
Underlying conditions (inflammatory eye disease, autoimmune disorders, cancerous growths, and others) that lead to serous retinal detachments need to be treated appropriately in order to control fluid buildup. In rhegmatogenous and tractional detachments, a surgical procedure will usually be necessary.
What are the chances of getting retinal detachment?
Dec 23, 2020 · The most common cause of tractional retinal detachment is diabetic retinopathy — an eye condition in people with diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy damages blood vessels in the retina and can scar your retina. As the scars get bigger, they can pull on your retina and detach it from the back of your eye.
What is retinal detachment and why is it so dangerous?
Apr 12, 2022 · Rhegmatogenous. The most common type of retinal detachment (rhegmatogenous retinal detachment) is caused by a tear or hole in the retina that permits fluid to pass into and collect beneath the retina. Gradually, the retina pulls away, causing blood loss and a …
What are the signs or symptoms for retinal detachment?
This can be caused by the following: Proliferative diabetic retinopathy Inflammatory or infectious conditions Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) Sickle cell retinopathy Proliferative vitreoretinopathy
Can a retinal detachment heal on its own?
Aug 28, 2020 · Rhegmatogenous detachments are caused by a hole or tear in the retina that allows fluid to pass through and collect underneath the retina, pulling the retina away from underlying tissues. The areas where the retina detaches lose their blood supply and stop working, causing you to lose vision.
Which treatment is best for retinal detachment?
- Laser surgery (photocoagulation). The surgeon directs a laser beam into the eye through the pupil. ...
- Freezing (cryopexy). After giving you a local anesthetic to numb your eye, the surgeon applies a freezing probe to the outer surface of the eye directly over the tear.
What is the most common cause of retinal detachment?
How do doctors treat retinal detachment?
How do you treat a detached retina without surgery?
Can retinal tear heal itself?
What are the warning signs of a detached retina?
- dots or lines (floaters) suddenly appear in your vision or suddenly increase in number.
- you get flashes of light in your vision.
- you have a dark "curtain" or shadow moving across your vision.
- your vision gets suddenly blurred.
How long does a detached retina take to heal?
How can retinal detachment be prevented?
Is retinal laser surgery painful?
Can rubbing eyes cause retinal detachment?
What is the success rate of retinal detachment surgery?
Is retinal detachment surgery painful?
How to fix retinal detachment?
Depending on how much of your retina is detached and what type of retinal detachment you have, your eye doctor may recommend laser surgery, free zing treatment, or other types of surgery to fix any tears or breaks in your retina and reattach your retina to the back of your eye. Sometimes, your eye doctor will use more than one of these treatments at the same time.
What are the different types of retinal detachment?
There are 3 types of retinal detachment: rhegmatogenous, tractional, and exudative. Each type happens because of a different problem that causes your retina to move away from the back of your eye. Learn more about what causes each type of retinal detachment.
Why do you need a dilated eye exam?
A dilated eye exam can help your eye doctor find a small retinal tear or detachment early, before it starts to affect your vision.
How to move retina back into place?
Surgery. If a larger part of your retina is detached from the back of your eye, you may need surgery to move your retina back into place. You may need to get these surgeries in a hospital. Treatment for retinal detachment works well, especially if the detachment is caught early.
What is a dark shadow on the side of your eye?
A dark shadow or “curtain” on the sides or in the middle of your field of vision. Retinal detachment is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms of a detached retina, it’s important to go to your eye doctor or the emergency room right away. The symptoms of retinal detachment often come on quickly. If the retinal detachment isn’t treated right ...
What diseases can cause the retina to thin?
Certain other eye diseases, including retinoschisis (when the retina separates into 2 layers) or lattice degeneration (thinning of the retina)
What does it mean when your eyes are floaters?
A sudden increase in floaters (small dark spots or squiggly lines that float across your vision), flashes of light in one eye or both eyes, a “curtain” or shadow over your field of vision. If you have symptoms of retinal detachment, go to your eye doctor or the emergency room right away.
How to prevent retinal detachment?
When a retinal tear or hole hasn't yet progressed to detachment, your eye surgeon may suggest one of the following procedures to prevent retinal detachment and preserve vision. Laser surgery (photocoagulation). The surgeon directs a laser beam into the eye through the pupil. The laser makes burns around the retinal tear, ...
How to repair a detached retina?
The type of surgery your surgeon recommends will depend on several factors, including how severe the detachment is. Injecting air or gas into your eye.
What is the procedure called when you inject air into your eye?
Injecting air or gas into your eye. In this procedure, called pneumatic retinopexy (RET-ih-no-pek-see), the surgeon injects a bubble of air or gas into the center part of the eye (the vitreous cavity). If positioned properly, the bubble pushes the area of the retina containing the hole or holes against the wall of the eye, stopping the flow of fluid into the space behind the retina. Your doctor also uses cryopexy during the procedure to repair the retinal break.
