care.
What is the PUs?
Types. Causes. Treatment. Prevention. Pus is a thick fluid matter produced as part of the body's inflammatory response to an infection. It consists of a buildup of degenerating white blood cells, dead or living bacteria (or other microorganisms), and tissue debris.
How to treat pus infection?
In mild cases, a warm and wet piece of sterile cloth can be used to compress and drain the pus.
How to prevent pus and pus wounds?
While it is impossible to completely prevent the onset of pus and pus wounds, one can still decrease the likelihood of getting these by practicing the following methods: Not sharing shaving equipment such as razors. Keeping wounds clean, dry, and covered. Scratching pimples or trying to pick them with any sharp object.
What is pus in a blister?
It is a sticky thick yellowish or pale greenish fluid that is often contained in the blisters or rashes formed due to microbial infections. These pus-filled blisters are mainly seen in bacterial or fungal infections. Pus is rich in a protein-type fluid called “liquor puris”.
How to get rid of pus after surgery?
If the point of pus bursts open on its own, then wipe the entire area with a clean piece of cotton and press the end of the wounds to expel the pus completely. Apply antibiotic cream/ointment and cover the area with a clean bandage.
Why is pus brown?
The greenish color is attributed to a bacterial pigment known as pyocyanin. Brownish pus is formed in liver abscesses caused by the amoeba. It is also foul-smelling and resembles an “anchovy-paste”. In general, an abscess is formed when an amount of pus gets trapped in a tissue space.
Why is pus yellowish?
Generally, it has a yellowish white color. In some cases, due to the presence of a myeloperoxidase, which is an antibacterial protein of greenish color, the pus may have a greenish tinge. Pseudomonas infection can form greenish, bad-smelling pus. The greenish color is attributed to a bacterial pigment known as pyocyanin.
What is the toxin that kills neutrophils?
The latter releases granules which kill the pathogen. The pathogen, in turn, releases toxin known as leukocidins which helps in resisting the immune response. This can cause the death of the neutrophils due to destruction by the macrophages. This eventually leads to the formation of pus.
What is it called when you have pus on your skin?
When the buildup is on or near the surface of the skin, it is called a pustule or pimple. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is called an abscess.
Why is my pus green?
Pus can sometimes be green because some white blood cells produce a green antibacterial protein called myeloperoxidase. A bacterium called Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) produces a green pigment called pyocyanin. Pus from infections caused by P. aeruginosa is particularly foul-smelling.
How to heal a pimple that is infected with pus?
The pus may be drained at home. Soaking a towel in warm water and holding it against the infected pus for 5 minutes will reduce the swelling and open up the pimple or skin abscess for a faster healing process.
Why is my pus yellow after surgery?
Pus is a whitish-yellow, yellow, or brown-yellow protein-rich fluid called liquor puris that accumulates at the site of an infection. It consists of a buildup of dead, white blood cells that form when the body’s immune system responds to the infection. When the buildup is on or near the surface of ...
What is the immune system that responds to infection?
Pus is the result of the body’s natural immune system automatically responding to an infection, usually caused by bacteria or fungi. Leukocytes, or white blood cells, are produced in the marrow of bones. They attack the organisms that cause infection. Neutrophils, a type of leukocyte, have the specific task of attacking harmful fungi or bacteria.
Which type of leukocyte is responsible for detecting dead bacteria?
Neutrophils, a type of leukocyte, have the specific task of attacking harmful fungi or bacteria. For this reason, pus also contains dead bacteria. Macrophages, another type of leukocyte, detect the foreign bodies and release an alarm system in the form of small, cell-signaling protein molecules called cytokines.
Can a weakened immune system cause no pus?
In a patient with weakened immunity, the system may not respond correctly. There may be an infection with no pus. This can occur if the person: is receiving chemotherapy. is taking immunosuppressant medications following an organ transplant. has HIV. has poorly controlled diabetes.
What causes pus to form?
One of the most common types of bacteria that cause pus formation is Staphylococcus aureus, although any bacterial infection may produce pus. An infection that leads to the production of pus is called a purulent infection. When pus forms within enclosed spaces in the tissues, it causes abscesses. When it forms on the skin surface, it causes lumps ...
What to do if you have pus?
Seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you, or someone you are with, have pus formation along with other serious symptoms including:
Why does pus form?
Pus is caused by the breakdown of neutrophils, which are inflammatory cells produced by the body to fight infection. Typically, pus forms during the course of a bacterial infection. Although neutrophils initially engulf and kill bacteria, they themselves are eventually broken down and become a major constituent of pus.
What is pus made of?
What is pus? Pus is a thick, whitish to yellowish material composed primarily of dead cells that generally forms as a by-product of bacterial infections.
What are the symptoms of pus?
Pus may accompany symptoms that affect the whole body including: Body aches. Coughing up clear, yellow, light brown, or green mucus. Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing. Discharge from the eye. Fainting or change in level of consciousness or lethargy. Fatigue.
What is the name of the lumps on the skin?
