
The three most common chlorine-containing substances used in water treatment are chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, and calcium hypochlorite. The choice of the chlorine type to be used often depends on cost, on the available storage options and on the pH conditions required.
What is chlorine used for in water treatment?
Chlorine (Cl2) has been used for many years to treat potable water, municipal and industrial water and wastewaters to control microorganisms because of its capacity to inactivate most pathogenic microorganisms quickly. The effectiveness of chlorine is dependent on the chlorine concentration, time of exposure, and the pH of the water.
What chemicals are used in water treatment?
“Pure chlorine” is seldom used for water treatment. The three most common chlorine-containing substances used in water treatment are chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, and calcium hypochlorite.
What is injection chlorine?
(1) Injection Chlorine injection of small amounts of chlorine directly into water line with no retention tank, and not using well for retention. Most commonly used for sulfur smell (rotten egg smell) removal.
Why are chlorine and chloramines used in disinfection?
It is for this reason that water supplies are treated with chlorine and chloramines by most municipalities. Before chlorine and chloramines were used during the disinfection process, deadly waterborne diseases, such as cholera, typhoid and dysentery were common.
See more
Which chemical is used for chlorination of water?
Chloramines are a group of chemical compounds that contain chlorine and ammonia. The particular type of chloramine used in drinking water disinfection is called monochloramine which is mixed into water at levels that kill germs but are still safe to drink.
What is used to control the injection of liquid chlorine into water?
The chlorine gas or liquid hypochlorite may be injected directly into the water system. Directly injecting the chlorine into the water system requires a chlorine monitor to control the chlorine dose.
What chemicals are added to water for treatment?
The most commonly used chemicals for water treatment process are:Algicide.Chlorine.Chlorine dioxide.Muriatic acid.Soda ash or Sodium bicarbonate.
What is chlorine injection?
This system dispels iron, bacteria, and hydrogen sulfide. To do this, a chemical feed pump injects chlorine into the incoming water on an on-demand basis. From there, the chlorine undergoes a chemical reaction (oxidation) with the iron, bacteria, and hydrogen sulfide in the water in a mixing tank.
What is in sodium hypochlorite?
Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is a solution made from reacting chlorine with a sodium hydroxide solution. These two reactants are the major co-products from most chlor-alkali cells. Sodium hypochlorite, commonly referred to as bleach, has a variety of uses and is an excellent disinfectant/antimicrobial agent.
What kind of chlorine is used in a chlorinator?
trichlor chlorine tabletsWhat Kind of Chlorine Is Used in a Pool Chlorinator? Pool chlorinators work best with slow-dissolve trichlor chlorine tablets or pucks. These tablets last longer than liquid chlorine or granules, giving you more time between pool chemical additions.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 5 steps of water treatment?
The 5 major unit processes include chemical coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection (described below). There are chemicals added to the water as it enters the various treatment processes.
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
They typically consist of several steps in the treatment process. These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
How do you inject chlorine into water?
Metering pumps are used to inject a small amount of chlorine (sodium hypochlorite solution, or calcium hypochlorite solution) into the water, usually in conjunction with a contact tank. The pumps draw chlorine bleach from a solution tank and pump it into a pipe under pressure.
How much does a chlorine injection system cost?
Key FeaturesDescriptionItem #PriceChemical Injection Pump 110v (includes injector/hoses) complete kit4701-15$364Chemical Injection Pump 220v (includes injector/hoses) complete kit4702-15$364Chlorine Solution Tank (16 gallon)4713$99.Chlorine Solution Tank (35 gallon)4714$149.1 more row
How much chlorine should I put in my well water?
CALCULATE AND POUR: Pour 3 pints of chlorine bleach per 100 gallons of water plus an additional 3 pints into your well as described above. MIX: Attach a clean garden hose to the outdoor faucet nearest the well and place the end of the hose inside the well.
Why is chlorine used in disinfection?
Chlorination and Disinfection: Chlorine (Cl2) has been used for many years to treat potable water, municipal and industrial water and wastewaters to control micro organisms because of its capacity to inactivate most pathogenic microorganisms quickly. The effectiveness of chlorine is dependent on the chlorine concentration, time of exposure, ...