What is the procedure called when you put silicone on your eye?
This procedure, called scleral (SKLAIR-ul) buckling, involves the surgeon sewing (suturing) a piece of silicone material to the white of your eye (sclera) over the affected area. This procedure indents the wall of the eye and relieves some of the force caused by the vitreous tugging on the retina.
What is the procedure called to remove the vitreous?
Draining and replacing the fluid in the eye. In this procedure, called vitrectomy (vih-TREK-tuh-me), the surgeon removes the vitreous along with any tissue that is tugging on the retina. Air, gas or silicone oil is then injected into the vitreous space to help flatten the retina.
What is the procedure to repair a retinal tear?
Surgery is almost always used to repair a retinal tear, hole or detachment. Various techniques are available. Ask your ophthalmologist about the risks and benefits of your treatment options. Together you can determine what procedure or combination of procedures is best for you.
What test is used to check for retinal bleeding?
Ultrasound imaging. Your doctor may use this test if bleeding has occurred in the eye, making it difficult to see your retina.
What happens when the retinal cells detach?
When detachment occurs, retinal cells cannot get the nourishment and oxygen needed from blood vessels.
How many types of retinal detachment are there?
There are three types of retinal detachment, including:
How does cryopexy repair retinal tear?
Once they’ve halted the flow , the surgeon uses cryopexy or laser to repair the retinal tear. The bubble of air or gas and any liquid is absorbed into the eye, allowing the retina to adhere back into place.
What happens to the retina as you age?
This type of retinal detachment is usually linked to age. As someone ages, the vitreous liquid in their eyes changes consistency.
Is retinal detachment painless?
Retinal detachment is painless. Do not assume that lack of discomfort or pain means there isn’t a problem .
How long does it take for vision to improve after a cataract surgery?
Vision usually improves gradually in the months following the procedure. Sometimes a second procedure is needed to further improve vision.
What happens to the injected material in a space?
The injected material is eventually absorbed and the space refills with fluid.
What causes a detachment of the retina?
Exudative detachment can be caused by age-related macular degeneration, injury to the eye, tumors or inflammatory disorders.
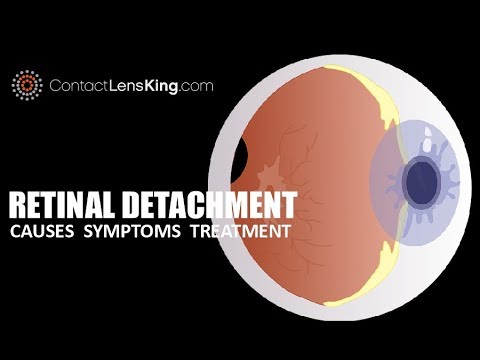
What is retinal detachment?
Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a critical layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from the layer of blood vessels that provides it with oxygen and nutrients. Retinal detachment is often accompanied by flashes and floaters in your vision. Retinal detachment describes an emergency ...
What causes the retina to pull away from the back of the eye?
This type of detachment can occur when scar tissue grows on the retina's surface , causing the retina to pull away from the back of the eye. Tractional detachment is typically seen in people who have poorly controlled diabetes or other conditions. Exudative.
What happens to the vitreous as you age?
As you age, the gel-like material that fills the inside of your eye, known as the vitreous (VIT-ree-us), may change in consistency and shrink or become more liquid. Normally, the vitreous separates from the surface of the retina without any complications — a common condition called posterior vitreous detachment (PVD).
How many different types of retinal detachment are there?
There are three different types of retinal detachment:
What is the name of the disease that causes the retina to thinning?
Previous other eye disease or disorder, including retinoschisis, uveitis or thinning of the peripheral retina (lattice degeneration)
Is retinal detachment painless?
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as:
What is a detached retina?
A detached retina is where the retina is lifted away from the back of the eye. A torn retina requires immediate treatment to prevent further problems (like vision loss ). Jump to topic.
What happens when your retina tears?
When the retina tears, you may see flashes of light or floaters . Sometimes blood can leak into the vitreous. This is known as a vitreous hemorrhage. A vitreous hemorrhage can cause a large number of floaters.
How to check for retinal tear?
Your eye doctor or ophthalmologist will check for retinal tears by placing drops in your eyes to dilate the pupil. They will look through a special lens to assess any changes inside the eye. This is the most efficient way to see if you have a retinal tear or early retinal detachment.
What are the early stages of eye disease?
Most eye diseases and issues do not cause symptoms in the early stages. These include retinal weakness and vitreous changes.
What does it mean when your retina is torn?
A torn retina is a severe eye problem that can make your vision blurry. A torn retina will have a tear or hole resembling a rip in cloth. It often leads to a more serious condition called a detached retina. A detached retina is where the retina is lifted away from the back of the eye. A torn retina requires immediate treatment to prevent further ...
How to tell if you have a torn retina?