When it forms on the skin surface, it causes lumps known as pustules or pimples. Pus can also form when infections develop in internal organs, such as the bones, brain, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract.
What causes swelling in the brain?
Encephalitis (inflammation and swelling of the brain due to a viral infection or other causes) Meningitis (infection or inflammation of the sac around the brain and spinal cord) Myocarditis (infection of the middle layer of the heart wall) Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
How to tell if you have pus on your wound?
The area will usually look red and swollen. It may be warm to the touch and the infected spot could be painful. If the situation gets worse, you might notice symptoms like fever, aches, or chills as your body fights the infection.
Why does pus have no scent?
It may have no scent at all. But pus is a natural part of the healing process for wounds. Pus is a sign that a wound is infected but it is also a sign that your body is trying to fight the infection and heal the injury. Once an infection has started, your immune system begins trying to fight it off.
What happens if you don't get treatment for a wound infection?
If you don’t get treatment, the infection can worsen or spread. Surgical wounds are also at risk for infections. You may notice new or worsening pain around the incision if it gets infected. Swelling and redness are signs of infection, along with any pus that soaks through bandages or comes out in a drainage tube.
What are the symptoms of MRSA?
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) bacteria causes skin infections with the following signs and symptoms: cellulitis, abscesses, carbuncles, impetigo, styes, and boils. Normal skin tissue doesn't usually allow MRSA infection to develop. Individuals with depressed immune systems and people with cuts, abrasions, or chronic skin disease are more susceptible to MRSA infection.
What is the thick fluid that builds up when an injury becomes infected?
Pus is a thick fluid that builds up when an injury becomes infected. But pus isn't the only sign of an infection. The word “pus” conjures all kinds of unpleasant images. It’s linked with injuries and infection and no one likes to think about that. Pus is a thick fluid that builds up when an injury becomes infected.
How to treat an abscess in the dental office?
Dental abscesses can be treated in the office. Your dentist will numb the area and clean out the infection. You will probably need a root canal to solve the problem. After the pus is cleaned out of the wound, your doctor may give you antibiotics to prevent it from coming back.
Why should wounds not be closed?
Wounds should not be closed if there is a high risk of infection and in other situations. Wounds may be classified as acute or chronic or open or closed. They may be caused by penetrating objects, nonpenetrating trauma and other miscellaneous causes.
Why does my ear have pus?
If this symptom is paired with intense pain, a head injury, or hearing loss, seek immediate medical attention.
What does it mean when you have pus in your ear?
If you notice fluid, blood, or pus accumulating in your ear or drainage from your ear, this may be an indication of a serious condition. Following are some of the potential causes of drainage or pus from your ear.
What is the name of the infection in the middle of the ear?
Ear infection. Middle ear infections — also known as acute otitis media — are common, particularly in children. They’re often caused by a bacterial or viral infection affecting the middle portion of the ear. Common symptoms of an ear infection include: pain. pus or drainage. difficulty hearing.
What is the infection in the outer ear?
Swimmer’s ear. Swimmer’s ear is a type of infection that affects the outer ear canal (otitis externa). It can happen when water becomes trapped in your ear, after swimming, for example, allowing bacteria or fungus to grow.
What to do for swimmer's ear infection?
swollen lymph nodes. Treating a swimmer’s ear infection and other outer ear infections requires medicated ear drops. Antibiotics or antifungal medication may also be needed depending on the cause of your infection. Your doctor may also recommend pain medication for temporary relief.
Why do I have pus in my urine?
Tuberculosis. Polycystic kidney disease. Kidney stones. Fungal infections. Autoimmune diseases, such as Kawasaki disease. Experiencing pus in your urine can also be the result of long-term medication use. Drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and combination antibiotics can lead to this condition if taken for extended periods of time.
What causes pyuria in the urinary tract?
A UTI is the most common cause of pyuria, as bacteria in the urinary tract can lead to pus being excreted out in your urine. Other causes of pyuria include: STDs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, syphilis, and HIV. Viral infections. Interstitial cystitis.
Can pyuria be a sign of pregnancy?
Pyuria during pregnancy. Pregnancy is a time of many changes in the female body and pyuria can be one of them. A routine urinalysis may show pyuria when testing the urine, but this is a common occurrence during pregnancy and due to excess vaginal discharge contaminating the results. While the most common cause of pyuria is a UTI, ...
Can UTI cause pyuria?
For example, if a UTI causes pyuria, you may also experience a burning sensation when urinating, pain, and increased frequency of your bathroom trips. General symptoms of pyuria due to any cause include cloudy urine, foul smell, increased urination frequency, discomfort when urinating, and in some cases, fever.
Can a pregnant woman have pyuria?
While the most common cause of pyuria is a UTI, pregnant women generally don’t present with the typical symptoms of the infection . Any abnormalities found on urine testing will be further investigated by your doctor with the necessary treatments carried out if need be. In most cases, discovering pus in the urine of pregnant women is not ...
Can you treat pyuria with antibiotics?
If a person is asymptomatic or if no infection was found, then treatment will not be administered. Pyuria is commonly treated with antibiotics, but your doctor will ultimately decide on the most suitable mode of treatment based on your diagnostic results.
