Struvite solubility is a function of the pH. As pH increases, struvite solubility decreases. Anaerobic digestion processes, which show a higher pH than the previous stages of the wastewater treatment, are more susceptible to struvite formation. Struvite precipitation is not simply a problem of BNR treatment works.
Full Answer
What causes struvite to form?
Struvite scale formation is a major operational issue at both conventional and biological nutrient removal wastewater treatment plants. Factors affecting the formation of struvite scales were investigated including supersaturation, pH and pipe material and roughness. A range of control methods have …
How do you control struvite formation?
Mar 12, 2018 · What causes struvite stones? Bacteria in your urinary tract produce struvite when they break down the waste product urea into ammonia. For struvite to be produced, your urine needs to be alkaline....
How does struvite precipitation affect wastewater treatment?
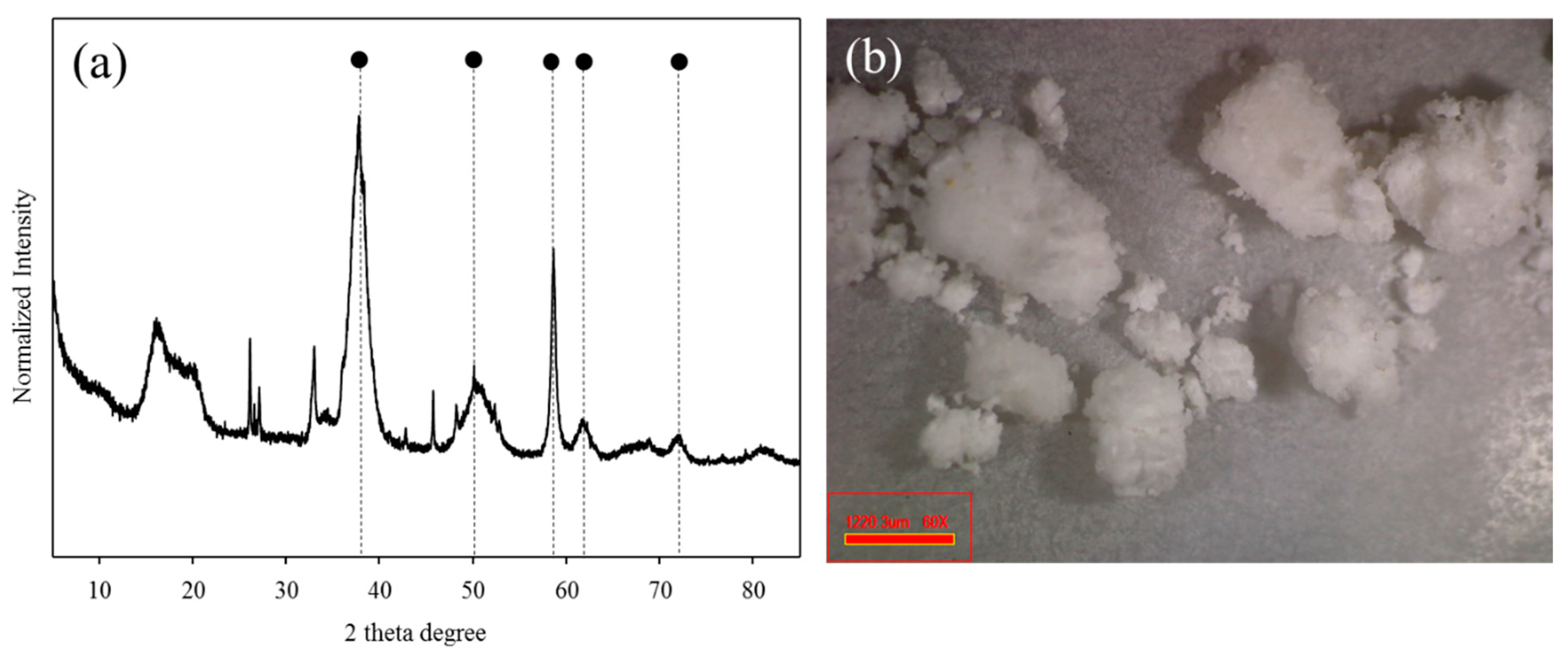
Struvite is MgNH4PO4 x 6H2O and this paper reviews the formation, control and recovery of struvite from primarily municipal wastewater and other waste streams. Treatment op … Recent legislation on the removal of nutrients from wastewater has led to a number of operation problems with struvite scaling.
Can a urinary tract infection cause struvite?