A torn retina must be checked by an ophthalmologist or eye doctor immediately. Otherwise, your retina may detach, resulting in vision loss . Speak with an ophthalmologist immediately if you notice any of these warning signs: You see flashing lights. Some people say this is like viewing stars after being hit in the eye.
Where do they do retinal surgery?
It is usually performed in your eye doctor or ophthalmologist’s office. The surgeon or eye doctor uses a special probe that provides intense and cold energy to the eye retina. This freezes the retina around the tear and produces scar tissue. The scars seal the retina to the eyewall.
Which part of the eye is sensitive to light?
The retina is the rearmost part of the eye (the one at the rear of the eye) and it is a kind of projection screen on which light falls after it has traveled through the vitreous humor (the liquid medium of the eyeball). It is the only structure of the eye that is truly sensitive to light..
Does retinal detachment cause pain?
Retinal detachment causes a series of symptoms that we must be aware of. It is important to remember that it does not cause pain, but it does generate a series of clinical signs that warn of its development. If we go to the doctor immediately after experiencing them, the prognosis will be very good.
Can retinal detachment be repaired?
Before discussing the ways to treat retinal detachment, it is important to consider several things: not all detachments can be repaired, vision is not always fully restored and the prognosis depends on both the location of the detachment and its magnitude , as well as the time it takes us without receiving medical attention.
What is the best treatment for retinal detachment?
Surgery serves as the best way of treating retinal detachment, through which eye doctors identify and seal different types of retinal detachments and there’s a high risk of total vision loss if you delay surgical treatment.
What is detached retina?
This type of detached retina is also named as serous retinal detachment and exudative retinal detachment. It happens as a result of fluid build-up under the retina due to an injury, inflammation or vascular abnormalities and there is no tear, break or whole involved.
What is the term for the tissue that pulls the sensory retina from the retinal pigment epithelium?
When fibrovascular tissue pulls the sensory retina from the retinal pigment epithelium due to an injury, inflammation or neovascularization, the phenomenon is referred as ‘tractional retinal detachment’.
How many eyes does retinal detachment take place?
Usually, retinal detachment takes place only in one eye, and should be considered and treated as a severe medical emergency.
How long does it take for silicone oil to be extracted from the retina?
The wound needs to be stitched after the procedure and the silicone oil needs to be extracted anywhere between 2-8 months of the procedure.
What is laser eye treatment?
Eye doctors user a laser beam for this type of treatment, which is directed at the tear in the retinal tissue through a contact lens or ophthalmoscope. This results in burning around the retinal tear, which produces scar tissue, which fuses back the tissue together later on.
What happens when you apply pressure to your retina?
The applied pressure eventually leads the retina to reattach to the wall at the back of the eye, thu s fixing the detachment.
What is retinal detachment?
There are three main causes of retinal detachment, each with its own set of risk factors. The most common type is called a “rhegmatogenous” detachment, and is caused by a tear or hole in the retina. The retina is the thin, light-sensitive tissue ...
What are the risk factors for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment?
Risk factors for rhegmatogenous retinal detachments include aging, cataract surgery, thinning of the outer retina known as lattice degeneration, a high degree of nearsightedness (also called high myopia ), and head trauma.
What is the risk of rhegmatogenous detachment?
Other risk factors for rhegmatogenous detachments include a family history of retinal detachment and certain congenital or hereditary eye diseases. A less common type of retinal detachment is called a “tractional” detachment. This occurs when vitreous tugs on the retina over time, gradually causing the retina to tent up off the back of the eye.
How does cataract surgery affect the eyes?
Cataract surgery involves replacing the large, cloudy human lens inside the eye with a thinner plastic lens implant. This creates extra room inside the eye, like removing some clothes from a tightly packed suitcase. As vitreous flows into the newly created space, it can tug on the retina and occasionally create a retinal tear. Lattice degeneration is the name of a lace-like thinning at the edges of the retina that can make the retina more vulnerable to tears. Nearsightedness of more than 5 diopter powers is associated with a greater risk of retinal tears, possibly because nearsighted eyes are longer than normal and the retina is stretched thinner than normal. It may also be that high nearsightedness is associated with vitreous that is attached to the retina more tightly. A sudden blow to the head or eye, such as hitting a windshield or having an air bag deploy, can also create a tear in the retina. Head trauma is also among the most common causes of retinal detachment in children. Other risk factors for rhegmatogenous detachments include a family history of retinal detachment and certain congenital or hereditary eye diseases.
How old is too old to tear a vitreous?
This usually occurs between 55 and 65 years of age. If the vitreous is attached tightly enough to the retina, the separating vitreous can pull a tear in the retina, much like pulling a piece of tape off a piece of paper can rip a hole in the paper.
What happens to the vitreous as we age?
As we age, our vitreous gradually changes from a thick, gelatin-like consistency to a consistency more like egg white. The vitreous is attached to the retina. As it becomes thinner and moves around more inside the eye, it tugs on the retina and eventually tugs free of the retina.