How is chlorine gas dosed?
Chlorine gas is dosed from bulk cylinders or drums using remote vacuum gas chlorination equipment. The vacuum regulator is mounted directly on the cylinder isolation valve using a lead gasket. Chlorine gas under pressure is fed to the inlet pressure reducing valve, the needle of which is seated on a diaphragm.
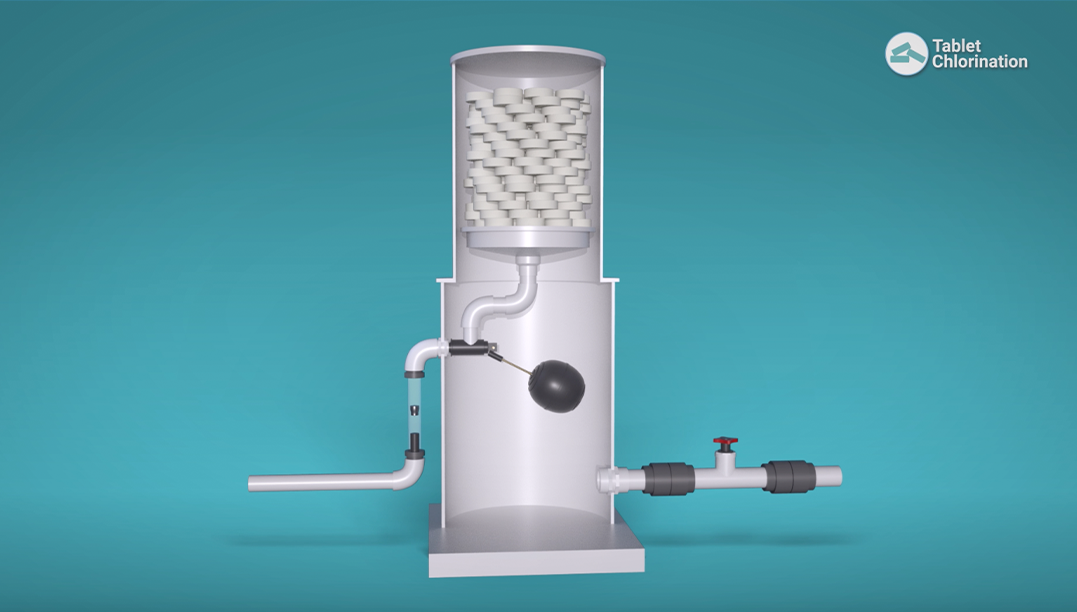
How is calcium hypochlorite used?
Calcium hypochlorite is available as granules or tablet form. The tablets can be used with erosion feeder . Tablets are placed in a hopper where they are stored dry. Water is allowed to run past the bottom layer of tablets where slow erosion will occur. The chlorinated water then drops into a buffer storage tank where flushing and dilution occurs. The diluted (<500ppm) solution is continually pumped to the process water header for disinfection. Control of chlorination is by a residual chlorine controller (Chlorine Analyzer). This controller gives a pulse duration control signal to the feeder and the feeder controls the tablet erosion water valve. b. Sodium Hypochlorite Sodium Hypochlorite is a commercially available disinfectant chemical usually the concentration ranges from 10 – 12.5%. This liquid disinfectant is normally dosed with solenoid operated dosing pumps or motor-driven metering pumps for smaller applications The dosing system comprises of chemical day tanks and metering pumps prefabricated in compact skids with all relevant accessories. Design and construction of these dosing skids could be made suitable for all industries including strict oil and gas field standards. The discharge rate from the dosing pumps could be varied to meet different dosing requirements. Sodium hypochlorite undergoes gasification as it decomposes to give off oxygen gas. This gasification may cause problems in chemical metering pumps as the gas will accumulate in the metering pump suction line, eventually making its way into the liquid end where there is loss of priming. Larger metering pumps (>20 L/hr) don’t usually suffer from loss of prime as the valves are comparatively bigger and the associated volume of chemical being pumped is also larger.