Sep 01, 2002 · This combination of ions found in sludges derived from nutrient removal processes, specifically biological nutrient removal (BNR), can result in the formation of a tenacious mineral. This mineral, composed of magnesium ammonium phosphate, is …

Why does urine have struvite?
Bacteria in your urinary tract produce struvite when they break down the waste product urea into ammonia. For struvite to be produced, your urine needs to be alkaline. Having a urinary tract infection can make your urine alkaline. Struvite stones often form in women who have a urinary tract infection.
What is a struvite stone?
Takeaway. What are struvite stones? Struvite stones are a type of hard mineral deposit that can form in your kidneys. Stones form when minerals like calcium and phosphate crystallize inside your kidneys and stick together. Struvite is a mineral that’s produced by bacteria in your urinary tract.
How do kidney stones form?
Stones form when minerals like calcium and phosphate crystallize inside your kidneys and stick together. Struvite is a mineral that’s produced by bacteria in your urinary tract. About 10 to 15 percent of all kidney stones are made from struvite. This type of stone is more common in women. than in men.
What are the symptoms of kidney stones?
See your doctor if you have kidney stone symptoms like back and side pain, fever, and frequent urination. Your doctor can do tests to find out if you have urinary stones and what type they are.
What is PNL surgery?
PNL is the preferred treatment for people with stones that are too large to be broken up by SWL. The surgeon makes a small incision in your back and inserts a scope and several small instruments. Then the stone is removed through the incision. You’ll be asleep during the surgery.
How does SWL work?
SWL uses intense shock waves directed from a machine outside your body to break up the stones into tiny pieces. After this treatment, the pieces of stone will pass through your urinary tract and come out in your urine.
Does diet help with struvite stones?
Diet may not be effective at preventing struvite stones because they’re caused by infections. But certain fluids may make the environment in your urinary tract more inhospitable to stone growth. These include: As well, try to drink extra fluids. Crystals are less likely to form in dilute (watery) urine.
Can struvite be recovered from wastewater?
Struvite can be recovered from wastewater and sludge liquors if the chemical constituents of the sludge are such that the Ksp value is exceeded. The liquors’ chemical constituents can be adjusted deliberately so that struvite precipitation occurs in a designated location and thus recovery can be facilitated.
Is struvite recovered from landfill?
Struvite recovery is not confined to municipal wastewater treatment systems, other waste streams offer opportunities for struvite recovery since the chemistry of the waste liquors meets the requirements for struvite precipitation ( Table 12 ). Struvite has been recovered from landfill leachate, swine wastewaters and abattoir wastes and certain waste streams have the potential to recover over 1000 mg of struvite per litre of waste.
What is eutrophication in a lake?
Alternatively, a natural phenomenon that increases the organic load in a lake due to the seasonal increase in nutrients.
How can struvite deposition be ameliorated?
Struvite deposition can be ameliorated by chemical, physical or biological methods. These controls fit into three main categories:#N#•#N#those that affect solubility,#N#•#N#those that alter the growth mechanisms of the crystals,#N#•#N#preferential formation.
Is struvite a good fertiliser?
Struvite has been suggested to display excellent fertiliser qualities under specific conditions when compared with standard fertilisers [14]. Qualities include its low solubility and nitrogen and phosphorus components although extensive field trials are yet to be undertaken using struvite as a fertiliser or as a fertiliser additive [15], [86]. Other factors that support struvite use as a fertiliser include the low heavy metal content of the product when compared to phosphate baring rocks that are mined and supplied to the fertiliser industry [74]. A factor that must be addressed is that struvite may require supplementation with potassium to meet the NPK (nitrogen:phosphorus:potassium) requirements of certain specific crops [86]. This would inevitably add to processing and production costs. Essentially, phosphorus has been the key component that struvite contains that has generated interest in recovery and reuse options. Since supplies of phosphorus and the quality of phosphate baring rock are decreasing, a means of phosphorus recovery could become an increasingly appealing opportunity [86].
What is used to recover phosphorus?
A common process used for phosphorus recovery is the fluidised bed reactor. These reactors commonly consist of a standard columnar reactor with a seed material placed within upon which struvite precipitates. Seed materials used include quartz and silica sands [44], minerals such as anthracite (The DHV Crystallactor plant quoted by Greaves et al. [73], magnesia clinker, pumice [59] and clays [48] have all been applied as supports upon which struvite crystals grow and proliferate. The materials that the reactors are designed to remove such as calcium phosphates and struvite have also been used as the media within the reactor. There are four practical reasons why this may be done: First, should the product be sold then it may be a necessity to produce as pure a product as possible, seed materials may reduce the purity of the product. Second, the transport and removal of the seed material could also cause problems when processing the product [74], [94]. Third, the utilisation of a small proportion of the recovered product as the media also may influence the kinetics at which the products form. Since crystal growth upon like crystals requires less energy and is thus preferential to growing upon foreign seed materials. Finally, there is an inherent cost in providing a seed material thus if the seed material can be recycled then this reduces the running costs of the plant [75].