Is pyuria more common in older women?
Women are generally considered more at risk for developing pyuria compared to men. Older adults are also more likely to get it compared to their younger counterparts, with older women being having the greatest risk overall.
How to get rid of pustules on face?
Gently wash the area with soap twice a day. Use clean cloths each time. Apply an over-the-counter treatment like calamine lotion, cortisone cream, salicylic acid, or benzoyl peroxide gel. Stay away from products that can irritate your skin, like cosmetics or sunscreens. Don’t touch, pick at, or pop pustules.
What is the name of the disease that turns your immune system on itself?
Pustules are also a symptom of this rare disease that makes your immune system turn on itself. Smallpox. Pustules were one of the most obvious signs of this deadly disease that killed millions of people in past centuries.
What is a bulging pimple called?
A pustule is a bulging patch of skin that's full of a yellowish fluid called pus. It's basically a big pimple. Several conditions, ranging from something as common as acne to the once-deadly disease smallpox, can cause pustules.
Can chickenpox cause pustules?
But a form of the disease known as inflammatory rosacea can trigger pustules. Chickenpox. This childhood disease and other illnesses caused by a related virus cause skin lesions that become pustules as the disease progresses. IgA pemphigus.
What color is a pus?
Pus is generally white or a yellow-white color, but it can be greenish, blood-tinged, blue (in rare cases) or even a brown color. It can also have a foul odor. Pus can be present in a surgical incision that is becoming infected and is a sign that further treatment is needed.
What is it called when a large collection of fluids does not leak out of the body?
A collection of infectious drainage that does not leak out of the body, a condition called an abscess, can happen almost anywhere in the human body. 3 .
Why do you need a swab for wound culture?
The swab is used to perform a wound culture to determine the nature of the infection and which antibiotic will be most effective. Often, you'll be given an antibiotic at the first sign of infection. 1 If a culture later indicates another antibiotic may be more effective, you doctor may have you switch.
What to do if you have drainage coming from a wound?
It is far better to call and find out that there is no need to worry than to ignore a problem and have it lead to a serious infection because it wasn't treated quickly. Healing and Recovering From Surgery.
Can you clean pus from a wound?
Don't clean the site or try to remove the pus, as the surgeon may need to take a swab of the site. Once the swab is collected, you may require antibiotics, a change in your wound care regimen, or both.
Is it necessary to call a surgeon for a sepsis?
At the very least, a call to the surgeon is absolutely necessary, as a surgical infection can become serious quickly. When an infection spreads and reaches the bloodstream, a condition referred to as sepsis, 2 the infection can become life-threatening.
Can you scrub a surgical wound with pus coming from it?
Resist the urge to scrub a surgical wound with pus coming from it. While you might want to get the area as clean as possible, you will likely do more harm than good by removing the drainage before it can be seen by a provider.
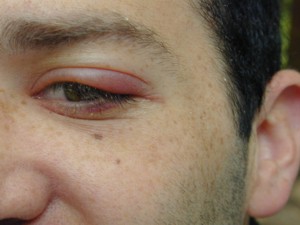
Function
Types
- Pus can be visible on the surface of the skin. It may also form internally as a complication of an infection or injury.
Causes
- Punctures, scrapes, scratches, or other openings in the skin can allow bacteria that live on the skin to enter the body and cause an infection. This includes surgical incisions. There can also be deep internal infections with pus that occur after surgery, injuries, or illnesses. Certain factors and underlying conditions can put you at risk for infections and wound complications with pus. They …
Treatment
- Treatments for infections with pus may include: 1. Antibiotic medications 2. Drainage procedures 3. Surgical removal of infected tissues
Prevention
- There are simple things you can do to reduce your risk of developing an infection with pus: 1. Wash cuts and other wounds gently with soap and water. 2. Follow your healthcare provider's care instructions after surgery or hospitalization for injuries. 3. Wash your hands thoroughly and regularly.4 4. Don't squeeze pus out of pimples or boils. Instead, gently apply a warm compress …
When to Call Your Healthcare Provider
- Some symptoms are a sign of infection. Always contact your healthcare provider if: 1. You see pus, especially after physical trauma or surgery 2. You have any redness or pain with a wound Do not ignore a surgical incision with pus. But many types of drainage are normal. Clear fluid or blood-tinged fluid that is largely clear is considered normal unless there is a large quantity comi…
Summary
- Your body produces pus as a response to infection. It is made up of degenerating white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Openings in the skin, such as cuts and wounds, allow bacteria to enter. When the bacteria enters, it can cause an infection. Making sure you avoid touching cuts and wounds with dirty hands can help prevent infection. Following your surgeon's orders after su…
A Word from Verywell
- One of the most important things you can do to avoid an infection with pus is to wash your hands often. This is crucial before and after caring for skin bumps, an incision, or wounds. If it is too late to prevent an infection, plan to take the time needed to clean the affected area properly. Check the wound regularly for any signs of infection, and be sure to protect it when necessary.