Why is electro chlorination important?
The main advantage of electro chlorination is that dangerous chlorine gas can be avoided where brine or sea water is abundantly available.
How does chlorine gas flow through a vacuum?
Chlorine Gas under vacuum then flows through a regulating device (needle valve V notch) and through the vacuum tube to the venturi where it is dissociated in water. d. Electrochlorination. Electro-chlorination is a chemical process which uses water, common salt and electricity to produce Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl).
Why does sodium hypochlorite gasify?
Sodium hypochlorite undergoes gasification as it decomposes to give off oxygen gas. This gasification may cause problems in chemical metering pumps as the gas will accumulate in the metering pump suction line, eventually making its way into the liquid end where there is loss of priming.
Is chlorine a gas?
There are many applications of Chlorine, apart from Disinfection. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature and pressure and is soluble in water. Chlorine hydrolyses with water to form hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid according to the following equation:
When was chlorine first used?
Chlorine was first used in the United States as a major disinfectant in 1908 in Jersey City, New Jersey. Chlorine use became more and more common in the following decades, and by 1995 about 64% of all community water systems in the United States used chlorine to disinfect their water.
What is the process of adding chloramine to drinking water to disinfect it and kill germs?
Chloramination is the process of adding chloramine to drinking water to disinfect it and kill germs. It is sometimes used as an alternative to chlorination. Chloramines are a group of chemical compounds that contain chlorine and ammonia.
What is the best disinfectant for drinking water?
Several major U.S. cities such as Philadelphia, San Francisco, Tampa Bay, and Washington, D.C. use chloramine to disinfect drinking water. Chloramine is recognized as a safe disinfectant and a good alternative to chlorine.
What is the EPA's water treatment system?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) allows drinking water treatment plants to use chloramine and chlorine to disinfect drinking water. Water system pipes develop a layer of biofilm (slime) that makes killing germs more difficult.
What is the EPA's hotline for chloramine?
EPA provides guidance for local water authorities switching to chloramine on how to minimize lead and copper levels. If you are concerned about lead or copper levels in your household water, call EPA’s Safe Drinking Water Hotline at 800-426-4791 for testing information.
Where is chloramine used?
Chloramine has been used as a drinking water disinfectant in the United States in places like Cleveland, Ohio, Springfield, Illinois, and Lansing, Michigan since 1929. In 1998, an EPA survey estimated 68 million Americans were drinking water disinfected with chloramine.
What is the purpose of water in dialysis?
During dialysis, large amounts of water are used to clean waste products out of a patient’s blood. Dialysis centers must treat the water to remove all chemical disinfectants, including chlorine and chloramine, before the water can be used for dialysis.
How is chlorine injected into water?
Thirdly, Chlorine is injected with a chemical injection pump (commonly known as a chemical injection pump, a chemical feed pump or a chemical dosing pump ) into the water between the well and the bladder (or pressure) tank. It then runs through a large storage tank to allow contact time. A backwashing carbon tank removes ...
What is the best product to use to remove calcium and magnesium from water?
Other Products Include: Water Softener -Used in water treatment to remove calcium and magnesium from the water to create soft water and prevent calcium or scale build up and to make soaps more efficient. Acid Neutralizer -Used in water treatment to neutralize acidic water and to raise the pH level.
What is a carbon backwash tank?
A backwashing carbon tank removes the chlorine and other contaminates like tastes, odors, organics and chemicals. Then a water softener removes hardness and calcium (gives you great suds and softer skin). A sediment filter is recommended for wells with any sediment or dirt problems.
How to kill sulfur smell in water?
Chlorine is injected directly into the water line to kill sulfur smells. Much less chlorine is used than with the other two methods. You simply mix a small amount of chlorine (like ordinary household bleach) with water in a 16 gallon chlorine container. Of course less is accomplished with the water.
What is reverse osmosis water filter?