What causes a struvite stone?
Struvite stones are caused by an upper urinary tract infection (UTI) from bacteria. Ammonia produced as a waste product by the bacteria can make the urine less acidic (or more alkaline). Struvite stones form when the urine becomes more alkaline. The main chemicals in a struvite stone include struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) ...
How to prevent struvite stones?
To prevent future struvite stones, your doctor may prescribe certain medicines. Acetohydroxamic acid (AHA) is used to stop the bacteria from making ammonia, which can cause struvite stones to grow. You might also be given antibiotics for a while after a stone is removed. This may help prevent future UTIs, which can lead to stones.
How to know if a stone is too big?
A stone that is small enough can pass through with no symptoms. However, a stone that is too large to pass through may cause significant pain, back-up of urine, and other health problems. Speak with a healthcare professional if you feel any of these symptoms: 1 Severe pain on either side of your lower back 2 Nausea or vomiting 3 Fever and chills 4 Frequent need to urinate 5 Pain when you urinate 6 Blood in the urine 7 Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy
How to diagnose kidney stones?
Diagnosis of a kidney stone starts with a medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, urine and blood testing, and stone analysis. Blood and urine can be tested for abnormal levels of certain chemicals. You may be asked to collect your urine for 24 hours to test for uric acid or other chemicals.
Where do stones go after they form?
After formation, the stone may stay in the kidney or travel down the urinary tract into the ureter. Stones that don't move may cause significant pain, urinary outflow obstruction, infection, or other health problems.
Can a stone cause back pain?
However, a stone that is too large to pass through may cause significant pain, back-up of urine, and other health problems. Speak with a healthcare professional if you feel any of these symptoms: Severe pain on either side of your lower back. Nausea or vomiting. Fever and chills.
What does it mean when you urinate?
Pain when you urinate. Blood in the urine. Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy. Symptoms related to a UTI include a persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, or passing frequent and small amounts of urine. Urine that looks red, pink or dark means there is blood in the urine.
What is the best treatment for struvite stones?
It may lower chances of stone growth. Diet: Although it has had only modest success, a diet of low-phosphorus, low calcium, and aluminum hydroxide gel has been used to treat struvite stones.
Can a kidney stone be a struvite?
While kidney stones are familiar to most people, struvite kidney stones may not be. Struvite kidney stones have sharp, uneven edges and they tend to grow quickly, leading to a malfunction of the kidney. This type of stone requires immediate medical attention. The kidney plays an important role in the human body.
What percentage of kidney stones are struvite?
In the U.S., it is estimated that anywhere between 10 and 15 percent of all stones are struvite.
What is the pain of a kidney stone?
Struvite related pain tends to be less localized and dull. Back pain: Lower back pain is common in those suffering from kidney stones.
Can kidney stones cause blood in urine?
Blood in urine: There are situations where the stones can damage the inner lining of the urinary tract, which can cause blood in the urine.
What is the best way to flush out kidney stones?
Avoid magnesium-rich foods: Foods such as peanuts, spinach, tofu, and almonds should not be consumed in large amounts. Try watermelon seeds: These seeds are a natural diuretic, known to help flush out particles of stones from the kidney.
Why is urine acidic?
Kidney stones are formed from crystals. Normally, urine is slightly acidic, but if a person has a bacterial infection, the urine becomes more alkaline. This is due to the fact that bacteria can convert urea in the urine into ammonia. Ammonia raises alkaline pH in urine.
How is struvite formed?
The formula tells us that struvite crystals are created when magnesium, ammonia, and phosphate combine in water in a mole to mole to mole ratio of 1:1:1. WWTP’s was tewater temperature and its pH are also contributing factors to struvite precipitation. The higher the wastewater pH, the more likely the mole to mole to mole balance will be affected, ...
What are the elements that make up struvite?
Struvite formation most frequently occurs in wastewater treatment plants that have anaerobic digesters, but can other form in other operations and industries. Three things contribute to struvite precipitation and crystal formation: 1 Magnesium, a major ingredient and contributor of hard water 2 Ammonia, a byproduct of urea and urine 3 Phosphate, which is a major element in the organic matter processed at the plant