After treating and softening or conditioning the water we recommend reverse osmosis (drinking water filter) to remove contaminates such as nitrates, sodium and total dissolved solids from the water. The system recommendations below include reverse osmosis at the kitchen sink.
What is the purpose of an iron retention tank?
Iron bacteria and retention tanks. This system addresses iron and iron bacteria, e-coli bacteria, coliform bacteria and other contaminants that need contact time. But contact time is usually only essential for removing harmful bacteria such as e-coli and coliform.
How many people can use a 30,000 grain water softener?
A water softener is recommended in addition to the de-chlorination system. And a 30,000 grain water softener is usually more than sufficient for families of up to 4 people. Most water softeners use salt (sodium chloride) to regenerate or clean themselves.
How does a chlorine pump work?
Chlorine is injected with a pump (commonly known as a chemical injection pump, a chemical feed pump or a chemical dosing pump) into the water between the well and the bladder (or pressure) tank. It then runs through a large retention tank to allow contact time. A backwashing Terminox™ ISM tank removes the chlorine and other contaminants like iron, ...
What is a chlorine feed pump?
Chlorine feed pumps can be used for many things in a water filtration system. They can be used to treat bacteria, bad odors, to raise pH and to oxidize iron or sulfur. Well water chlorine systems also come in many different types such as, well water chemical feed pumps, pallet droppers, and chlorine aeration systems and can be used in conjunction ...
How to kill sulfur smell in water?
Chlorine is injected by a chemical feed pump directly into the water line to kill sulfur smells. Much less chlorine is used than with the other two methods. You simply mix a small amount of chlorine (like ordinary household bleach) with water in a 16 gallon chlorine container. Of course less is accomplished with the water.
What is the best product to use to remove calcium and magnesium from water?
Other Products Include: Water Softener - For use in water treatment to remove calcium and magnesium from the water to create soft water and prevent calcium or scale build up and to make soaps more efficient. Acid Neutralizer - To neutralize acidic water and to raise the pH level.
What is the best filter for water softener?
Commonly used to greatly reduce the sodium content after a water softener. Iron Filters - Used in water treatment to remove iron, heavy metals, odors and colors. A good iron filter will remove iron, sulfur, manganese, taste and odor from the water.
Does chlorine need to be in a retention tank?
Iron bacteria alone requires no retention time or retention tanks normally when a chlorine injection pump is used in conjunction with a Terminox Filter®.
Why is water treated with chlorine?
A number of contaminants, including disease causing bacteria and other organisms, can affect water quality and purity. It is for this reason that water supplies are treated with chlorine and chloramines by most municipalities. Before chlorine and chloramines were used during the disinfection process, deadly waterborne diseases, such as cholera, ...
How does chlorine water work?
Chlorinated well water also removes iron and contaminants through a process called oxidation. Stains caused by iron contamination, foul rotten egg smell and other water quality issues caused by iron bacteria and contaminants are eliminated by chlorine water treatment systems.
How to get well water to be chlorinated?
One way to obtain chlorinated well water is to apply high levels of chlorine directly into the well through a process known as “shock chlorination.”.
What is the purpose of a well-chlorinated water pump?
This allows the water to have enough “contact time” with the chlorine in order for complete disinfection and oxidation to occur. Older chlorine injection systems use well-chlorination pumps that are tied into the well’s pump. This means that when the water pump is running and drawing water from the well, the chlorination pump is activated ...
How does a whole house chlorine system work?
Whole house chlorine injection systems disinfect and make the water safe to drink by removing the contaminants that affect the water's taste, appearance and smell. A carbon filter then removes the chlorine before the water is delivered to the home.
What happens when water has high levels of chlorine?
When water contains high levels of chlorine, the taste and smell of the water can be affected. Chloramines can impact water quality and purity, too. Efficient chlorination systems operate on an accurate proportional feed of chlorine into the water supply, so overdosing does not occur.
How does a carbon filter remove chlorine?
The carbon filter oxidizes the chlorine and removes it through periodic backwashing. Backwashing filters are pre-programmed for maximum efficiency.
What chemicals are used in water treatment?
The broad categories of these chemicals include: Oxygen scavengers. Flocculants. Neutralising agents. pH conditioners. Scale inhibitors. Corrosion inhibitors. Coagulants.
What are neutralizing agents in water treatment?
Neutralising agents in water treatment neutralise acids and basics. Their dosage will depend on the pH of the water. Some neutralising agents increase pH levels, and some will cause them to decline. Neutralising agents include solutions of sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate, and diluted sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid.
What is the role of oxidants in water treatment?
Oxidants can act as disinfecting agents in water treatment, removing contaminants.
What are flocs used for?
Flocs are cloudy suspensions of cells, formed from bacterial cells and fungal species. These organisms can help to reduce organic matter and reduce biological oxygen demand in water. They are used as part of sewage treatment.
What are coagulants in water?
Coagulants. Coagulants can remove suspended solids in water. They are made up of positively-charged molecules, and may be organic, inorganic or a combination of both. Chemicals commonly used as coagulants in drinking water treatment include: Aluminium sulphate. Polyaluminium chloride. Ferric sulphate.
What are disinfectants and biocides used for?
Disinfectants and biocides are used in various industries, for preparing drinking water, treating process water, preparing ultra-pure water and for disinfecting surfaces. They kill micro-organisms in water and include: Chlorine. Chlorine dioxide.
What is the best way to reduce pH in water?
pH Conditioners. pH conditioners help adjust pH water levels. This can help to reduce corrosion in pipes and prevent any lead dissolving into water supplies. You can reduce or increase pH levels using basics or acids.
What is water treatment?
In water treating, chemicals aid in producing suitable water for discharge or injection. A wide range of chemicals is available for water treating. A chemical-injection package enables various types of chemicals to be dosed into the water stream to optimize the treatment process. In many operations, each chemical-injection stream is equipped ...
What is the purpose of water clarification?
Water clarification. (Flocculants) The purpose of water clarification is to improve the water quality to meet discharge or injection requirements. Water-clarification chemicals aid in coagulating and flocculating the oil and solid particles into larger ones to enhance their separation from water.
How do corrosion inhibitors reduce corrosion?
Corrosion inhibitors reduce the corrosion rate by interrupting the electrochemical corrosion cell setup between the metal and the liquid or by stopping the deterioration of metal by a chemical reaction. One method of interrupting the electrochemical cell is to form a film on the metal surface, which stops the transfer of ions. One method of chemical protection uses an absorption inhibitor, such as a surface-active amine, which forms a chemisorption bond to the metal, rendering it incapable of dissolving into the fluid.
What pH is used for aluminum coagulants?
For instance, aluminum coagulants require a minimum pH of 6 to 7, while iron salts are effective in a pH range of 5 to 11.
What is the function of inhibitors to prevent scale?
The ability of an inhibitor to prevent scale is its primary function in an application. Dynamic tube-blocking tests permit ranking of inhibitors to prevent scale. Different temperatures can be used to mimic changing field conditions.
How to evaluate a biocide?
To evaluate a biocide, a bacteria culture is first obtained from the field. The culture is usually a mixed strain of the organisms that can grow in the media used. If a field culture is not available, cultures of bacteria can also be obtained from a commercial laboratory. One or more of the following methods are then used to select a biocide.
What is a polyelectrolite?
Polyelectrolites refers to all water-soluble organic polymers. The polyelectrolites are long chain molecules, frequently polyamines or polyacrylamides. Their overall charge and size destabilize colloids and provide agglomeration of solids (flocculation). In water treating, the term “polyelectrolyte” is generally used in reference to two types of chemicals.
Can you use iron filters for landscape irrigation?
Iron filters aren't ideal for landscape irrigation applications, where daily use of hundreds of gallons of water at high flow rates is common. Filters used in irrigation may be oversized, and multiple systems may be required.
Is a well pro dry pellet chlorinator good?
Well Pro dry pellet chlorinators offer some advantages over liquid chlorine-feed systems. They free you of the messy and unpleasant job of chlorine solution preparation, they're trouble-free and easy to install, and they often require no retention tank.
